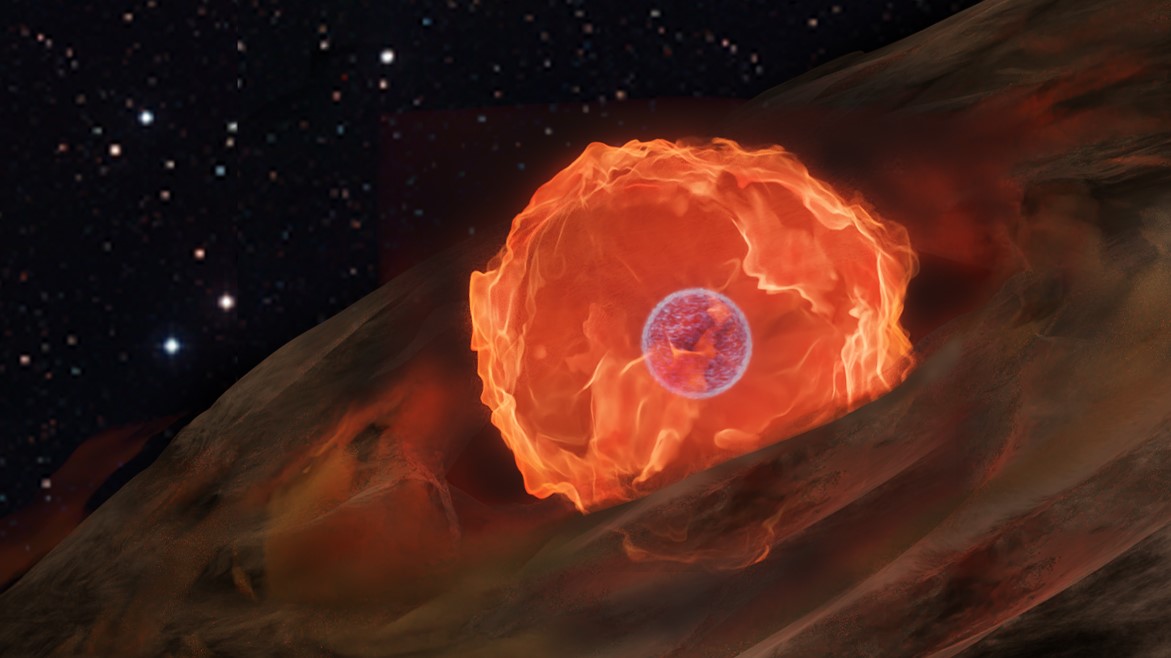
Sunlike stars and those smaller than the Sun end their lives as white dwarfs. Without a continued source of energy from hydrogen fusion, these stars eventually collapse under their own weight. They would continue collapsing were it not for the pressure of electrons. As long as the remaining mass of a star is less than about 1.4 Suns, the electron pressure and gravitational pull will balance each other, creating a white dwarf.
Continue reading “One Side of This White Dwarf is Covered in Hydrogen While the Other Side is Helium.”A White Dwarf is Starting to Crystallize into Diamond
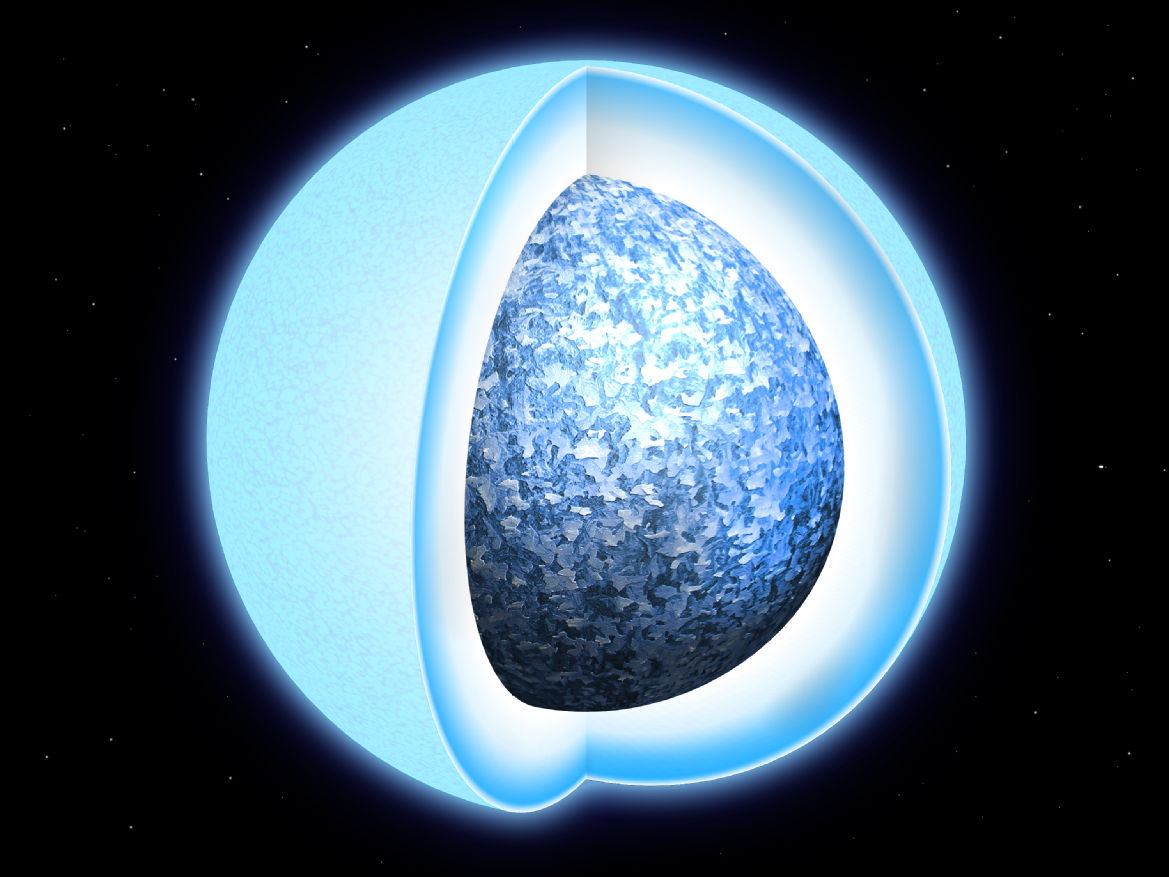
White dwarfs are the stellar remnants of stars like our Sun. They’re strange objects, and astrophysicists think their cores can crystallize into enormous diamonds. But they need to find more of these strange objects, and they need to know their ages, to understand how and when it happens.
Continue reading “A White Dwarf is Starting to Crystallize into Diamond”A White Dwarf is Surrounded by Torn-up Pieces of its Inner Planets and its Kuiper Belt

What will happen to our Sun?
In several billion years, it’ll cease fusion, shrivel into a white dwarf, and emanate only remnant heat. There it’ll sit, dormant and comatose.
But the Sun anchors the entire Solar System. What will happen to Earth? To the rest of the planets? To the rest of the objects in the Solar System?
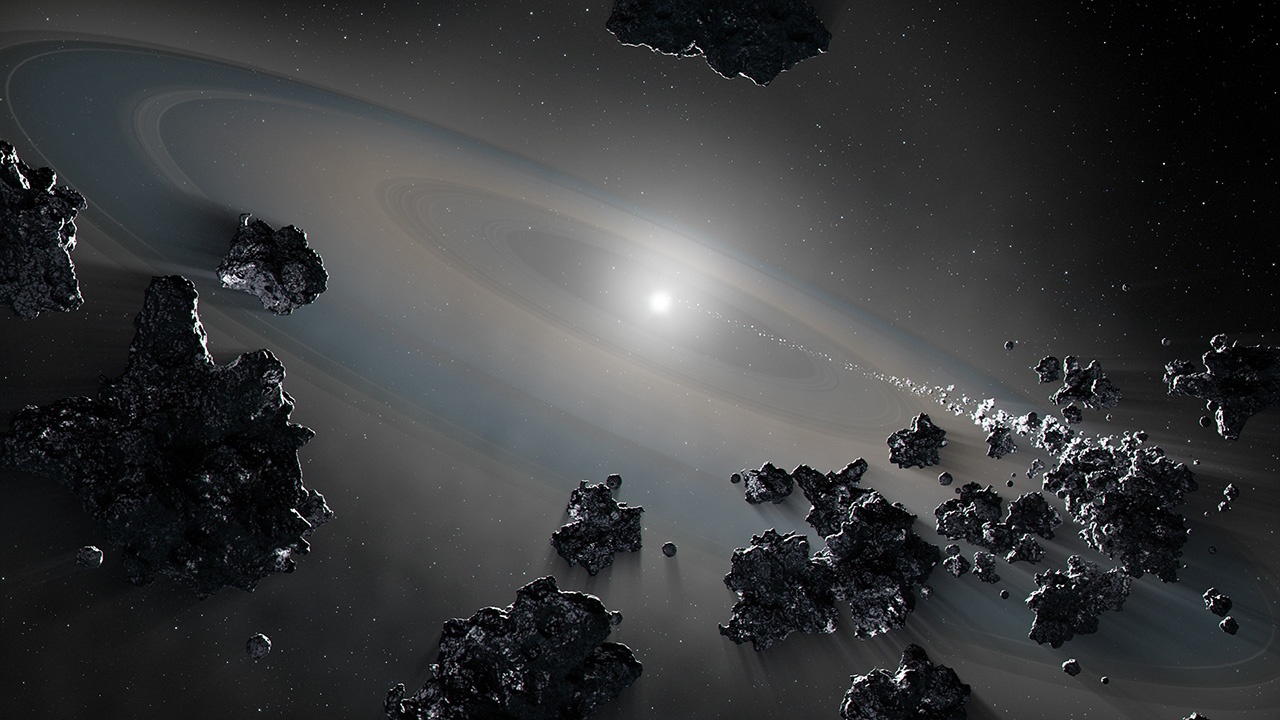
Continue reading “A White Dwarf is Surrounded by Torn-up Pieces of its Inner Planets and its Kuiper Belt”Astronomers Spot the Debris From Planets That Formed 10 Billion Years ago

The fate of the Sun is sealed. It was sealed by gravity in the earliest days of its formation. In several billion years the Sun will swell to a red giant, cast off much of its thin outer layers, then collapse to become a white dwarf. The white dwarfs we see in the nearby galaxy tell us of our Sun’s future. Its core will collapse to about the size of Earth, and then it will gradually cool as it fades into the dark. It’s a tale we’ve long known, but astronomers continue to learn learning interesting details, particularly regarding what might be the fate of the Sun’s planets.
Continue reading “Astronomers Spot the Debris From Planets That Formed 10 Billion Years ago”A Dying Star’s Last Act was to Destroy all Its Planets

When white dwarfs go wild, their planets suffer through the resulting chaos. The evidence shows up later in and around the dying star’s atmosphere after it gobbles up planetary and cometary debris. That’s the conclusion a team of UCLA astronomers came to after studying the nearby white dwarf G238-44 in great detail. They found a case of cosmic cannibalism at this dying star, which lies about 86 light-years from Earth.
If that star were in the place of our Sun, it would ingest the remains of planets, asteroids, and comets out to the Kuiper Belt. That expansive buffet makes this stellar cannibalism act one of the most widespread ever seen.
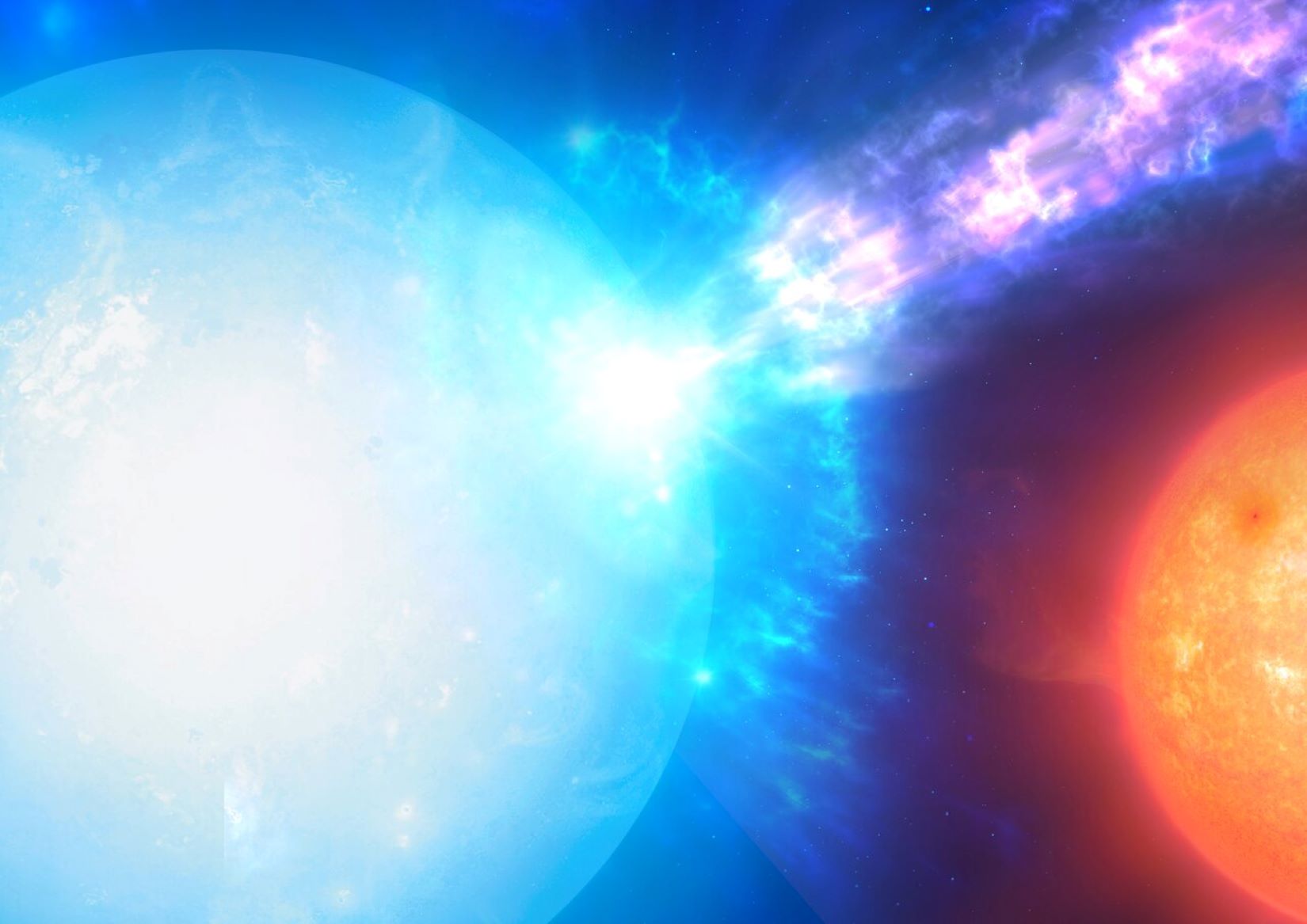
Continue reading “A Dying Star’s Last Act was to Destroy all Its Planets”Astronomers Finally Catch a Nova Detonating on a White Dwarf as it's Happening
On July 7, 2020, the X-ray instrument eROSITA captured an astronomical event that – until then – had only been theorized and never seen. It saw the detonation of a nova on a white dwarf star, which produced a so-called fireball explosion of X-rays.
“It was to some extent a fortunate coincidence, really,” said Ole König from Friedrich-Alexander-Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg (FAU), who led the team of scientists who have published a new paper on the discovery. “These X-ray flashes last only a few hours and are almost impossible to predict, but the observational instrument must be pointed directly at the explosion at exactly the right time.”
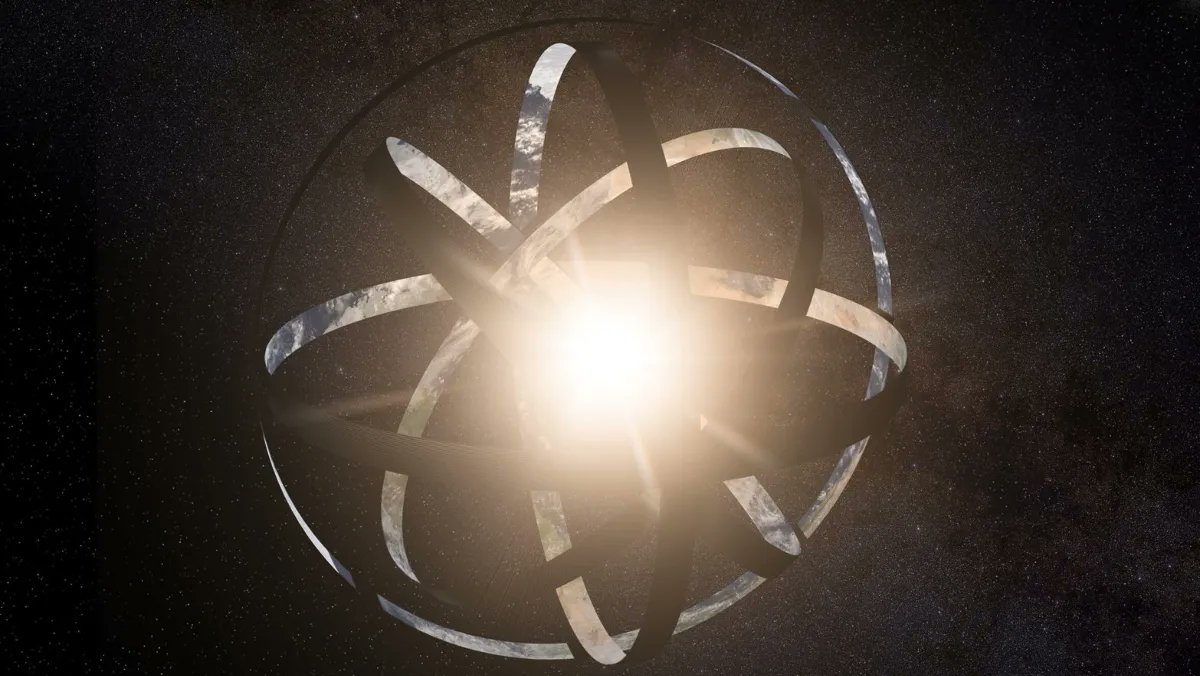
Continue reading “Astronomers Finally Catch a Nova Detonating on a White Dwarf as it's Happening”If There are Dyson Spheres Around White Dwarfs, We Should be Able to Detect Them
Searching for Dyson spheres, rings, or swarms remains a preoccupation of many astronomers. If there are any out there, they will eventually be found, and the person or research team to do so will go down in history for making one of the most momentous discoveries in the history of humanity. If you’re interested in claiming that accolade for yourself, an excellent place to look may be around white dwarfs. At least, that’s the theory put forward in a new paper by Benjamin Zuckerman, a now-retired professor of astrophysics at UCLA.
Continue reading “If There are Dyson Spheres Around White Dwarfs, We Should be Able to Detect Them”A New Kind of Stellar Explosion Has Been Discovered: Micronovae
The most energetic explosions in the Universe come from stars called supernovae. These galactic bombs have the energy of about 1028 mega-tons. After they detonate, the only thing left behind is either a neutron star or black hole. Another type of stellar explosion is known as a nova which has much less energy and covers the surface of a white dwarf.
Now, a team of astronomers recently discovered a new type of stellar explosion akin to supernovae and novae but with much less energy, and they’re calling it a micronova.
Continue reading “A New Kind of Stellar Explosion Has Been Discovered: Micronovae”Planet Found in the Habitable Zone of a White Dwarf

Most stars will end their lives as white dwarfs. White dwarfs are the remnant cores of once-luminous stars like our Sun, but they’ve left their lives of fusion behind and no longer generate heat. They’re destined to glow with only their residual energy for billions of years before they eventually fade to black.
Could life eke out an existence on a planet huddled up to one of these fading spectres?
Continue reading “Planet Found in the Habitable Zone of a White Dwarf”Astronomers see Dead Planets Crashing Into Dead Stars

When our Sun dies, the Earth will die with it. As a star of middling mass, the Sun will end its life by swelling into a red giant star. After a last cosmic moment of brilliance, the remnant core of the Sun will collapse into a white dwarf. This won’t occur for billions of years, but the mass and composition of the Sun means a white dwarf is its inevitable fate.
Continue reading “Astronomers see Dead Planets Crashing Into Dead Stars”



