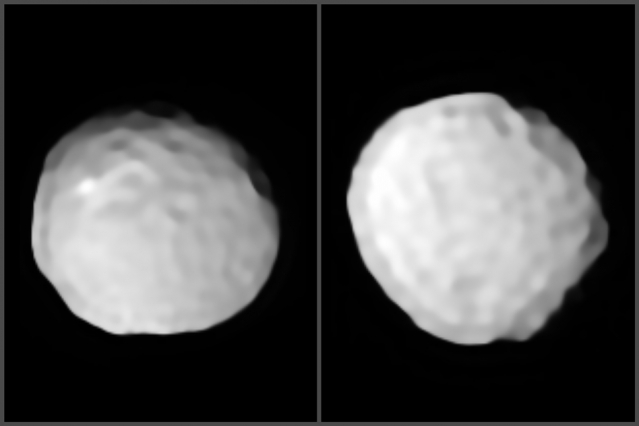
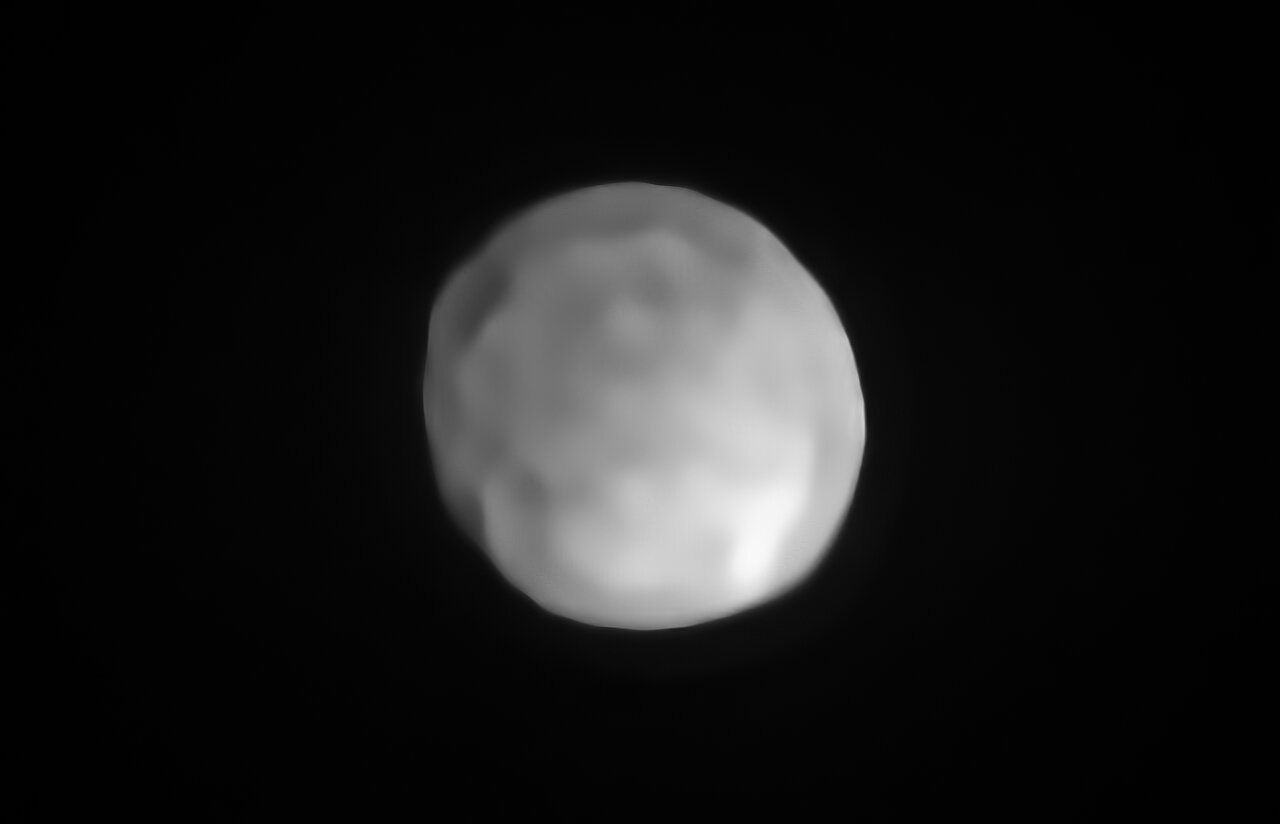
A huge team of astronomers have combined forces to use the European Southern Observatory’s Very Large Telescope (ESO’s VLT) to provide the sharpest view ever of 42 of the largest objects in the asteroid belt, located between Mars and Jupiter.
Fittingly, the collection of images was released on the 42nd anniversary of the publication of “The Hitchhiker’s Guide to the Galaxy” by Douglas Adams. In the book, the number 42 is the answer to the “Ultimate Question of Life, the Universe, and Everything.” These 42 images represent some of the sharpest views ever of these objects — which might contribute to answering these ultimate questions!
Plus, there’s a great poster of the asteroids, too:
Continue reading “Images of 42 of the Biggest Asteroids in the Solar System”