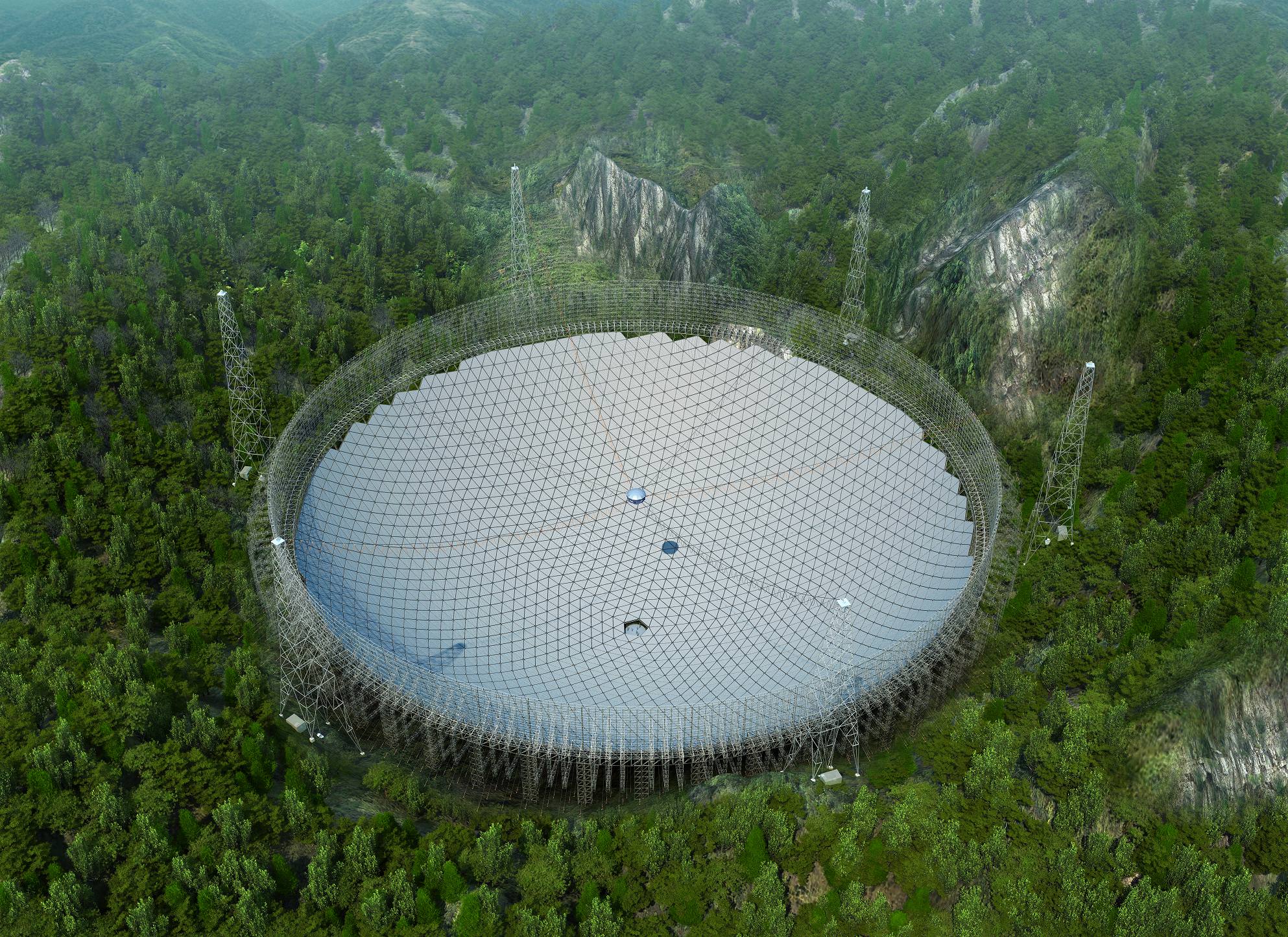
The 500-Meter Aperture Spherical Telescope (FAST), (aka. Tianyan, “Eye of Heaven”), is the largest radio observatory in the world. Since the observatory became operational in January 2020, this facility has made significant contributions to radio astronomy and the Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence (SETI). In particular, the observatory has been instrumental in detecting Fast Radio Burts (FRBs) and other cosmic phenomena that could be (but probably aren’t) possible indications of extraterrestrial communications.
Last week, while sifting through FAST data, the China Extraterrestrial Civilization Research Group (CECRG) from Beijing Normal University revealed that they discovered several signals that might be artificial in origin (a possible indication of an advanced civilization). These signals consisted of narrow-band electromagnetic radio transmission and were considered one of the best candidates for an extraterrestrial signal. Ah, but there’s a snag. According to subsequent news releases, those radio transmissions were apparently from Earth!
Continue reading “Chinese Astronomers Detect an Interesting (But NOT Alien) Signal With the FAST Radio Observatory”