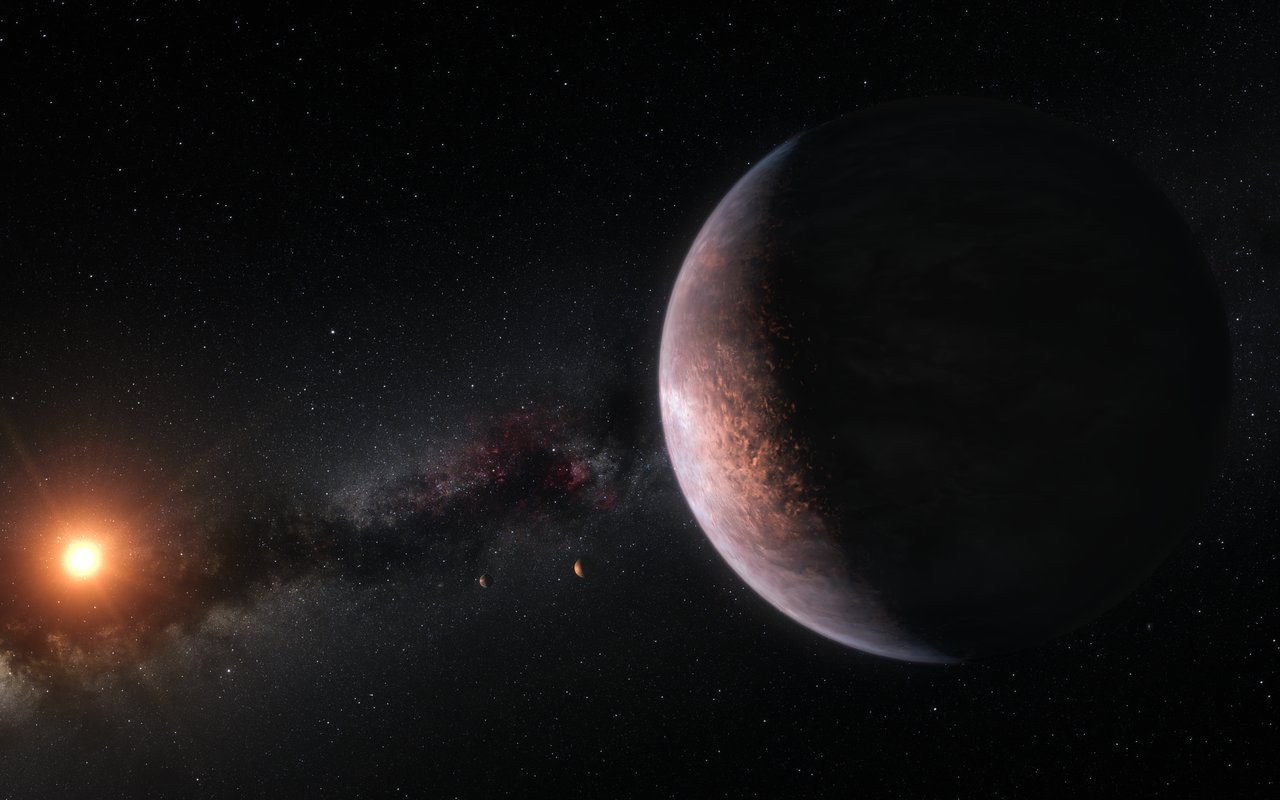
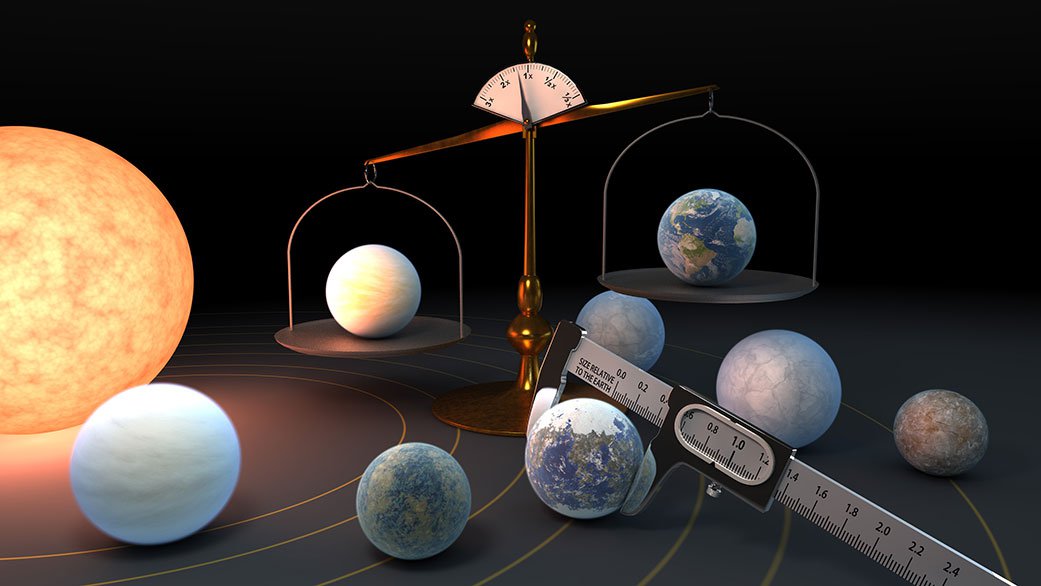
The TRAPPIST-1 system is a science-fiction writer’s dream. Seven Earth-sized worlds orbit a red dwarf star just 40 light-years away. Three of those worlds are within the habitable zone of the star. The system spans a distance less than 25 times that of the distance from the Earth to the Moon. Oh, what epic tales a TRAPPIST civilization would have! That is, if life in such a system is even possible…
Continue reading “Could Life at TRAPPIST-1 Survive the Star's Superflares?”Could Life at TRAPPIST-1 Survive the Star's Superflares?