Touring the Milky Way’s a blast with this brand new 360-degree interactive panorama. More than 2 million infrared photos taken by NASA’s Spitzer Space Telescope were jigsawed into a 20-gigapixel click-and-zoom mosaic that takes the viewer from tangled nebulae to stellar jets to blast bubbles around supergiant stars.

The new composite, using infrared images taken over the past decade, was compiled by a team led by UW-Madison astronomer Barbara Whitney and unveiled at a TEDactive conference in Vancouver, Canada Thursday. Unlike visual light, infrared penetrates the ubiquitous dust concentrated in the galactic plane to reveal structures otherwise obscured.
Catching a GLIMPSE of the Milky Way in this short video presentation
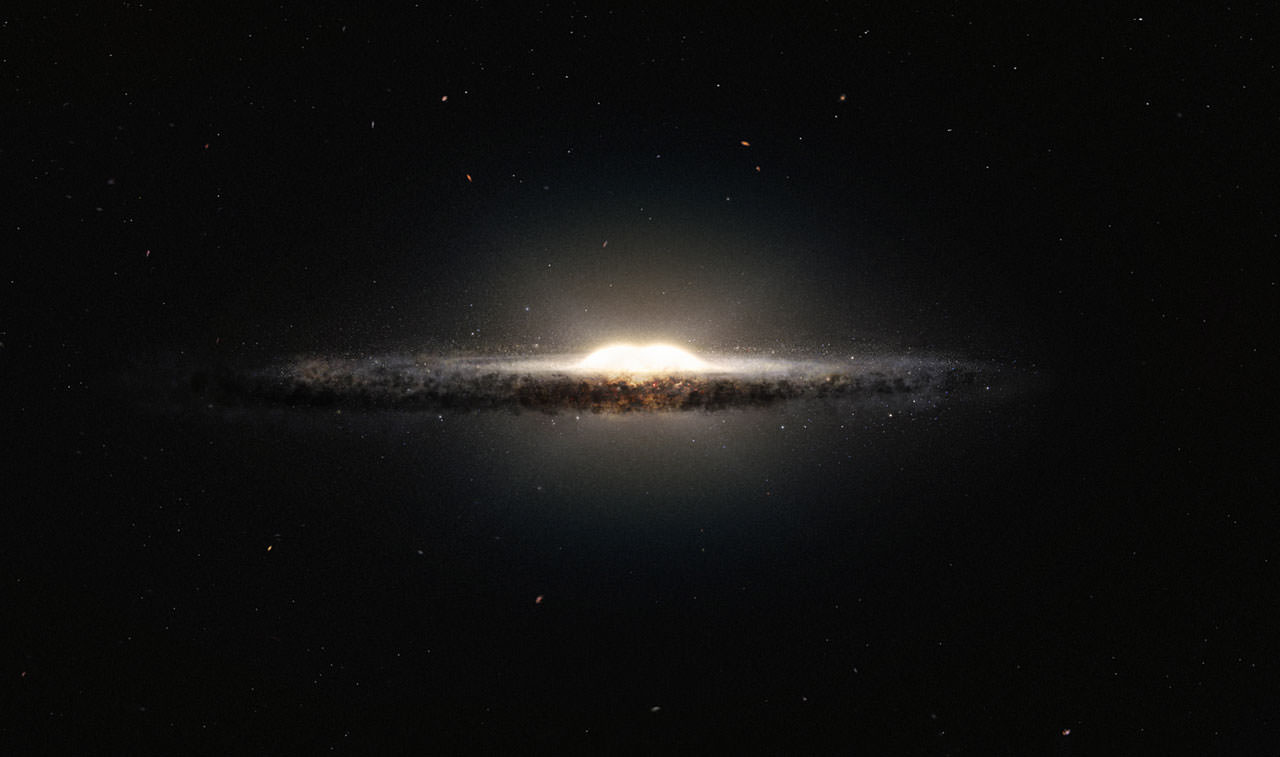
“For the first time, we can actually measure the large-scale structure of the galaxy using stars rather than gas,” explained Edward Churchwell, UW-Madison professor of astronomy and team co-leader. “We’ve established beyond the shadow of a doubt that our galaxy has a large bar structure that extends halfway out to the sun’s orbit. We know more about where the Milky Way’s spiral arms are.”
Named GLIMPSE360 (Galactic Legacy Mid-Plane Survey Extraordinaire project), the deep infrared survey captures only about 3% of the sky, but because it focuses on the plane of the Milky Way, where stars are most highly concentrated, it shows more than half of all the galaxy’s 300 billion suns.
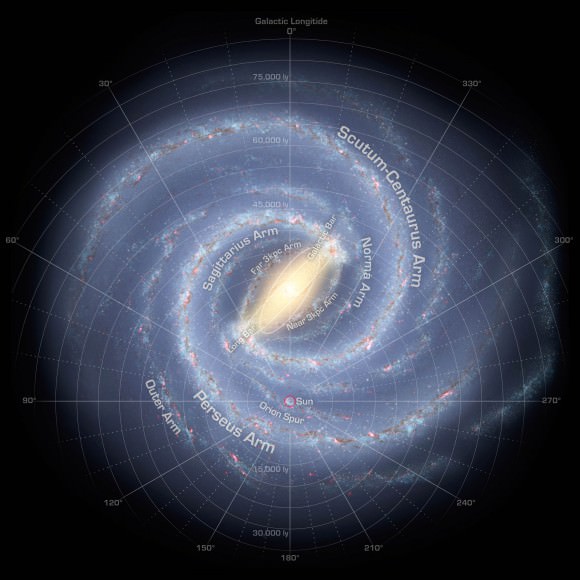
Using your imagination to hover high above the galactic plane, you’d see the Milky Way is a flat spiral galaxy sporting a stubby bar of stars crossing its central bulge. The solar system occupies a tiny niche in a minor spiral arm called the Orion Spur two-thirds of the way from the center to the edge. At 100,000 light years across, the Milky Way is vast beyond comprehension and yet it’s only one of an estimated 100 billion galaxies in the observable universe.

While you and I sit back and marvel at all the stellar and nebular eye candy, the Spitzer images are helping astronomers determine where the edge of the galaxy lies and location of the spiral arms. GLIMPSE images have already revealed the Milky Way to be larger than previously thought and shot through with bubbles of expanding gas and dust blown by giant stars.
Spitzer can see faint stars in the “backcountry” of our galaxy — the outer, darker regions that went largely unexplored before.

“There are a whole lot more lower-mass stars seen now with Spitzer on a large scale, allowing for a grand study,” said Whitney. “Spitzer is sensitive enough to pick these up and light up the entire ‘countryside’ with star formation.”
The new 360-degree view will also help NASA’s upcoming James Webb Space Telescope target the most interesting sites of star-formation, where it will make even more detailed infrared observations.
When you play around with the interactive mosaic, you’ll notice a few artifacts here and there among the images. Minor stuff. What took some getting used to was how strikingly different familiar nebulae appeared when viewed in infrared instead of visual light. The panorama is also available on the Aladin viewing platform which offers shortcuts to regions of interest.
Neil deGrasse Tyson, astrophysicist and host of the new Cosmos TV series, gave the third line of our “cosmic address” as the Milky Way after ‘Earth’ and ‘Solar System’. After a few minutes with GLIMPSE360 you’ll better appreciate the depth and breadth of our galactic home.