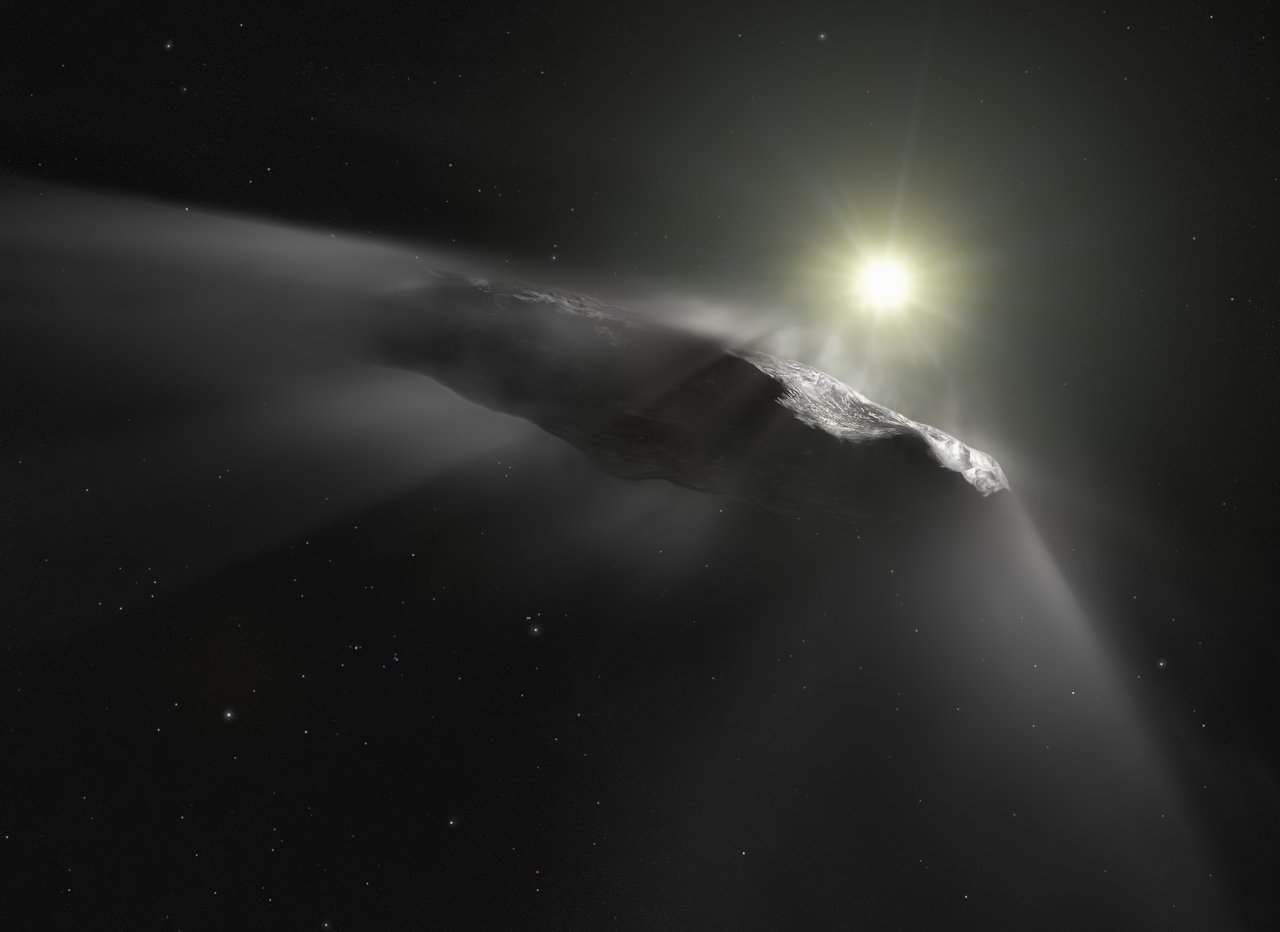
On October 19th, 2017, astronomers with the Pan-STARRS survey detected an interstellar object (ISO) passing through our Solar System for the first time. The object, known as 1I/2017 U1 Oumuamua, stimulated significant scientific debate and is still controversial today. One thing that all could agree on was that the detection of this object indicated that ISOs regularly enter our Solar System. What’s more, subsequent research has revealed that, on occasion, some of these objects come to Earth as meteorites and impact the surface.
This raises a very important question: if ISOs have been coming to Earth for billions of years, could it be that they brought the ingredients for life with them? In a recent paper, a team of researchers considered the implications of ISOs being responsible for panspermia – the theory that the seeds of life exist throughout the Universe and are distributed by asteroids, comets, and other celestial objects. According to their results, ISOs can potentially seed hundreds of thousands (or possibly billions) of Earth-like planets throughout the Milky Way.
Continue reading “Since Interstellar Objects Crashed Into Earth in the Past, Could They Have Brought Life?”