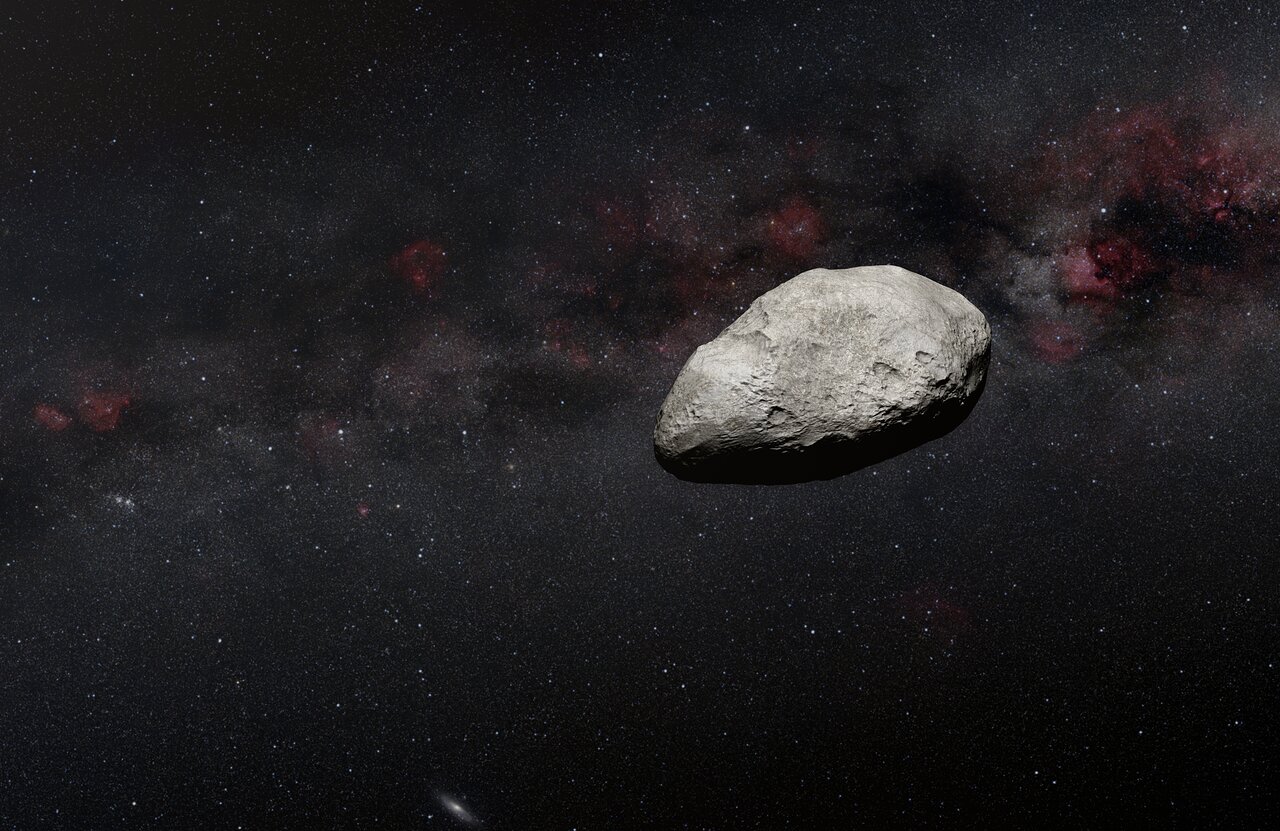
The venerable Hubble Space Telescope is like a gift that keeps on giving. Not only is it still making astronomical discoveries after more than thirty years in operation. It is also making discoveries by accident! Thanks to an international team of citizen scientists, with the help of astronomers from the European Space Agency (ESA) and some machine learning algorithms, a new sample of over one thousand asteroids has been identified in Hubble‘s archival data. The methods used represent a new approach for finding objects in decades-old data that could be applied to other datasets as well.
Continue reading “Hubble Has Accidentally Discovered Over a Thousand Asteroids”Hubble Has Accidentally Discovered Over a Thousand Asteroids