Ask me my favorite object in the Solar System, especially to see through a telescope, and my answer is always the same: Saturn.
Saturn is this crazy, ringed world, different than any other place we’ve ever seen. And in a small telescope, you can really see the ball of the planet, you can see its rings. It’s one thing to see a world like this from afar, a tiny jumping image in a telescope. To really appreciate and understand a place like Saturn, you’ve got to visit.
And thanks to NASA’s Cassini spacecraft, that’s just what we’ve been doing for the last 13 years. Take a good close look at this amazing ringed planet and its moons, and studying it from every angle.
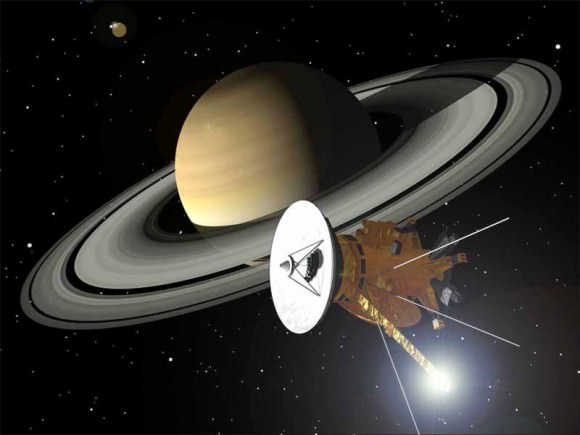

Throughout this article, I’m going to regale you with the amazing discoveries made by Cassini at Saturn. What it taught us, and what new mysteries it uncovered.
NASA’s Cassini spacecraft was launched from Earth on October 15, 1997. Instead of taking the direct route, it made multiple flybys of Venus, a flyby of Earth and a flyby of Jupiter. Each one of these close encounters boosted Cassini’s velocity, allowing it to make the journey with less escape velocity from Earth.
It arrived at Saturn on July 1st, 2004 and began its science operations shortly after that. The primary mission lasted 4 years, and then NASA extended its mission two more times. The first ending in 2010, and the second due to end in 2017. But more on that later.
Before Cassini, we only had flybys of Saturn. NASA’s Pioneer 11, and Voyagers 1 and 2 both zipped past the planet and its moons, snapping pictures as they went.
But Cassini was here to stay. To orbit around and around the planet, taking photos, measuring magnetic fields, and studying chemicals.
For Saturn itself, Cassini was able to make regular observations of the planet as it passed through entire seasons. This allowed it to watch how the weather and atmospheric patterns changed over time. The spacecraft watched lightning storms dance through the cloudtops at night.

Two highlights. In 2010, Cassini watched a huge storm erupt in the planet’s northern hemisphere. This storm dug deep into Saturn’s lower atmosphere, dredging up ice from a layer 160 kilometers below and mixing it onto the surface. This was the first time that astronomers were able to directly study this water ice on Saturn, which is normally in a layer hidden from view.
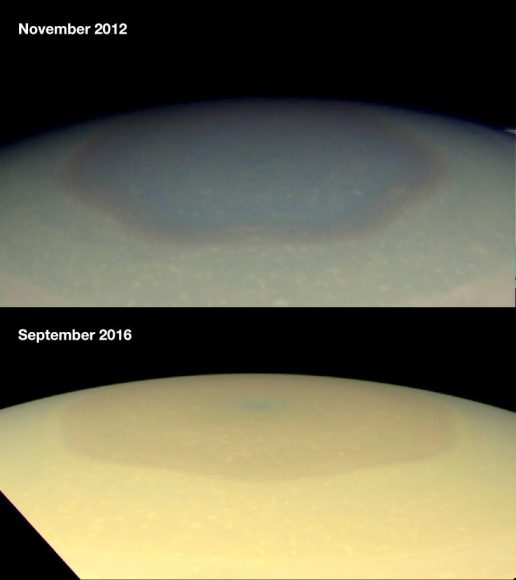

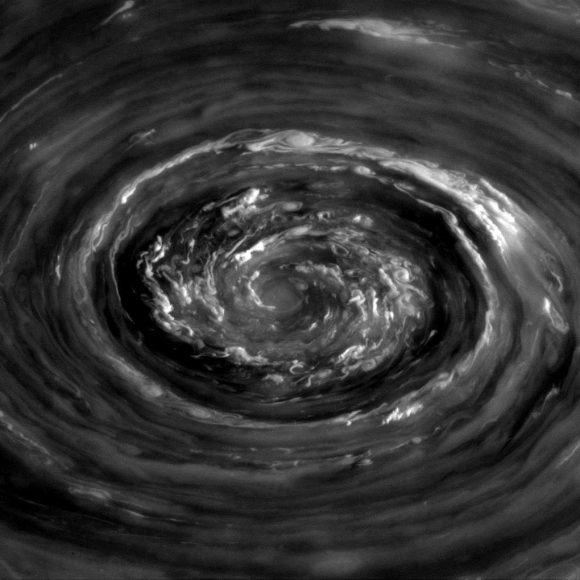
The second highlight, of course, is the massive hexagonal storm churning away in Saturn’s northern pole. This storm was originally seen by Voyager, but Cassini brought its infrared and visible wavelength instruments to bear.
Why a hexagon? That’s still a little unclear, but it seems like when you rotate fluids of different speeds, you get multi-sided structures like this.
Cassini showed how the hexagonal storm has changed in color as Saturn moved through its seasons.
This is one of my favorite images sent back by Cassini. It’s the polar vortex at the heart of the hexagon. Just look at those swirling clouds.
Now, images of Saturn itself are great and all, but there was so much else for Cassini to discover in the region.
Cassini studied Saturn’s rings in great detail, confirming that they’re made up of ice particles, ranging in size as small a piece of dust to as large as a mountain. But the rings themselves are actually quite thin. Just 10 meters thick in some places. Not 10 kilometers, not 10 million kilometers, 10 meters, 30 feet.
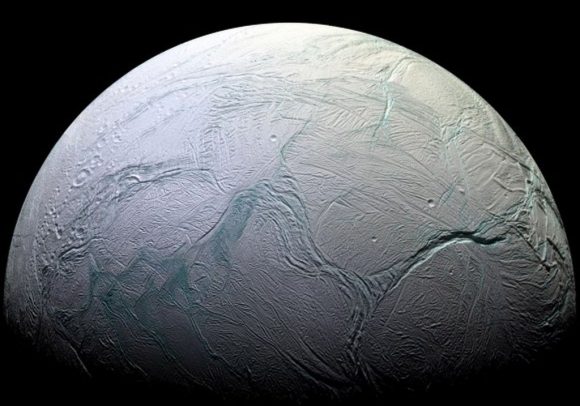
The spacecraft helped scientists uncover the source of Saturn’s E-ring, which is made up of fresh icy particles blasting out of its moon Enceladus. More on that in a second too.
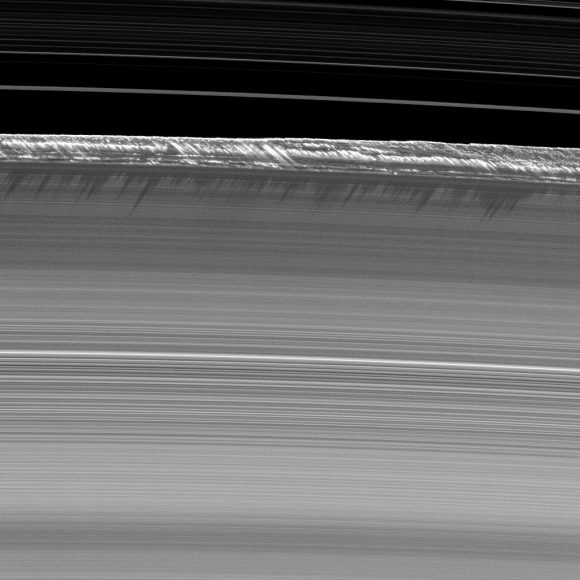
Here’s another one of my favorite images of the mission. You’re looking at strange structures in Saturn’s B-ring. Towering pillars of ring material that rise 3.5 kilometers above the surrounding area and cast long shadows. What is going on here?
They’re waves, generated in the rings and enhanced by nearby moons. They move and change over time in ways we’ve never been able to study anywhere else in the Solar System.

Cassini has showed us that Saturn’s rings are a much more dynamic place than we ever thought. Some moons are creating rings, other moons are absorbing or distorting them. The rings generate bizarre spoke patterns larger than Earth that come and go because of electrostatic charges.
Speaking of moons, I’m getting to the best part. What did Cassini find at Saturn’s moons?
Let’s start with Titan, Saturn’s largest moon. Before Cassini, we only had a few low resolution images of this fascinating world. We knew Titan had a dense atmosphere, filled with nitrogen, but little else.
Cassini was carrying a special payload to assist with its exploration of Titan: the Huygens lander. This tiny probe detached from Cassini just before its arrival at Saturn, and parachuted through the cloudtops on January 14, 2005, analyzing all the way. Huygens returned images of its descent through the atmosphere, and even images of the freezing surface of Titan.

But Cassini’s own observations of Titan took the story even further. Instead of a cold, dead world, Cassini showed that it has active weather, as well as lakes, oceans and rivers of hydrocarbons. It has shifting dunes of pulverized rock hard water ice.
If there’s one place that needs exploring even further, it’s Titan. We should return with sailboats, submarines and rovers to better explore this amazing place.
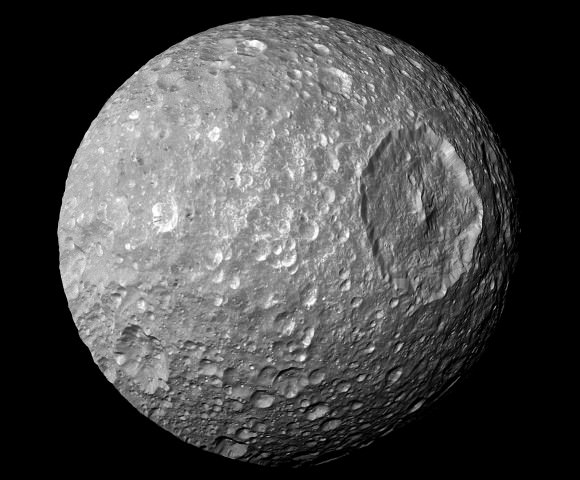

We learned, without a shadow of a doubt, that Mimas absolutely looks like the Death Star. No question. But instead of a megalaser, this moon has a crater a third of its own size.
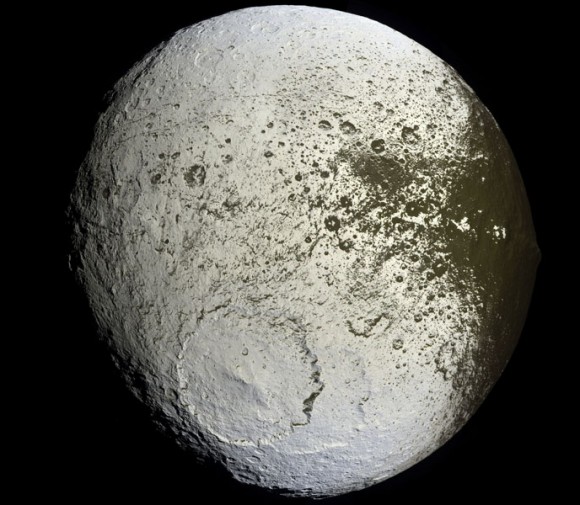

Cassini helped scientists understand why Saturn’s moon Iapetus has one light side and one dark side. The moon is tidally locked to Saturn, its dark side always leading the moon in orbit. It’s collecting debris from another Saturnian moon, Phoebe, like bugs hitting the windshield of a car.
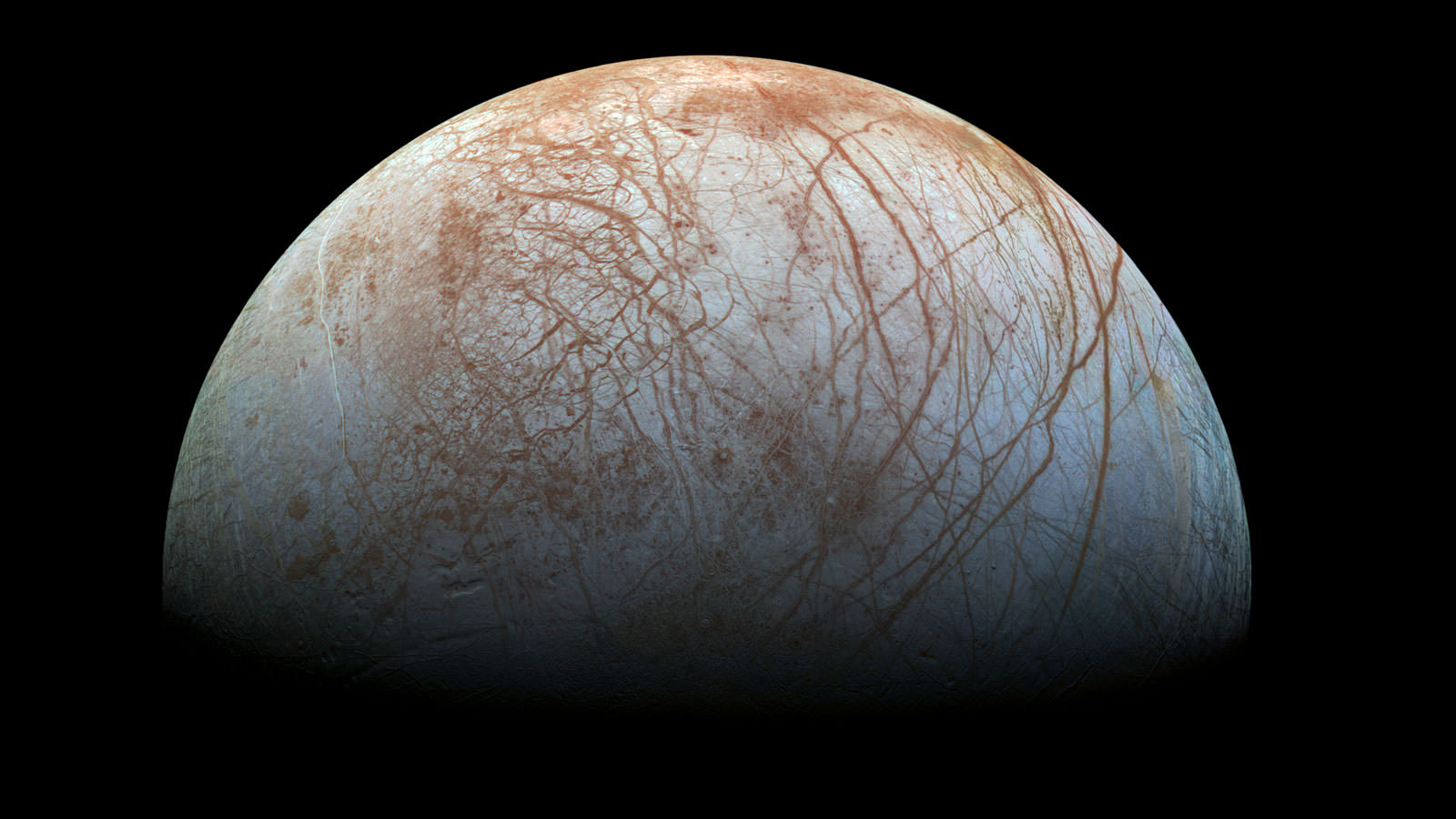
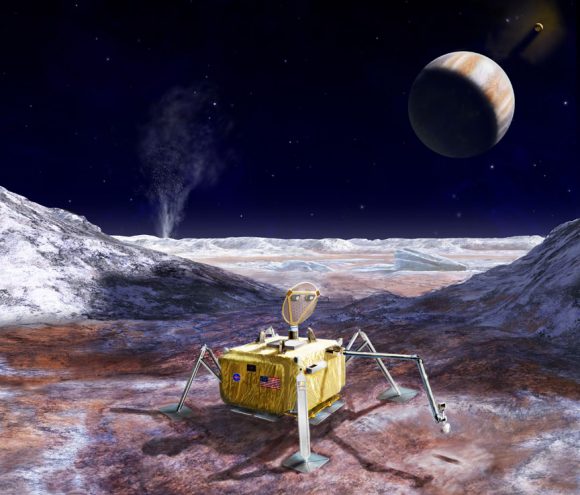
Perhaps the most exciting discovery that Cassini made during its mission is the strange behavior of Saturn’s moon Enceladus. The spacecraft discovered that there are jets of water ice blasting out of the moon’s southern pole. An ocean of liquid water, heated up by tidal interactions with Saturn, is spewing out into space.
And as you know, wherever we find water on Earth, we find life. We thought that water in the icy outer Solar System would be hard to reach, but here it is, right at the surface, venting into space, and waiting for us to come back and investigate it further.

On September 15, 2017, the Cassini mission will end. How do we know it’s going to happen on this exact date? Because NASA is going to crash the spacecraft into Saturn, killing it dead.
That seems a little harsh, doesn’t it, especially for a spacecraft which has delivered so many amazing images to us over nearly two decades of space exploration? And as we’ve seen from NASA’s Opportunity rover, still going, 13 years longer than anticipated. Or the Voyagers, out in the depths of the void, helping us explore the boundary between the Solar System and interstellar space. These things are built to last.
The problem is that the Saturnian system contains some of the best environments for life in the Solar System. Saturn’s moon Enceladus, for example, has geysers of water blasting out into space.
Cassini spacecraft is covered in Earth-based bacteria and other microscopic organisms that hitched a ride to Saturn, and would be glad to take a nice hot Enceladian bath. All they need is liquid water and a few organic chemicals to get going, and Enceladus seems to have both.
NASA feels that it’s safer to end Cassini now, when they can still control it, than to wait until they lose communication or run out of propellant in the future. The chances that Cassini will actually crash into an icy moon and infect it with our Earth life are remote, but why take the risk?
For the last few months, Cassini has been taking a series of orbits to prepare itself for its final mission. Starting in April, it’ll actually cross inside the orbit of the rings, getting closer and closer to Saturn. And on September 15th, it’ll briefly become a meteor, flashing through the upper atmosphere of Saturn, gone forever.
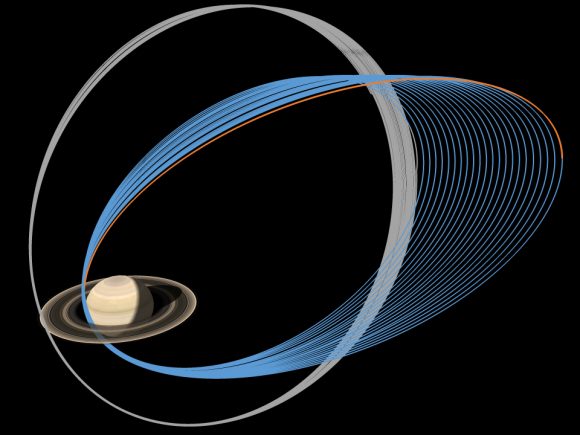

Even in its final moments, Cassini is going to be sciencing as hard as it can. We’ll learn more about the density of consistency of the rings close to the planet. We’ll learn more about the planet’s upper atmosphere, storms and clouds with the closest possible photographs you can take.
And then it’ll all be over. The perfect finale to one of the most successful space missions in human history. A mission that revealed as many new mysteries about Saturn as it helped us answer. A mission that showed us not only a distant alien world, but our own planet in perspective in this vast Solar System. I can’t wait to go back.
How have the photos from Cassini impacted your love of astronomy? Let me know your thoughts in the comments.