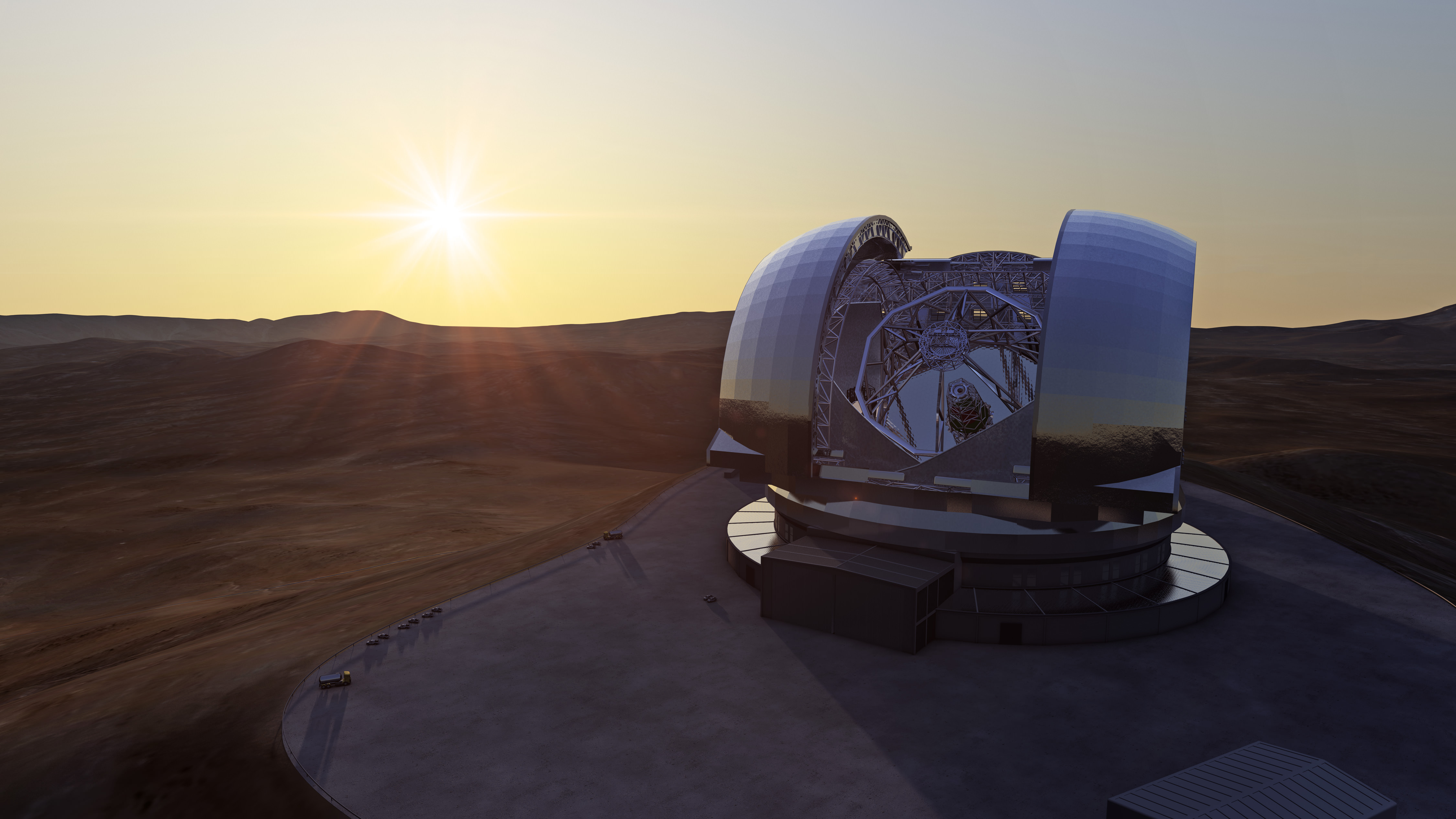
The field of astronomy is about to be revolutionized, thanks to the introduction of Extremely Large Telescopes that rely on primary mirrors measuring 30 meters (or more) in diameter, adaptive optics (AO), coronographs, and advanced spectrometers. This will include the eponymously-named Extremely Large Telescope (ELT), the Giant Magellan Telescope (GMT), and the Thirty Meter Telescope (TMT). These telescopes will enable astronomers to study exoplanets using the Direct Imaging (DI) method, which will yield valuable data on the composition of their atmospheres.
According to a new study by a team of researchers from Ohio State University (OSU), these telescopes will also allow astronomers to study “ultracool objects,” like very low-mass stars (VLMs), brown dwarfs, and exoplanets. In addition to being able to visualize magnetic starspots and determine the chemical compositions of these objects, ELTs will be able to reveal details about atmospheric dynamics and cloud systems. These types of studies could reveal a wealth of information about some of the least-studied objects in our Universe and significantly aid in the search for life beyond our Solar System.
Continue reading “The Next Generation of Telescopes Will Tell Us About the Weather on Other Worlds”