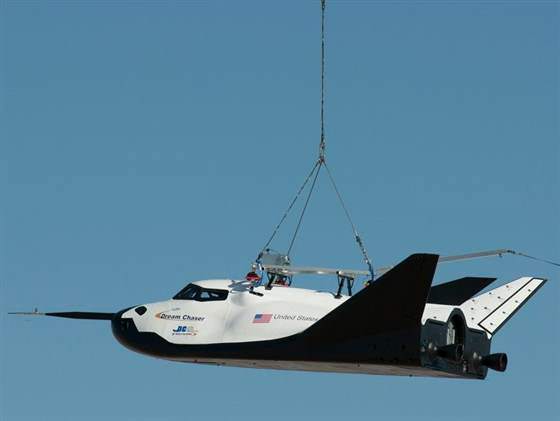
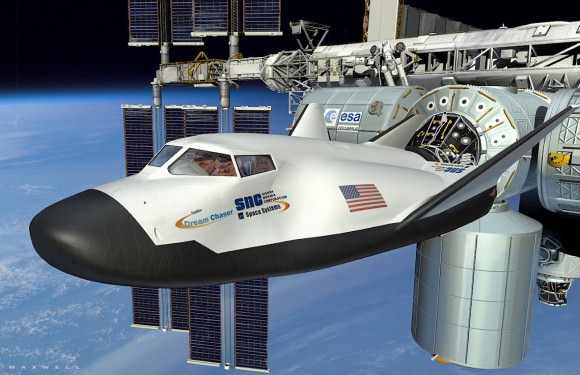
The engineering test article of the commercial Dream Chaser spaceship being developed by Sierra Nevada Corp (SNC) suffered some significant damage during its critical 1st ever approach-and-landing (ALT) drop test on Saturday, Oct. 26, in California due to an unspecified type of malfunction with the deployment of the left landing gear.
The Dream Chaser mini-shuttle suffered “an anomaly as it touched down on the Runway 22L at Edwards Air Force Base, Calif.,” according to a post-test statement from NASA.
A report at NASA Spaceflight.com indicated that the Dream Chaser “flipped over on the runway” after touchdown.
The full extent of damage to the winged vehicle or whether it can be repaired and reflown is not known at this time. No photos or details explaining the damage have yet emerged – beyond brief press releases issued by SNC and NASA.
The performance of the vehicles’ nose skid, brakes, tires and other flight systems is being tested to prove that it can safely land an astronaut crew returning from the space station after surviving the searing heat of re-entry from Earth orbit.
This initial atmospheric drop test was conducted in an automated mode. There was no pilot on board and no one was hurt on the ground.
“No personnel were injured. Damage to property is being assessed,” said NASA. “Edwards Air Force Base emergency personnel responded to scene as a precaution.
“Support personnel are preparing the vehicle for transport to a hangar.”
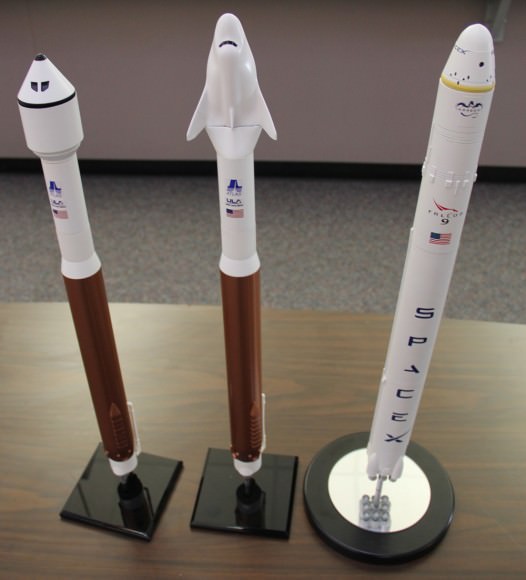
Dream Chaser is one of three private sector manned spaceships being developed with funding from NASA’s commercial crew program known as Commercial Crew Integrated Capability (CCiCap) initiative to develop a next-generation crew transportation vehicle.

The NASA seed money aims at restoring America’s manned spaceflight access to low Earth orbit and the International Space Station (ISS) – perhaps by 2017 – following the forced shutdown of the Space Shuttle program in 2011.
Until one of the American commercial space taxis is ready for liftoff, NASA is completely dependent on the Russian Soyuz capsule for astronaut rides to the ISS at a cost of roughly $70 million per seat.
SNC was awarded $227.5 million in the current round of NASA funding and must complete specified milestones including up to five ALT drop tests to check the aerodynamic handling.
To date this test vehicle has successfully accomplished a series of runway tow and airborne captive carry tests.
Development of crew versions of the SpaceX Dragon and Boeing CST-100 capsules are also being funded by NASA’s commercial crew program office.
Dream Chaser can carry a crew of up to seven and is the only reusable, lifting body shuttle type vehicle with runway landing capability among the three competitors.

Credit: Ken Kremer/kenkremer.com
During Saturday’s test, SNC was performing the first in a series of free-flight approach-and-landing tests with the Dream Chaser prototype test vehicle known as the ETA.
The prototype spaceship was released as planned from its carrier aircraft, an Erickson Air-Crane helicopter, at approximately 11:10 a.m. Pacific Standard Time (2:10 p.m. EDT), said SNC in a statement.

“Following release, the Dream Chaser spacecraft automated flight control system gently steered the vehicle to its intended glide slope. The vehicle adhered to the design flight trajectory throughout the flight profile. Less than a minute later, Dream Chaser smoothly flared and touched down on Edwards Air Force Base’s Runway 22L right on centerline,” according to the SNC press release.
SNC went on to say that reviews are in progress to determine the cause of the landing gear failure.
“While there was an anomaly with the left landing gear deployment, the high-quality flight and telemetry data throughout all phases of the approach-and-landing test will allow SNC teams to continue to refine their spacecraft design. SNC and NASA Dryden are currently reviewing the data. As with any space flight test program, there will be anomalies that we can learn from, allowing us to improve our vehicle and accelerate our rate of progress.”
The engineering test article (ETA) is a full sized vehicle.
Dream Chaser is a reusable mini shuttle that launches from the Florida Space Coast atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket and lands on the shuttle landing facility (SLF) runway at the Kennedy Space Center, like the space shuttle.
“It’s not outfitted for orbital flight. It is outfitted for atmospheric flight tests,” said Marc Sirangelo, Sierra Nevada Corp. vice president and SNC Space Systems chairman told Universe Today previously.
“The best analogy is it’s very similar to what NASA did in the shuttle program with the Enterprise, creating a vehicle that would allow it to do significant flights whose design then would filter into the final vehicle for orbital flight,” Sirangelo told me.
We’ll provide further details as they become known.