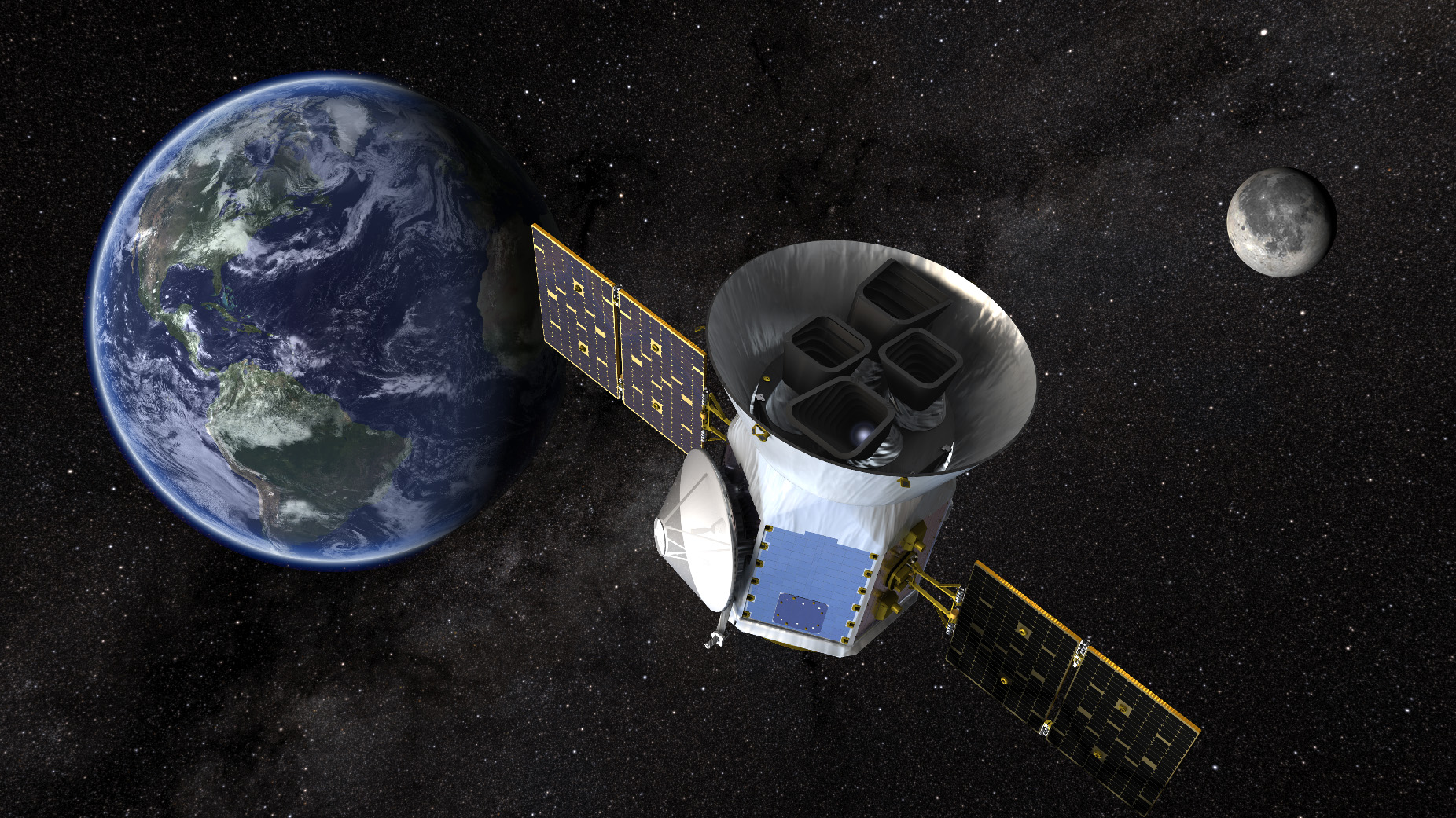
In April 2018, NASA launched the Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS), the successor to the Kepler Space Telescope that revolutionized the exoplanet studies field. Like its predecessor, TESS has been scanning almost the entire sky for five years for extrasolar planets using the Transit Method. This consists of monitoring thousands of stars for periodic dips in brightness, which may indicate a planet passing in front of the star relative to the observer. To date, TESS has made 243 confirmed discoveries, with another 4562 candidates – or TESS Objects of Interest (TOI) – awaiting confirmation.
On Monday, October 10th, fans of the TESS mission and the research it conducts got a bit of a scare as the observatory experienced a malfunction and had to be put into safe mode. Three days later, at around 06:30 PM EDT (03:30 PM PDT) on October 13th, NASA announced that their engineers had successfully powered up the instrument and brought it back online. While technicians at NASA are still investigating the cause of the malfunction, the spacecraft is now back in its fine-pointing mode and has resumed its second extended mission (EM2).
Continue reading “TESS has Resumed Normal Operations”