Oh glory! A rainbow-like optical phenomenon known as a ‘glory’ has been imaged for the first time on another planet. It was seen in the atmosphere of our nearest neighbor, Venus by ESA’s Venus Express orbiter.
Rainbows and glories occur when sunlight shines on cloud droplets. While rainbows arch across the sky, glories appear as circular rings of colored concentric rings centered on a bright core.

Glories are only seen when the observer is situated directly between the Sun and the cloud particles that are reflecting sunlight. On Earth, they can often be seen with the naked eye from airplanes, or when looking down upon fog or water vapor, such as when climbing a mountain.
On Earth, the simple ingredients needed for a rainbow are sunlight and raindrops. On Venus, the droplets are likely made of sulfuric acid.
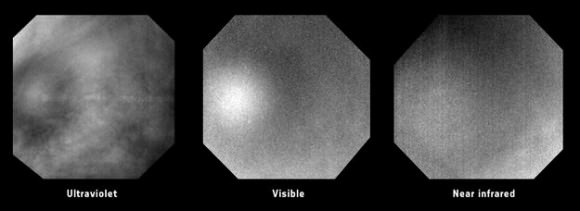
Seeing this glory was no accident: they made a calculated effort to image the clouds with the Sun directly behind the Venus Express spacecraft. The scientists were hoping to spot a glory in order to determine important characteristics of the cloud droplets.
Today, the team reported that they were successful. The glory in the images here was seen at the Venus cloud tops, 70 km above the planet’s surface, back on July 24, 2011. Their paper was just recently accepted for publication.
The glory was 1,200 km wide as seen from the spacecraft, 6,000 km away.
The Venus Express team deduced that from these observations, the cloud particles are estimated to be 1.2 micrometres across, roughly a fiftieth of the width of a human hair.
The fact that the glory is 1,200 km wide means that the particles at the cloud tops are uniform on this scale at least.
The variations of brightness of the rings of the observed glory is different than that expected from clouds of only sulphuric acid mixed with water, suggesting that other chemistry may be at play.
One idea is that the cause is the “UV-absorber,” an unknown atmospheric component responsible for mysterious dark markings seen in the cloud tops of Venus at ultraviolet wavelengths. More investigation is needed to draw a firm conclusion.
Scientists also think that it would be possible to see a rainbow — and perhaps even a glory — on Titan since the atmosphere on this moon of Saturn is likely filled with methane droplets.
Source: ESA

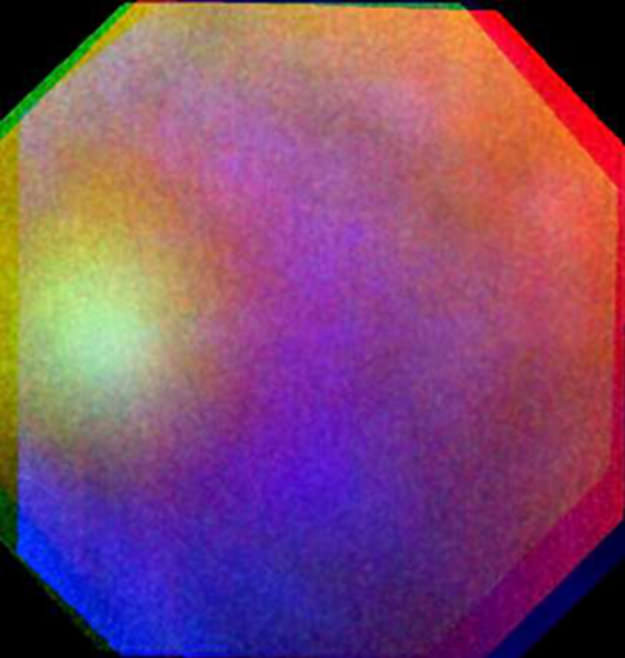
Wow! Would this be the first atmospheric optics effect ever observed on another world? Amazing!
“The variations of brightness of the rings of the observed glory is different than that expected from clouds of only sulphuric acid mixed with water”:
brightness isn’t mentioned in the abstract, they talk of the refractive index instead which is derived from the glory angular size, not brightness.
More about the glory mysteries here: http://www.atoptics.co.uk/droplets/glofeat.htm (and prev/next pages)
I wonder how the higher refractive index plays here.
Not sure, but I bet they’ve got some things from the Mars landers. They’ve had lots and lots of ops to catch things. Nancy, do you know? I bet Emily does. lol. This is a HUGE example of why eyes and ears (and noses and throats) all over the local worlds are VITAL to catching rare data points like this to help further our understanding in the Planetary Sciences…
On second thoughts I was probably wrong, as glory size depends on particle size. Question is: exclusively or not? I wish I could access this paper ;_;