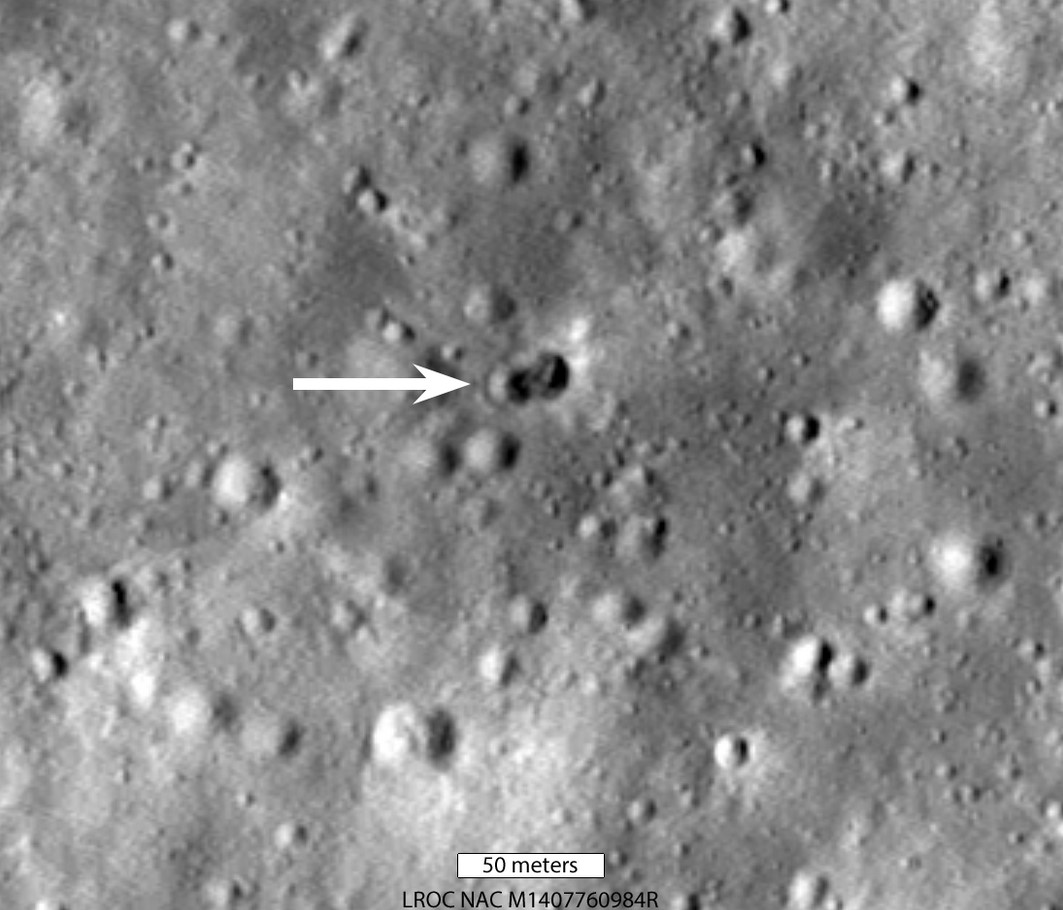
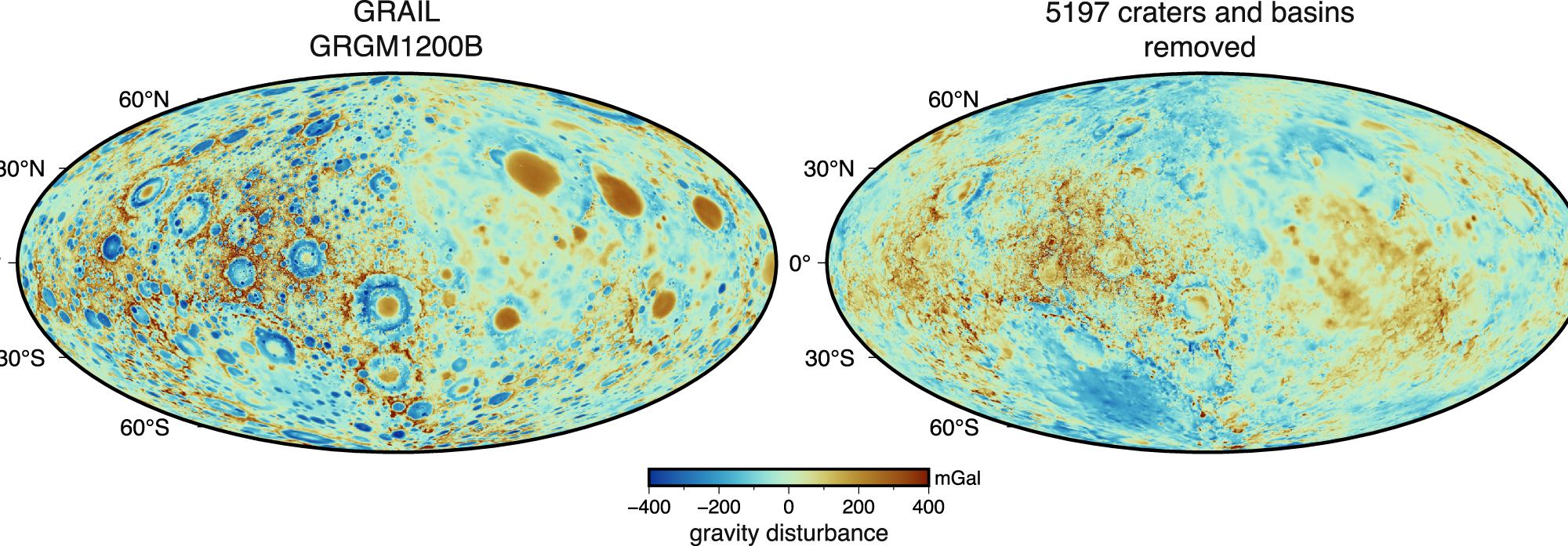
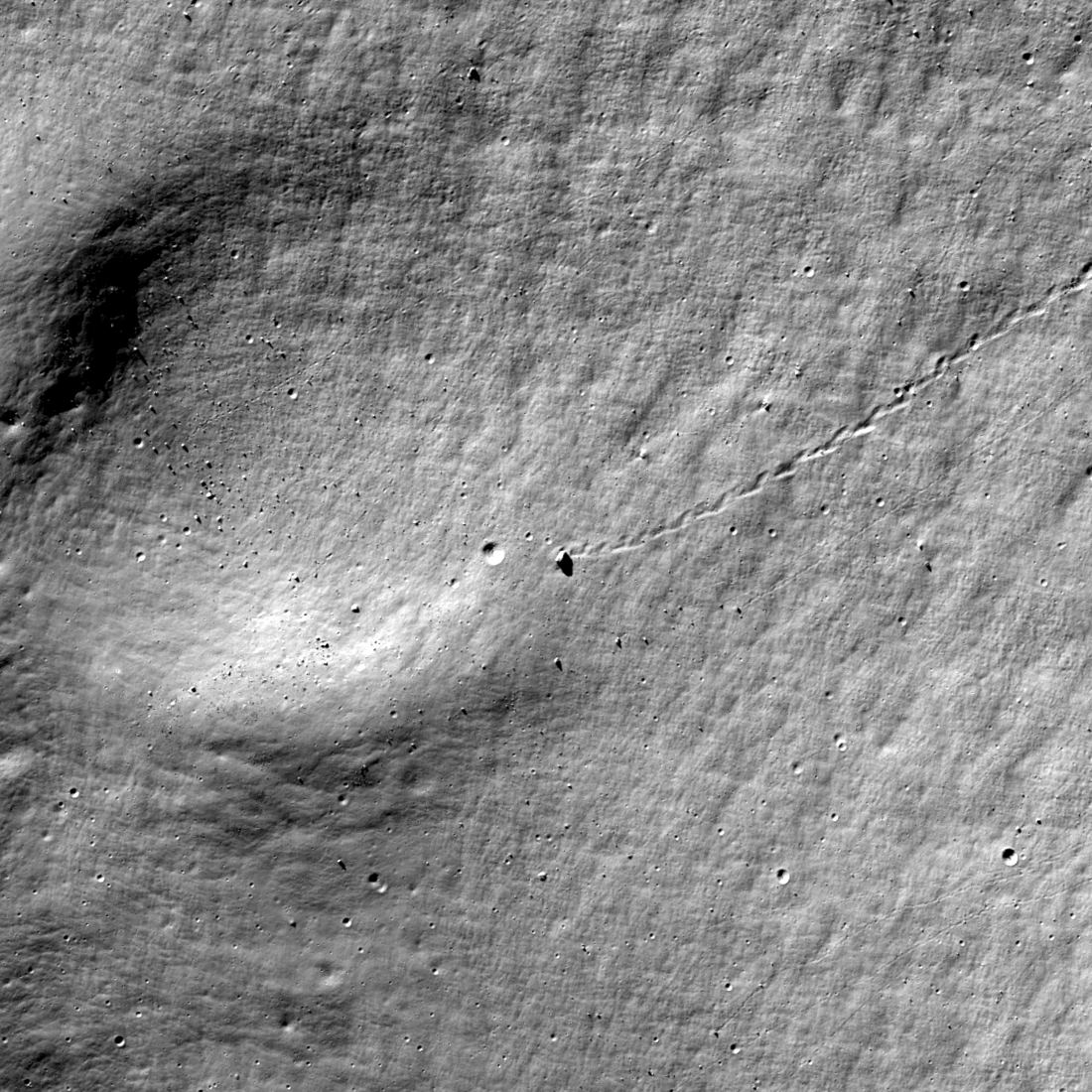
Last year, astronomers warned that a large piece of debris was on a collision course with the Moon. Initially, they speculated that it was a SpaceX booster but later zeroed in on a Chinese Long March 3C rocket booster that launched the Chang’e 5 mission. When it did impact on March 4, 2022, astronomers noted a strange double crater.
A new paper suggests that it couldn’t have been a single object breaking up since there’s no atmosphere on the Moon. Instead, the booster must have been carrying an additional, undisclosed payload.
Continue reading “A Chinese Booster (and Additional Secret Payload) Caused a Double Crater on the Moon”