CubeSats are taking on more and more responsibility for remote monitoring of the Earth. As they become more ubiquitous, they will also gain more varied propulsion systems. Or, in the case of a new set of monitoring CubeSats from INTA, Spain’s Institue of Aerospace Technology, no propulsion system at all.
Continue reading “A Flock of CubeSats Will Use Wings to Maneuver at the Edge of Space”One of the Brightest Stars in the Sky is Actually a Satellite
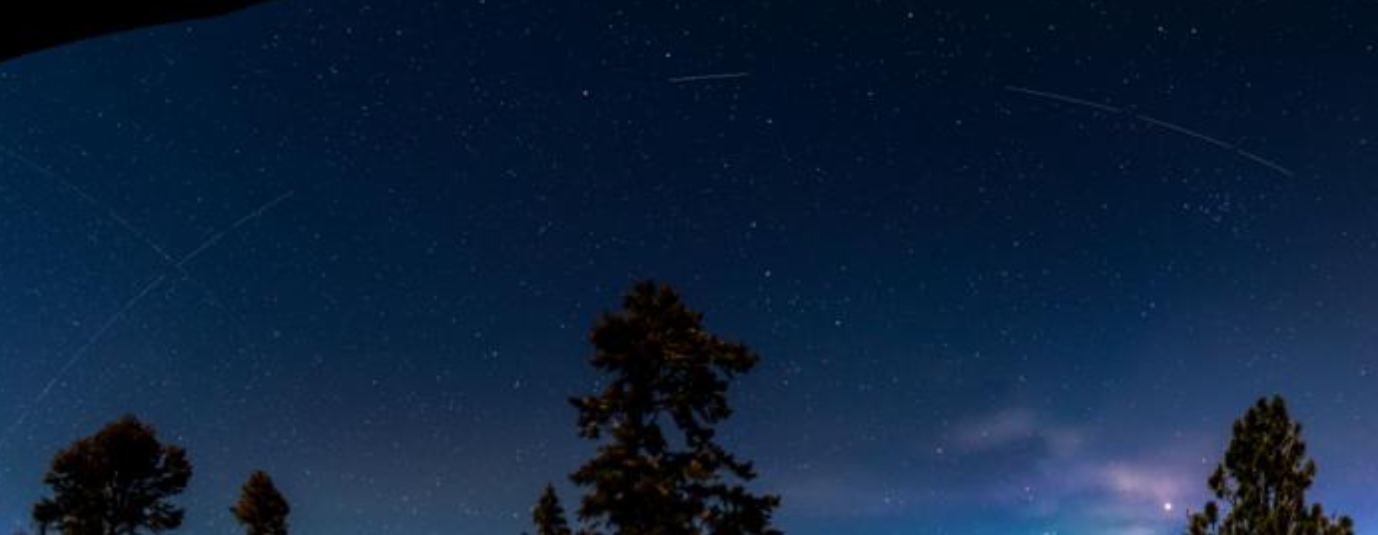

Back in the 70s, kids used to look up at the summer sky and try to be the first one to shout, “Satellite!” That seems like a relic from the past now, alongside Polaroid cameras and astronauts on the Moon. These days, it’s rare to spend any amount of time looking at the sky without seeing a satellite, or several of them.
A new satellite is emphasizing that fact. It’s a prototype communications satellite with a roughly 700-square-foot antenna, and it’s brighter than most stars.
Continue reading “One of the Brightest Stars in the Sky is Actually a Satellite”The Irony. ClearSpace-1 Couldn't Clean up Space Debris Because its Target Already Got hit by Space Debris, Creating Even More Space Debris.
We have a problem.
Ever since the launch of Sputnik 1 in 1957, we have been launching debris into space. Everything from space stations and large communication satellites to small CubeSats. With each launch, we also add things such as rocket parts and paint chips to the orbital pile. Right now there are more than a million objects orbiting Earth wider than a centimeter, and at least 130 million millimeter-sized objects. Most of it isn’t going to deorbit any time soon.
Continue reading “The Irony. ClearSpace-1 Couldn't Clean up Space Debris Because its Target Already Got hit by Space Debris, Creating Even More Space Debris.”A Satellite is Now Continuously Watching Lightning Strikes in Europe
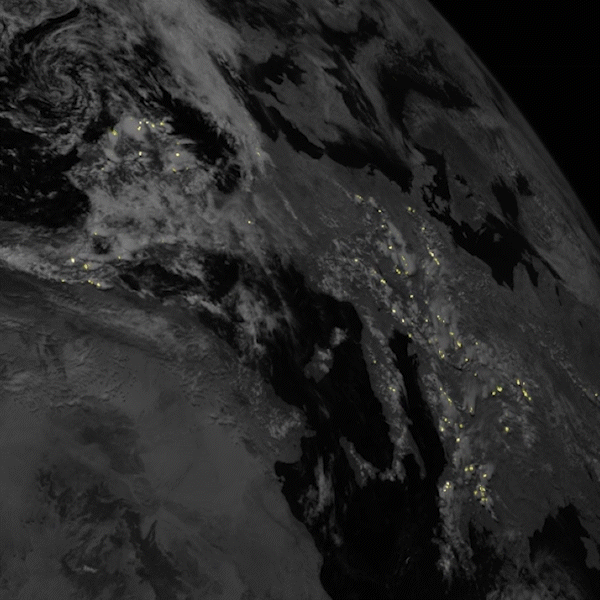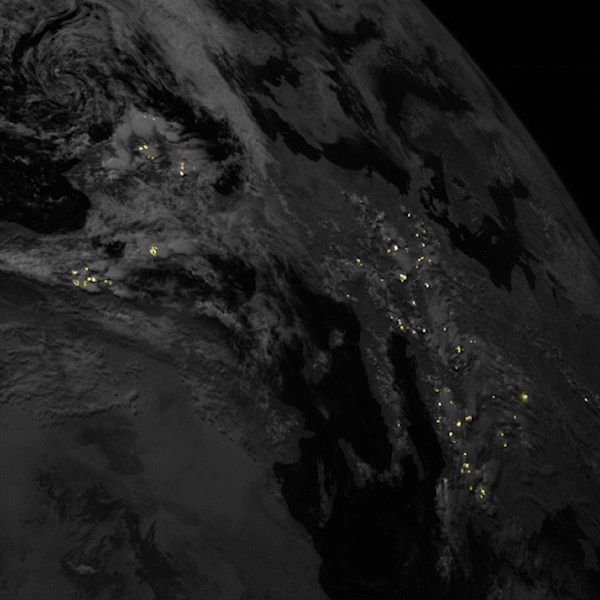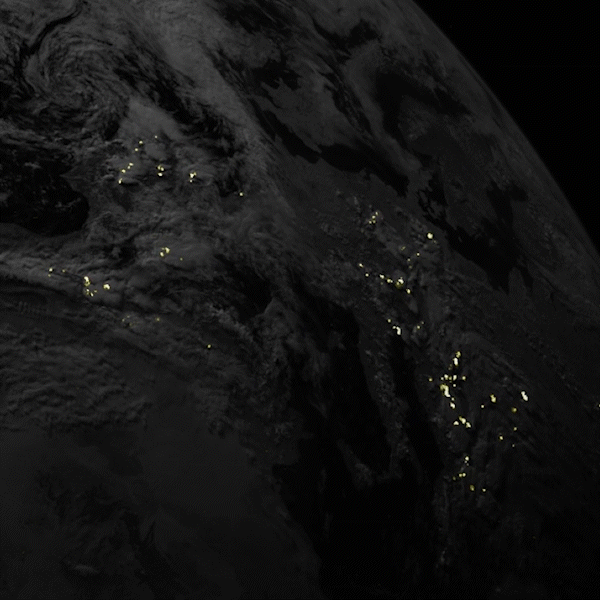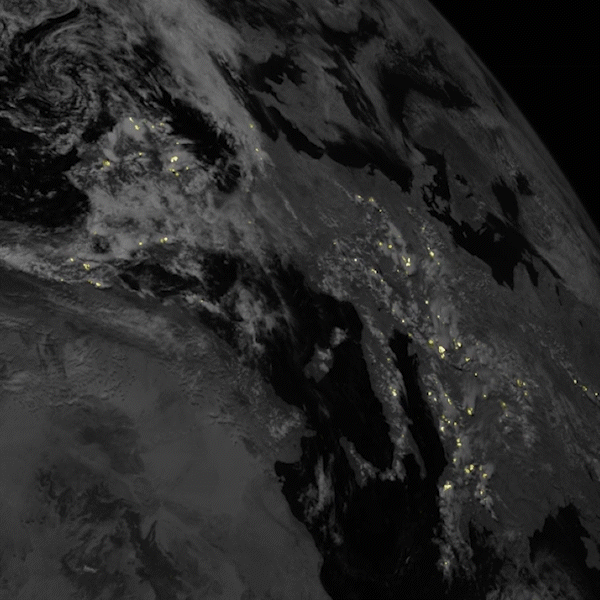
Satellites often offer new perspectives when they launch. Sometimes because of the location they are placed in – sometimes because of their instrumentation. A new satellite by a consortium of European companies and agencies now provides a new perspective on one of the most powerful and fleeting natural phenomena – lightning.
Continue reading “A Satellite is Now Continuously Watching Lightning Strikes in Europe”If There Were a War in Space, Debris Would Destroy all Remaining Satellites in About 40 Years

On one particular day in 2021, astronauts and cosmonauts aboard the ISS must have felt a pin-prick of fear and uncertainty. On November 15th of that year, Russia fired an anti-satellite missile at one of its own defunct military satellites, Tselina-D. The target weighed about 1,750 kg, and when the missile struck its target, the satellite exploded into a cloud of hazardous debris.
NASA woke the crew on the International Space Station in the middle of the night and told them to take precautions and prepare for a possible impact. The Chinese space station Tiangong was also in danger, and multiple countries and space agencies condemned Russia’s foolhardy behaviour.
But there was no way to contain the debris.
Continue reading “If There Were a War in Space, Debris Would Destroy all Remaining Satellites in About 40 Years”A New Mission Will Grab Dead Satellites and Push Them Into the Atmosphere to Burn Up
Plenty of news stories have focused on the danger posed by Kessler syndrome. In this condition, space is made inaccessible by a cloud of debris surrounding our planet that would destroy any further attempts to get into orbit. Therefore, plenty of companies have sprung up that problem to take care of the problem, from blasting derelict satellites with lasers to helping to refuel them; lots of business models have been created to capture this opportunity. One of the farthest along is Astroscale. This British start-up is tackling the problem with one of the more conventional techniques – linking up with an existing satellite to deorbit it. And recently, they released a promotional video for their new project – the ELSA-M.
Continue reading “A New Mission Will Grab Dead Satellites and Push Them Into the Atmosphere to Burn Up”Astronomers Have Figured Out Clever Tricks to Reduce the Impact of Satellite Trails
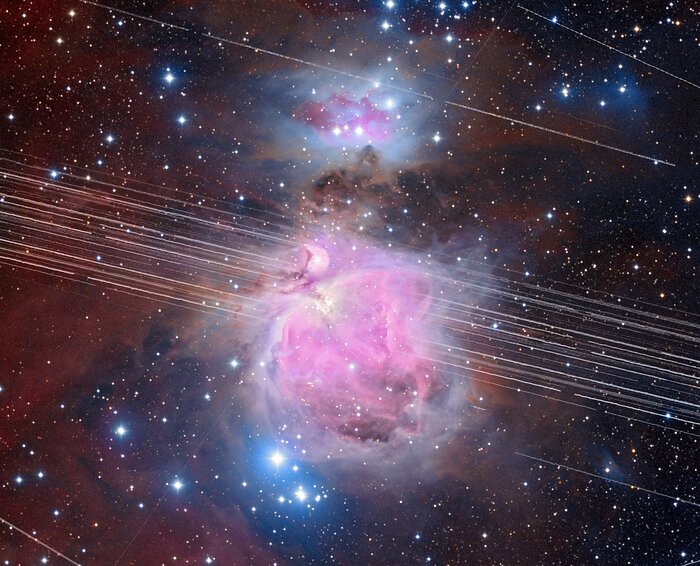

A clear sky is a prerequisite for most astronomers imaging the cosmos. However, with the proliferation of satellite trails, astronomers see a lot more streaks in their images. That’s particularly true for people using professional ground-based and orbiting telescopes. When Hubble Space Telescope opened its eye on the sky, there were less than 500 satellites orbiting our planet. Now, there are nearly 8,000 of them, leaving their mark across the sky.
Continue reading “Astronomers Have Figured Out Clever Tricks to Reduce the Impact of Satellite Trails”Two English Companies are Cooperating to Bring a Novel Antenna Architecture To Space
Technology Readiness Levels (or TRLs) are commonly used in the space industry to determine what level of development a technology has undergone. For space technologies, eventually, they get to a TRL where they have to be used in space. In some cases, that can be difficult, as getting a ride on a launch is both risky and expensive. So it’s good news for Oxford Space Systems (OSS) that they penned an agreement with Surrey Satellites Technology Ltd (SSTL) to prove one of their new technologies on an actual flight.
Continue reading “Two English Companies are Cooperating to Bring a Novel Antenna Architecture To Space”Researchers are Working on a Tractor Beam System for Space
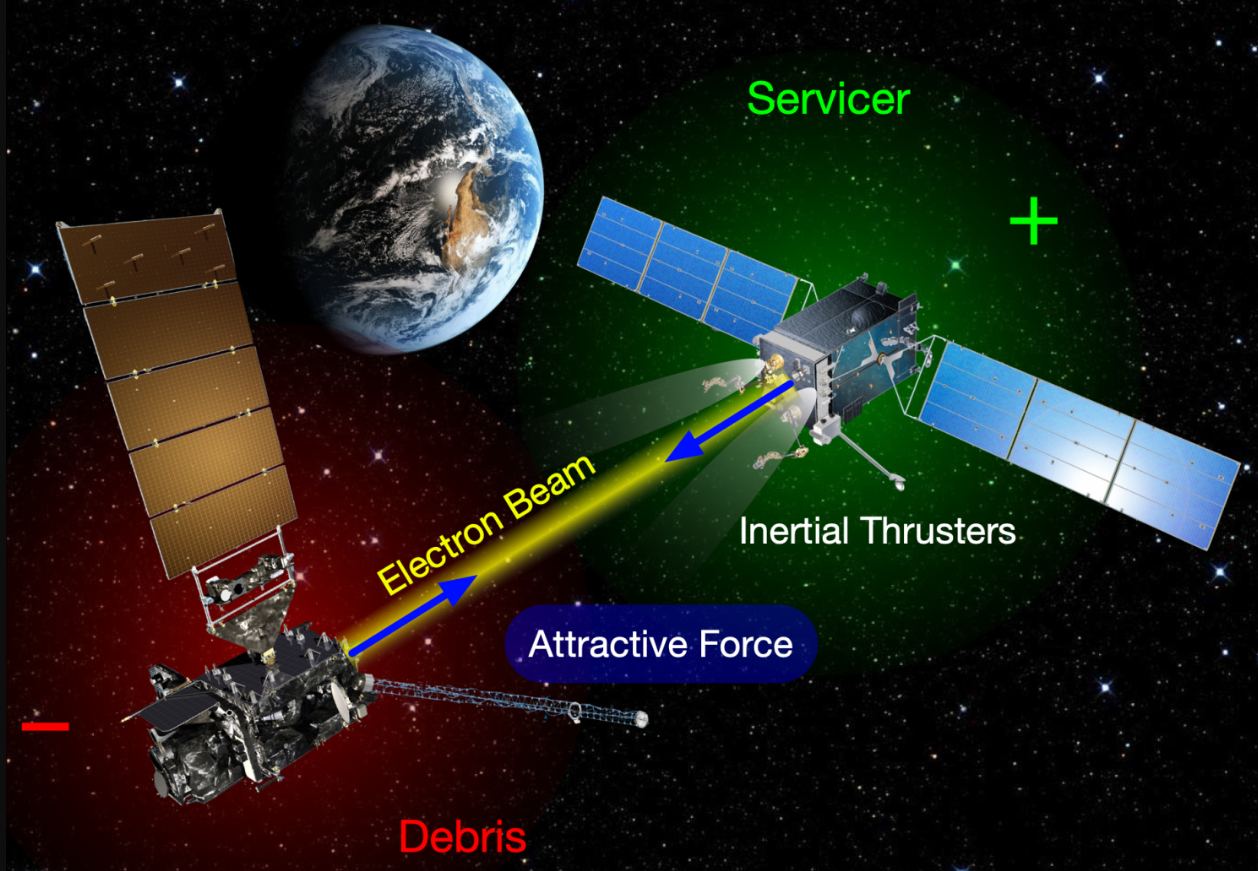
Human technology is crossing another threshold. Tractor beams have been common in science fiction for decades. Now a team of researchers is working on a real-life tractor beam that could help us with our burgeoning space debris problem.
Continue reading “Researchers are Working on a Tractor Beam System for Space”Building a Satellite out of Wood? Use Magnolia
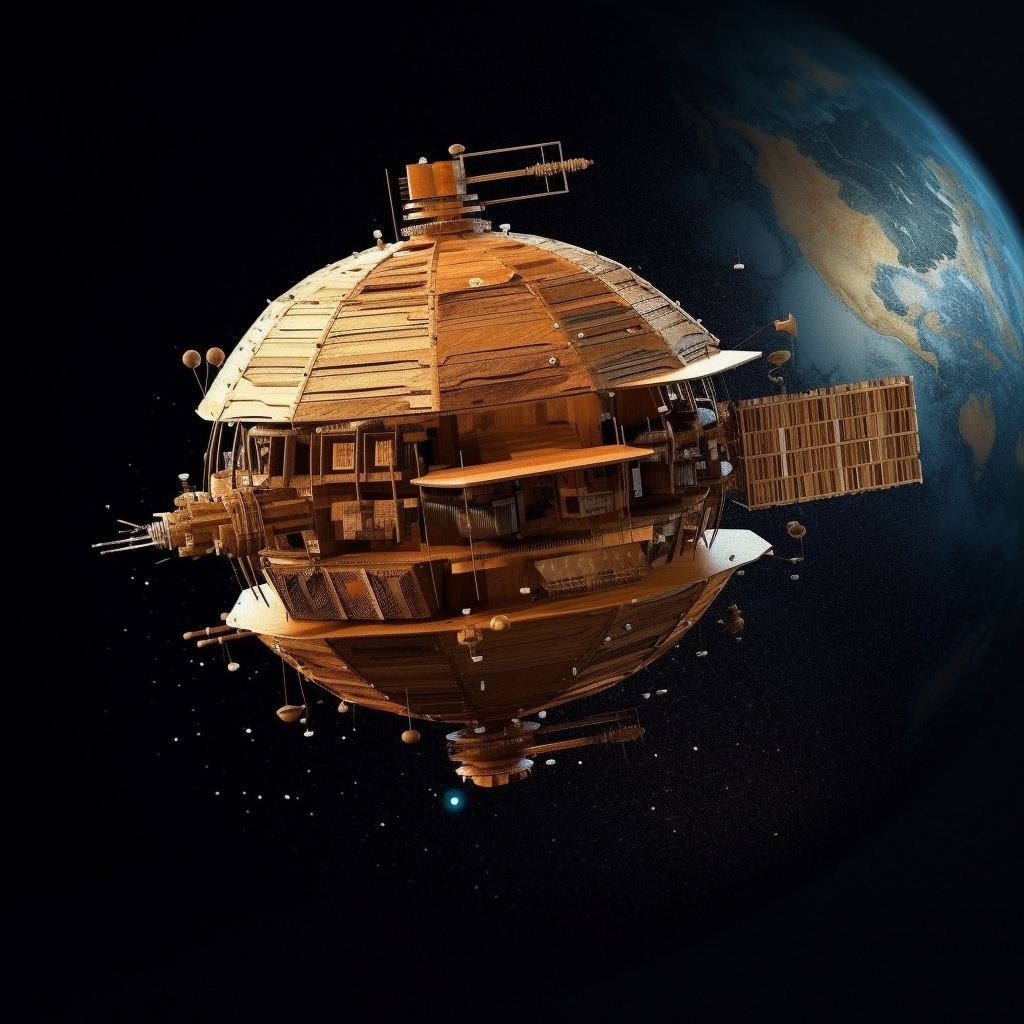
Typically when you think of a satellite, you think of a metal box with electronic components inside it. But that is simply because most satellites have been made that way throughout history. There is nothing against using other materials to build satellites. Now, a team of researchers from Japan has completed testing on another type of material that could eventually be used on an actual satellite – magnolia wood.
Continue reading “Building a Satellite out of Wood? Use Magnolia”