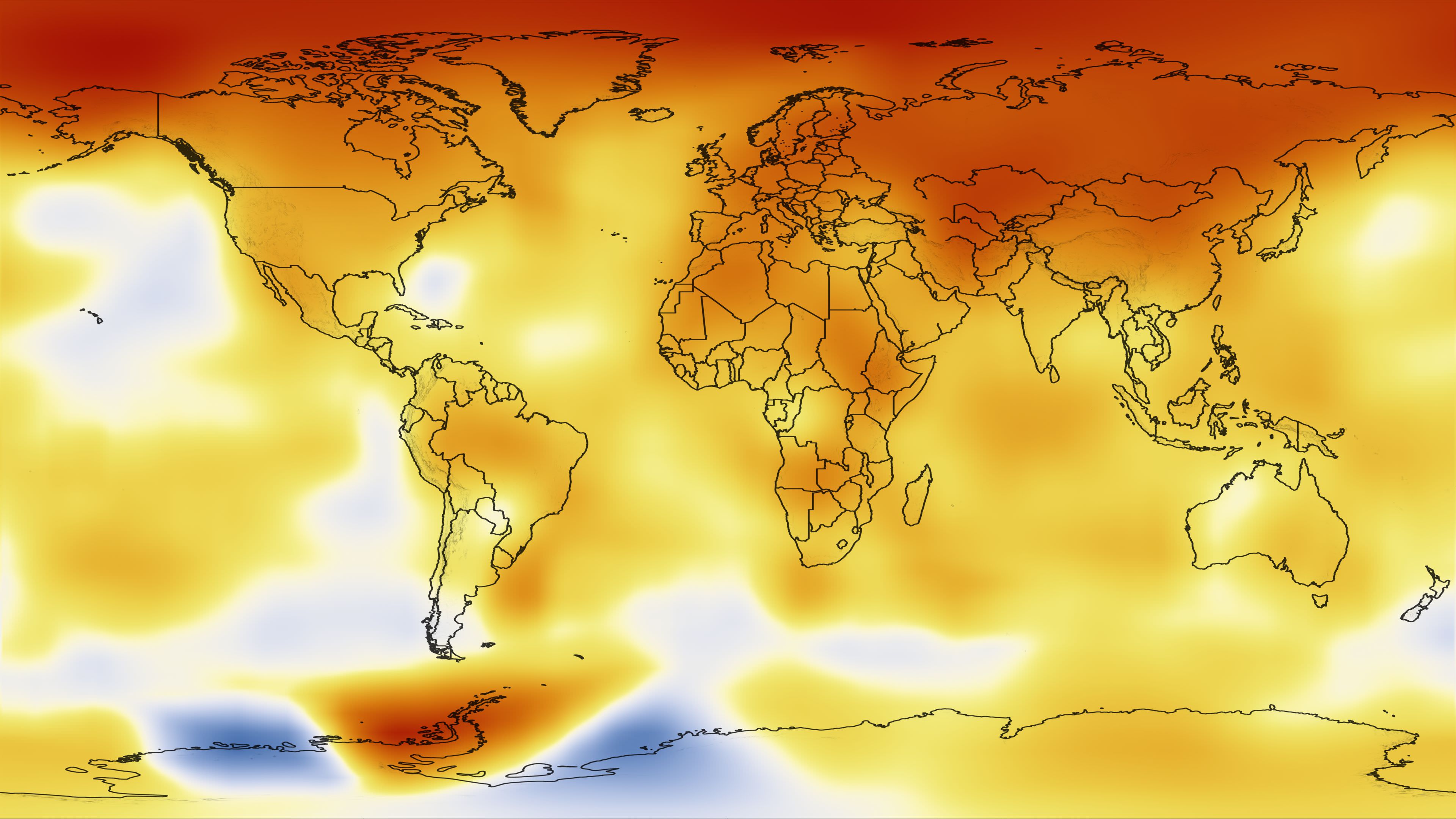
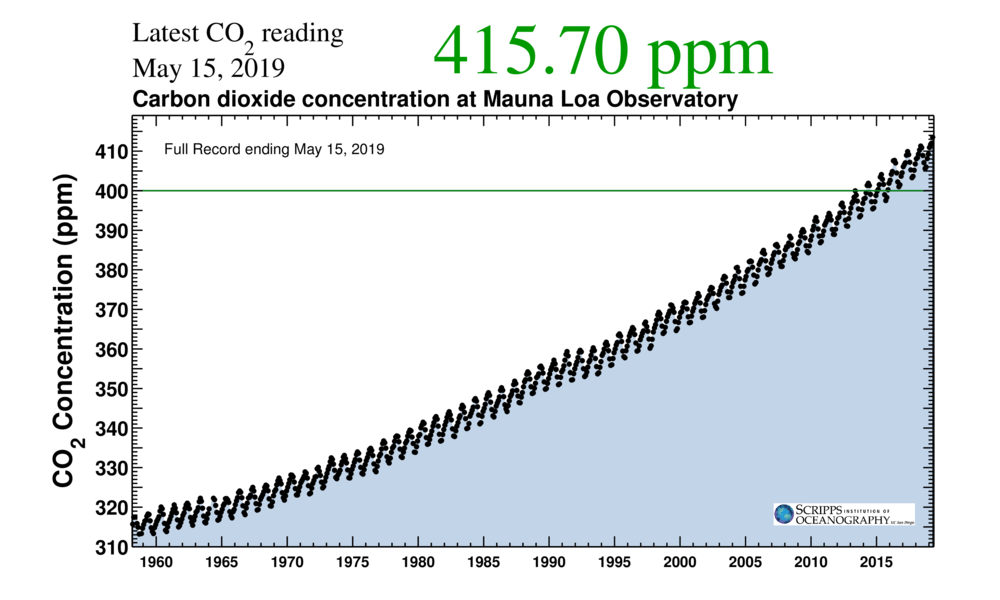
There is no doubt that climate change is a very serious (and worsening) problem. According to a recent report by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), even if all the industrialized nations of the world became carbon neutral overnight, the problem would continue to get worse. In short, it’s not enough to stop pumping megatons of CO2 into the atmosphere; we also have to start removing what we’ve already put there.
This is where the technique known as carbon capture (or carbon removal) comes into play. Taking their cue from nature, an international team of researchers from the University of Waterloo, Ontario, have created an “artificial leaf” that mimics the carbon-scrubbing abilities of the real thing. But rather than turning atmospheric CO2 into a source of fuel for itself, the leaf converts it into a useful alternative fuel.
Continue reading “This Artificial Leaf Turns Atmospheric Carbon Dioxide Into Fuel”





![This illustration shows the percentage of marine animals that went extinct during Earth's worst extinction at the end of the Permian era by latitude, from the model (black line) and from the fossil record (blue dots).A greater percentage of marine animals survived in the tropics than at the poles. The color of the water shows the temperature change, with red being most severe warming and yellow less warming. At the top is the supercontinent Pangaea, with massive volcanic eruptions emitting carbon dioxide. The images below the line represent some of the 96 percent of marine species that died during the event. [Includes fossil drawings by Ernst Haeckel/Wikimedia; Blue crab photo by Wendy Kaveney/Flickr; Atlantic cod photo by Hans-Petter Fjeld/Wikimedia; Chambered nautilus photo by John White/CalPhotos.]Justin Penn and Curtis Deutsch/University of Washington](https://www.universetoday.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/12/Penn_sumfig_final.jpg)