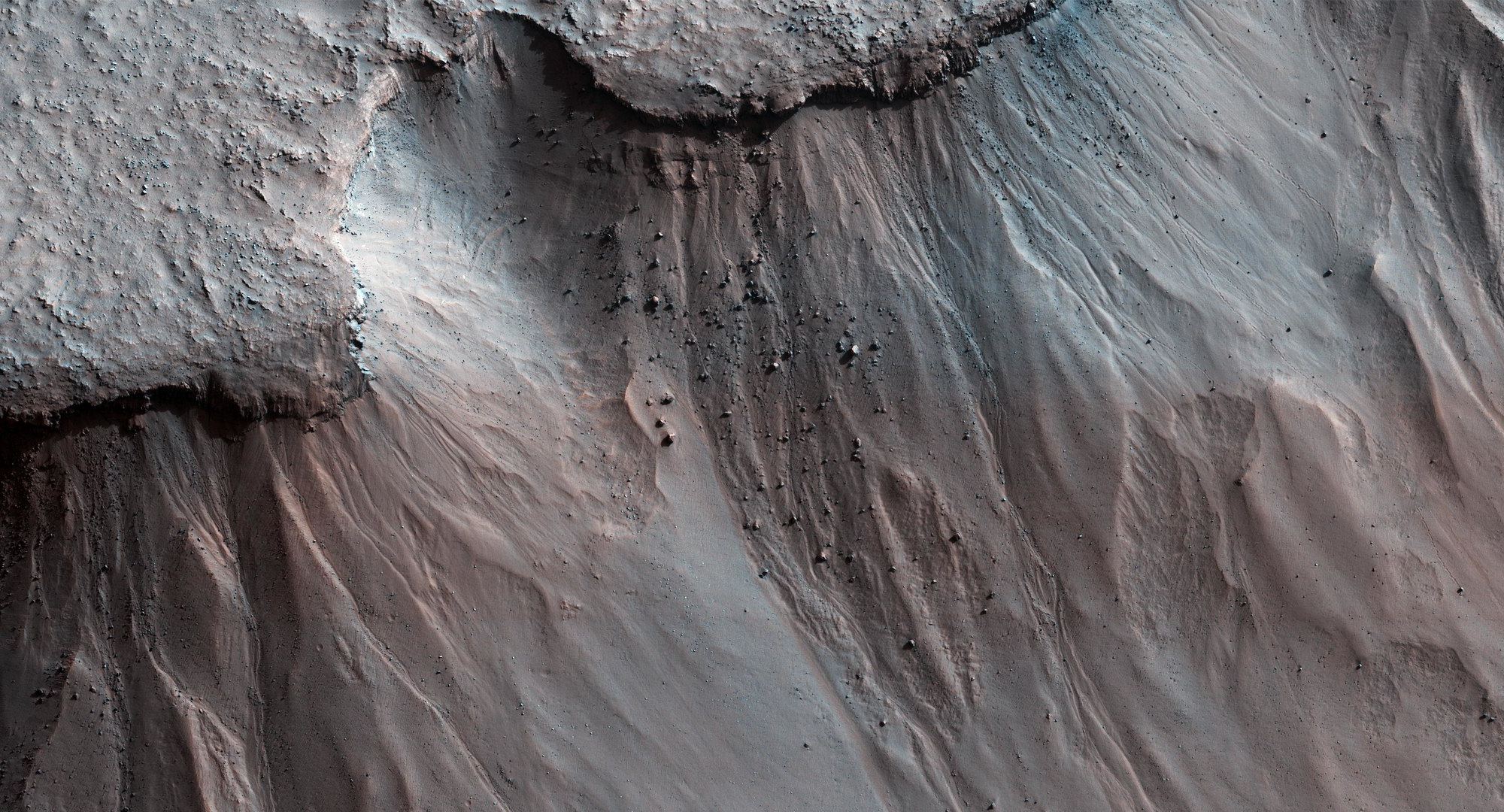
Some landslides, both here on Earth and on Mars, behave in a puzzling way: They flow a lot further than friction should allow them too.
They can also be massive, including a well-preserved one in Valles Marineris that is the same size as the state of Rhode Island. Scientists have speculated that it might be so large because a layer of ice that existed in the past provided lubrication. But a new study suggests that no ice is needed to explain it.
Continue reading “Landslides Work Differently on Mars, and Now We Might Know Why”