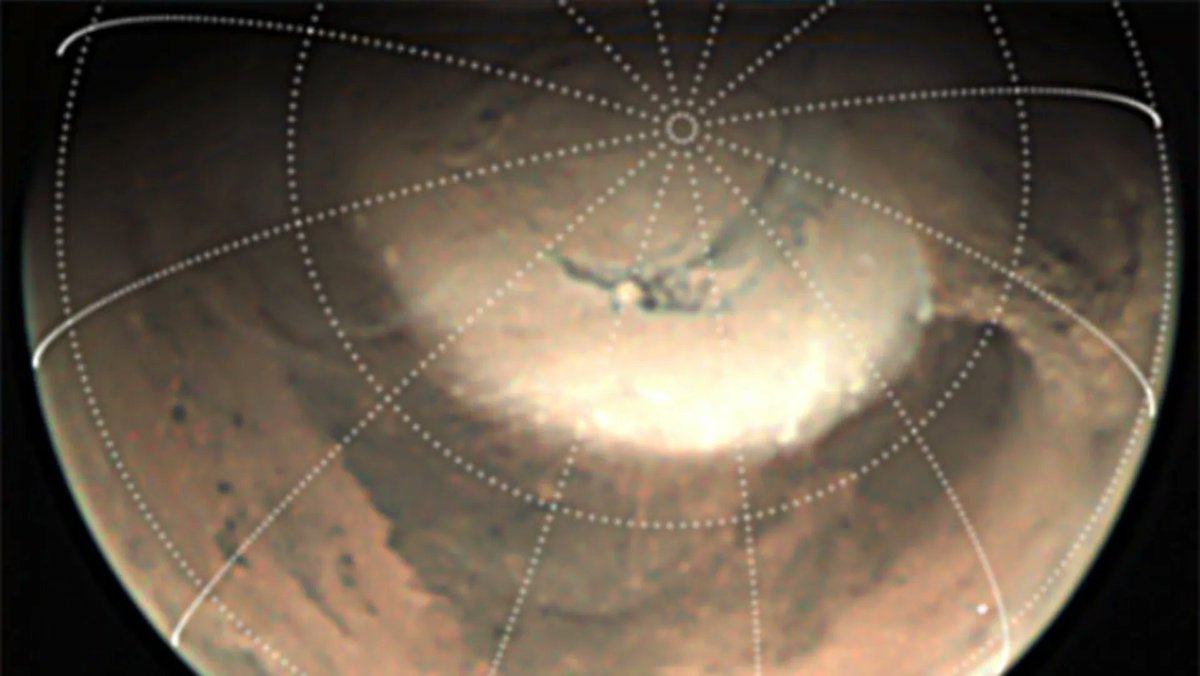
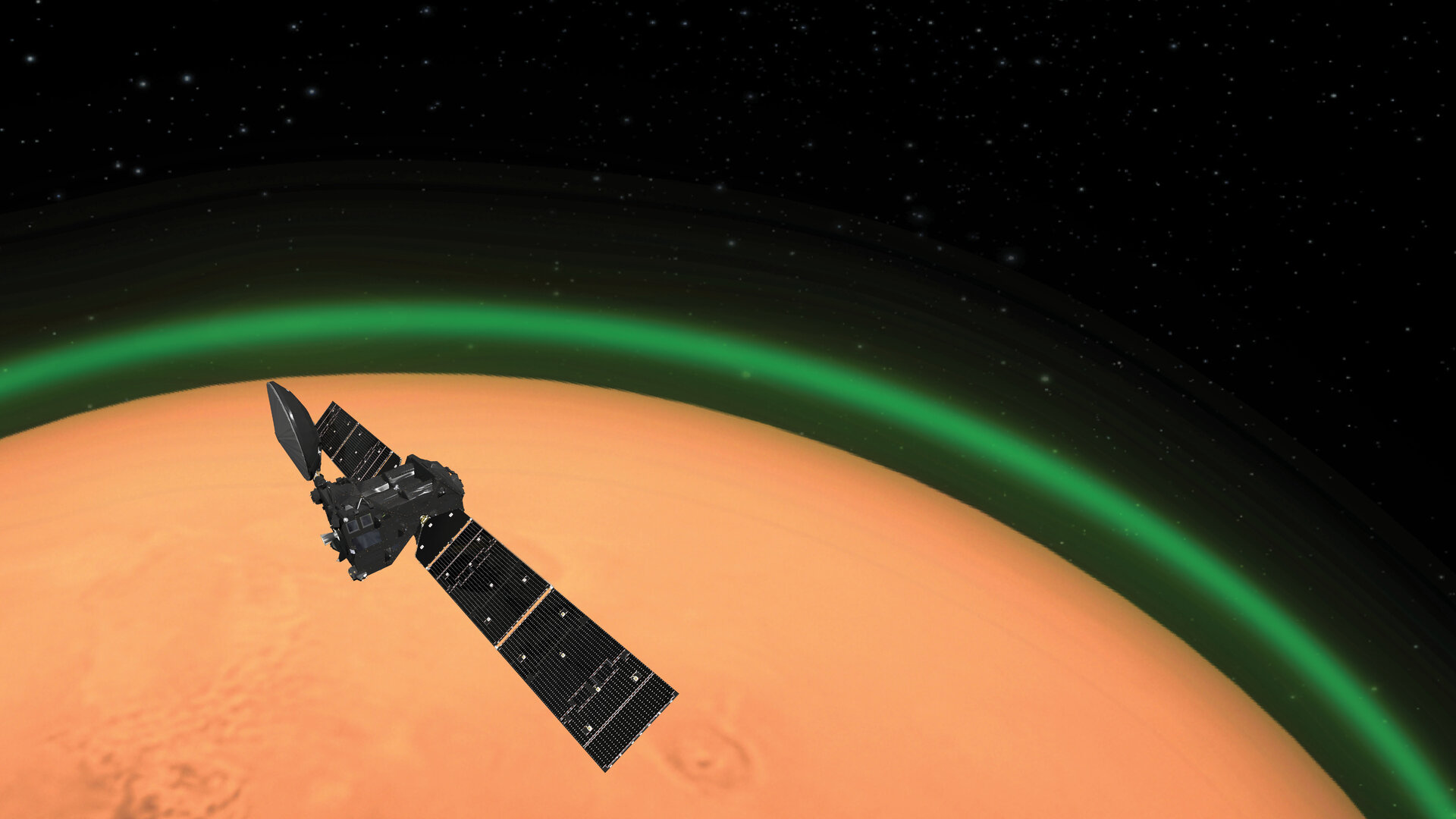
On Earth, there is a phenomenon known as nightglow, where the atmosphere experiences faint light emissions that prevent the night sky from becoming completely dark. This is caused by various processes in the upper atmosphere, like the recombination of atoms, cosmic rays striking the atmosphere, or oxygen and nitrogen interacting with hydroxyl a few hundred kilometers from the surface. Thanks to data obtained by the ESA’s ExoMars Trace Gas Orbiter (TGO), the same phenomenon has been observed in the Martian atmosphere for the first time.
While scientists have long suspected that Mars also experiences this atmospheric phenomenon, this is the first time that effectively proves it. The revelation was made by an international team of scientists based on their analysis of data from the TGO’s Nadir and Occultation for MArs Discovery (NOMAD) spectrometer. When astronauts and rovers explore Mars’ polar regions in the near future, they will see a green glow whenever they look up at the sky and could even use the glow to navigate and find their way in the dark of night.
Continue reading “Martian Green Nightglow Seen for the First Time”