There are some things that never cease to amaze me and the discovery of distant objects is one of them. The James Webb Space Telescope has just found the most distant galaxy ever observed! It has the catchy title JADES-GS-z14-0 and it has a redshift of 14.32. This means its light left when the Universe was only 290 million years old! That means the light left the source LOOOONG before even our Milky Way was here! How amazing is that!
Continue reading “Webb Finds the Farthest Galaxy Ever Seen (So Far)”Pluto Has an Ocean of Liquid Water Surrounded by a 40-80 km Ice Shell
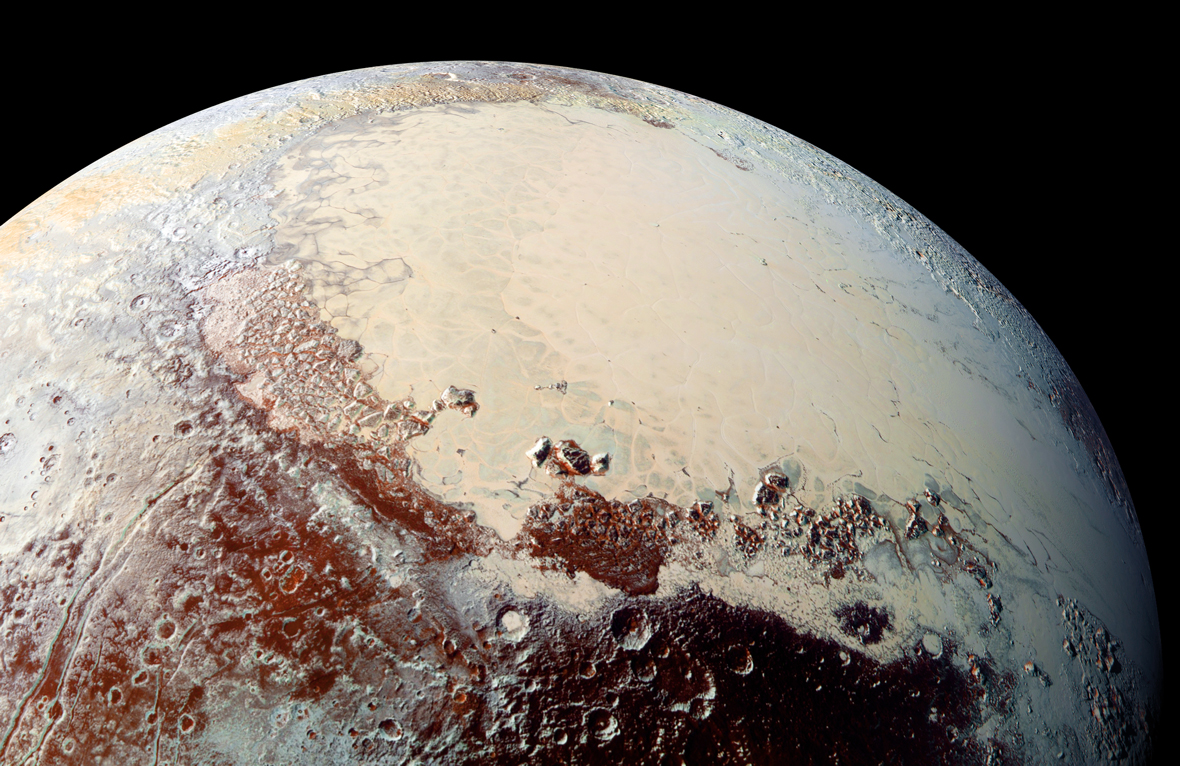

On July 14th, 2015, the New Horizons spacecraft conducted the first-ever flyby of Pluto, which once was (and to many, still is) the ninth planet of the Solar System. While the encounter was brief, the stunning images and volumes of data it obtained revealed a stunningly vibrant and dynamic world. In addition to Pluto’s heart, floating ice hills, nitrogen icebergs, and nitrogen winds, the New Horizons data also hinted at the existence of an ocean beneath Pluto’s icy crust. This effectively made Pluto (and its largest moon, Charon) members of the “Ocean Worlds” club.
Almost a decade after that historic encounter, scientists are still making discoveries from New Horizons data. In a new paper, planetary scientists Alex Nguyen and Dr. Patrick McGovern used mathematical models and images to learn more about the possible ocean between Pluto’s icy surface and its silicate and metallic core. According to their analysis, they determined that Pluto’s ocean is located beneath a surface shell measuring 40 to 80 km (25 to 50 mi), an insulating layer thick enough to ensure that an interior ocean remains liquid.
Continue reading “Pluto Has an Ocean of Liquid Water Surrounded by a 40-80 km Ice Shell”Where are All the Primordial Black Holes?
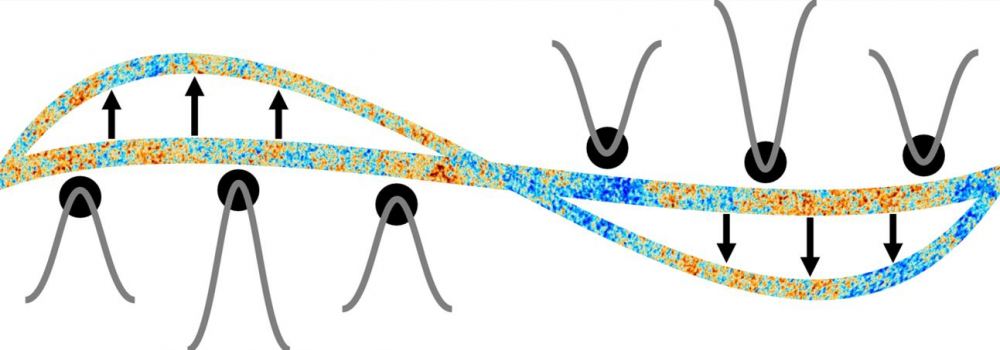
The earliest black holes in the Universe called primordial black holes (PBHs), are strong contenders to help explain why the Universe is heavier than it looks. There’s only one problem: these miniature monsters haven’t exactly been observed—yet. But, when astronomers do find them, they might turn out to be part of the Universe’s dark matter component.
Continue reading “Where are All the Primordial Black Holes?”A New Telescope Can Observe Even in Broad Daylight
Astronomy is a profession that, so far, has only been done at night, at least on Earth. Light from the Sun overwhelms any light from other stars, making it impractical for both professional and amateur astronomers to look at the stars during daytime. There are several disadvantages to this, not the least of which is that many potentially exciting parts of the sky aren’t visible at all for large chunks of the year as they pass too close to the Sun. To solve this, a team from Macquarie University, led by graduate student Sarah Caddy, developed a multi-camera system for a local telescope that allows them to observe during daytime.
Continue reading “A New Telescope Can Observe Even in Broad Daylight”Next-Generation Radar Will Map Threatening Asteroids
When the Arecibo Observatory dish in Puerto Rico collapsed in 2020, astronomers lost a powerful radio telescope and a unique radar instrument to map the surfaces of asteroids and other planetary bodies. Fortunately, a new, next-generation radar system called ngRADAR is under development, to eventually be installed at the 100-meter (328 ft.) Green Bank Telescope (GBT) in West Virginia. It will be able to track and map asteroids, with the ability to observe 85% of the celestial sphere. It will also be able to study comets, moons and planets in our Solar System.
“Right now, there is only one facility that can conduct high-power planetary radar, the 70-meter (230-foot) Goldstone antenna that is part of NASA’s Deep Space network,” said Patrick Taylor, the project director for ngRADAR and the radar division head for the National Radio Astronomy Observatory. “We had begun this process of developing a next generation radar system several years ago, but with the loss of Arecibo, this becomes even more important.”
Continue reading “Next-Generation Radar Will Map Threatening Asteroids”Hot Gas is Being Vented Away from the Center of the Milky Way

Studying gas in the Universe is no easy task. We often look to ‘non-visible’ wavelengths of the electromagnetic spectrum such as X-rays. The Chandra X-Ray observatory has been observing a vent of hot gas blowing away from the centre of the Milky Way. Located about 26,000 light years away, the jet extends for hundreds of light years and is perpendicular to the disk of the Galaxy. It is now thought the gas has been forced away from the centre of the Milky Way because of a collision with cooler gas lying in its path and creating shockwaves.
Continue reading “Hot Gas is Being Vented Away from the Center of the Milky Way”How Much Water Would a Self-Sustaining Moonbase Need?
As humanity returns to the Moon in the next few years, they’re going to need water to survive. While resupplies from Earth would work for a time, eventually the lunar base would have to become self-sustaining? So, how much water would be required to make this happen? This is what a recently submitted study hopes to address as a team of researchers from Baylor University explored water management scenarios for a self-sustaining moonbase, including the appropriate location of the base and how the water would be extracted and treated for safe consumption using appropriate personnel.
Continue reading “How Much Water Would a Self-Sustaining Moonbase Need?”Black Holes: Why study them? What makes them so fascinating?
Over the last few months, Universe Today has explored a plethora of scientific fields, including impact craters, planetary surfaces, exoplanets, astrobiology, solar physics, comets, planetary atmospheres, planetary geophysics, cosmochemistry, meteorites, radio astronomy, extremophiles, and organic chemistry, and how these various disciplines help scientists and the public better understand our place in the cosmos.
Continue reading “Black Holes: Why study them? What makes them so fascinating?”There’s Another, More Boring Explanation for those Dyson Sphere Candidate Stars
Dyson Spheres have been a tantalising digression in the hunt for alien intelligence. Just recently seven stars have been identified as potential candidates with most of their radiation given off in the infrared wavelengths. Potentially this is the signature of heat from a matrix of spacecraft around the star but alas, a new paper has another slightly less exciting explanation; dust obscured galaxies.
Continue reading “There’s Another, More Boring Explanation for those Dyson Sphere Candidate Stars”Hundreds of Massive Stars Have Simply Disappeared

The lifecycle of a star is regularly articulated as formation taking place inside vast clouds of gas and dust and then ending either as a planetary nebula or supernova explosion. In the last 70 years however, there seems to be a number of massive stars that are just disappearing! According to stellar evolution models, they should be exploding as supernova but instead, they just seem to vanish. A team of researchers have studied the behaviour of star VFTS 243 – a main sequence star with a black hole companion – and now believe it, like the others, have just collapsed, imploding into a black hole!
Continue reading “Hundreds of Massive Stars Have Simply Disappeared”





