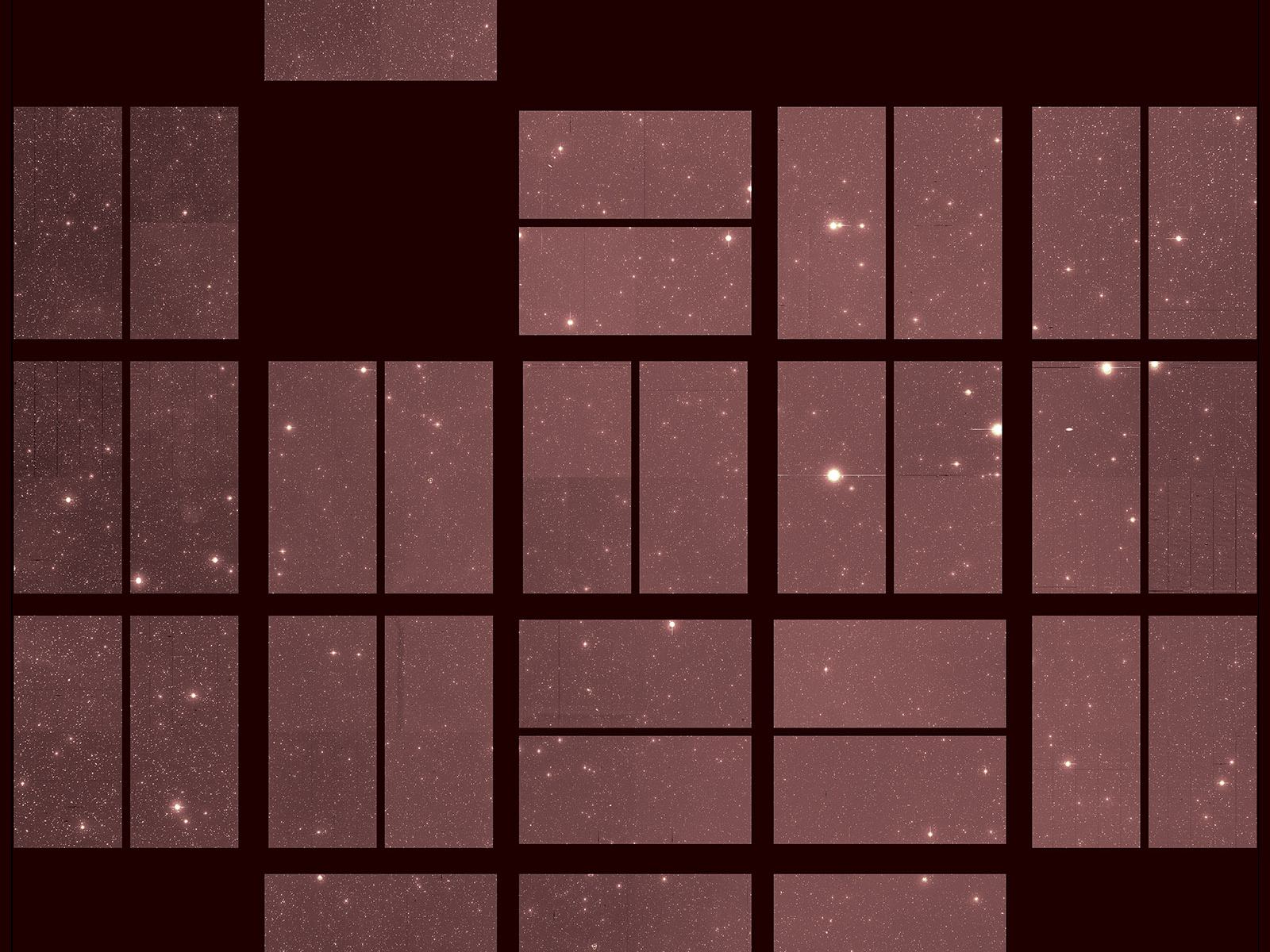
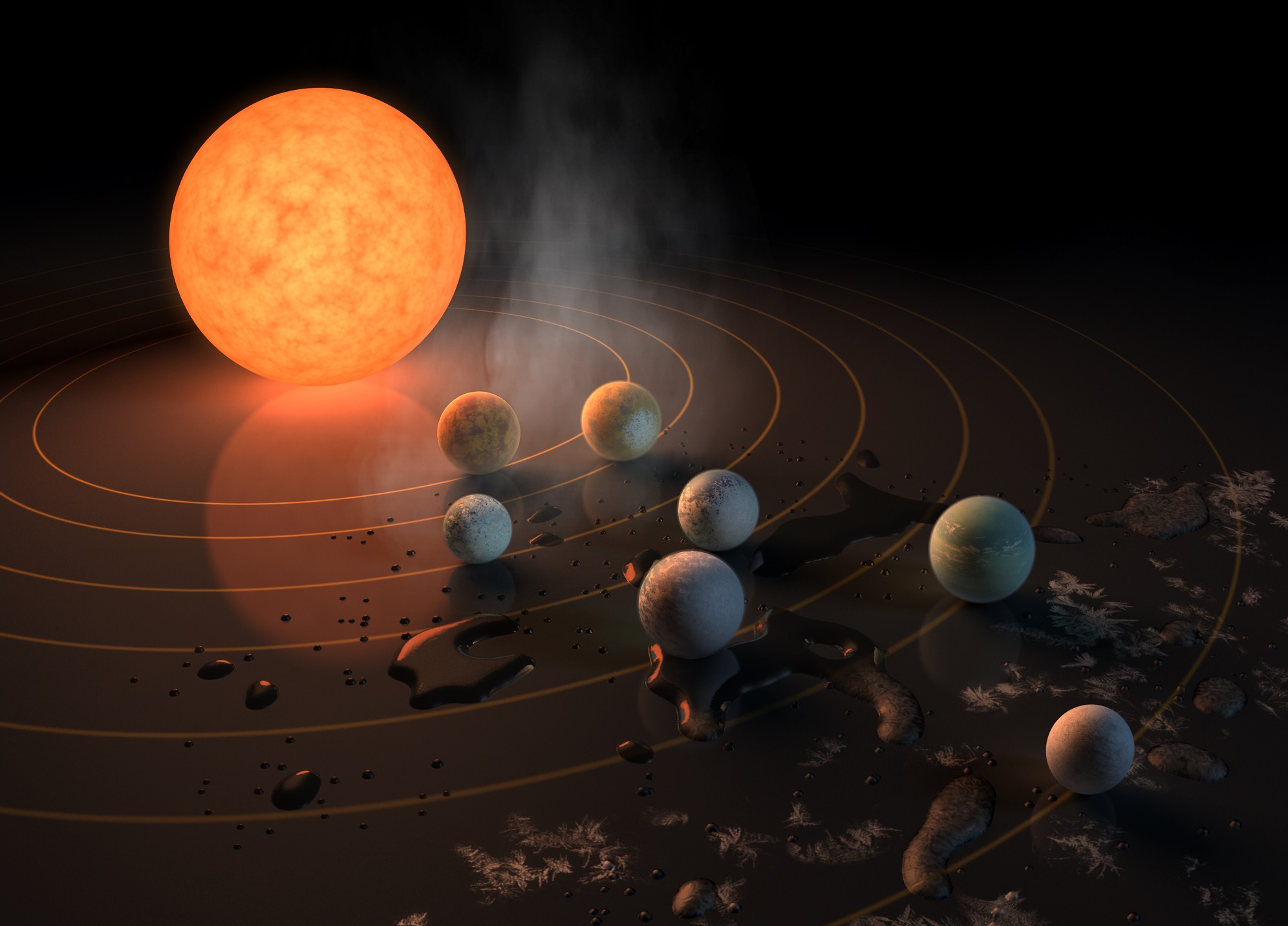
The TRAPPIST-1 system has long be studied by exoplanet hunters due to its unique quantity of planets that happen to also be Earth sized. In a recent paper, a team of scientists led by Eric Agol at the University of Washington, dove into more detail on the density of the seven known planets in the system, and, surprisingly, found that they were all very similar.
Continue reading “There are Seven Rocky Planets in the TRAPPIST-1 System and They’re Surprisingly Similar”Some Stars Could Support as Many as 7 Habitable Planets

In recent decades, over 4,000 extrasolar planets have been confirmed beyond our Solar System. With so many planets available for study, astronomers have learned a great deal about the types of planets that exist out there and what kind of conditions are prevalent. For instance, they have been able to get a better idea of just how common habitable planets are (at least by our standards).
As it turns out, a surprisingly high number of planets out there could support life. That is the conclusion reached by a team of astronomers and planetary scientists who conducted a study of the possible sizes of habitable zones (HZ) based on stellar classification. After considering many planets could stably orbit within them, they came to the conclusion that stars with no Jupiter-sized gas giants can have as many as seven habitable planets!
Continue reading “Some Stars Could Support as Many as 7 Habitable Planets”Do the TRAPPIST-1 Planets Have Atmospheres?

In February of 2017, the scientific community rejoiced as NASA announced that a nearby star (TRAPPIST-1) had a system of no less than seven rocky planets! Since that time, astronomers have conducted all kinds of follow-up observations and studies in the hopes of learning more about these exoplanets. In particular, they have been attempting to learn if any of the planets located in the stars Habitable Zone (HZ) could actually be habitable.
Many of these studies have been concerned with whether or not the TRAPPIST-1 planets have sufficient water on their surfaces. But just as important is the question of whether or not any have viable atmospheres. In a recent study that provides an overview of all observations to date on TRAPPIST-1 planets, a team found that depending on the planet in question, they are likely to have good atmospheres, if any at all.
Read moreAstronomers Find a Six-Planet System Which Orbit in Lockstep With Each Other

To date, astronomers have confirmed the existence of 4,152 extrasolar planets in 3,077 star systems. While the majority of these discoveries involved a single planet, several hundred star systems were found to be multi-planetary. Systems that contain six planets or more, however, appear to be rarer, with only a dozen or so cases discovered so far.
This is what astronomers found after observing HD 158259, a Sun-like star located about 88 light-years from Earth, for the past seven years using the SOPHIE spectrograph. Combined with new data from the Transiting Exoplanet Space Satellite (TESS), an international team reported the discovery of a six planet system where all were in near-perfect rhythm with each other.
Continue reading “Astronomers Find a Six-Planet System Which Orbit in Lockstep With Each Other”How Did the TRAPPIST-1 Planets Get Their Water?

In 2017, an international team of astronomers announced a momentous discovery. Based on years of observations, they found that the TRAPPIST-1 system (an M-type red dwarf located 40 light-years from Earth) contained no less than seven rocky planets! Equally exciting was the fact that three of these planets were found within the star’s Habitable Zone (HZ), and that the system itself has had 8 billion years to develop the chemistry for life.
At the same time, the fact that these planets orbit tightly around a red dwarf star has given rise to doubts that these three planets could maintain an atmosphere or liquid water for very long. According to new research by an international team of astronomers, it all comes down to the composition of the debris disk that the planets formed from and whether or not comets were around to distribute water afterward.
Read moreAstronomers Spot Rare Brown Dwarf Pair

Sometimes, the strangest stellar finds are right in our own cosmic neighborhood. Astronomers recently made an interesting discovery while putting a new set of telescopes through their paces: an eclipsing pair of sub-stellar brown dwarfs.
Continue reading “Astronomers Spot Rare Brown Dwarf Pair”This is Kepler’s Final Image
On October 30th, 2018, after nine years of faithful service, the Kepler Space Telescope was officially retired. With nearly 4000 candidates and 2,662 confirmed exoplanets to its credit, no other telescope has managed to teach us more about the worlds that exist beyond our Solar System. In the coming years, multiple next-generation telescopes will be deployed that will attempt to build on the foundation Kepler built.
And yet, even in retirement, Kepler is still providing us with impressive discoveries. For starters, NASA started the new year by announcing the discovery of several new exoplanets, including a Super-Earth and a Saturn-sized gas giant, as well as an unusually-sized planet that straddles these two categories. On top of that, NASA recently released the “last lighty” image and recordings obtained by Kepler before it ran out of fuel and ended its mission.
Continue reading “This is Kepler’s Final Image”One of the TRAPPIST-1 Planets Has an Iron Core
In February of 2017, a team of European astronomers announced the discovery of a seven-planet system orbiting the nearby star TRAPPIST-1. Aside from the fact that all seven planets were rocky, there was the added bonus of three of them orbiting within TRAPPIST-1’s habitable zone. Since that time, multiple studies have been conducted to determine whether or not any of these planets could be habitable.
In accordance with this goal, these studies have focused on whether or not these planets have atmospheres, their compositions and their interiors. One of the latest studies was conducted by two researchers from Columbia University’s Cool Worlds Laboratory, who determined that one of the TRAPPIST-1 planets (TRAPPIST-1e) has a large iron core – a finding which could have implications for this planet’s habitability.
Continue reading “One of the TRAPPIST-1 Planets Has an Iron Core”
Weekly Space Hangout: April 4, 2018: Mathew Anderson’s “Habitable Exoplanets”
Hosts:
Fraser Cain (universetoday.com / @fcain)
Dr. Paul M. Sutter (pmsutter.com / @PaulMattSutter)
Dr. Kimberly Cartier (KimberlyCartier.org / @AstroKimCartier )
Dr. Morgan Rehnberg (MorganRehnberg.com / @MorganRehnberg & ChartYourWorld.org)
Special Guests:
Mathew Anderson, author and good friend of the Weekly Space Hangout, joins us again this week to discuss his newest book, Habitable Exoplanets: Red Dwarf Systems Like TRAPPIST-1, in which he focuses on exoplanet properties and the chances for habitable planets around Red Dwarf stars.
As he did with his two prior books, Our Cosmic Story and its followup Is Anyone Out There, Mathew will be offering a free e-copy of Habitable Exoplanets: Red Dwarf Systems Like TRAPPIST-1 to viewers of the Weekly Space Hangout, so be sure to tune in this week to find out how to get your free copy of this fascinating book.
Announcements:
If you would like to join the Weekly Space Hangout Crew, visit their site here and sign up. They’re a great team who can help you join our online discussions!
We record the Weekly Space Hangout every Wednesday at 5:00 pm Pacific / 8:00 pm Eastern. You can watch us live on Universe Today, or the Weekly Space Hangout YouTube page – Please subscribe!
TRAPPIST-1 Planets Might Actually Have Too Much Water to be Habitable

In February of 2017, the world was astounded to learn that astronomers – using data from the TRAPPIST telescope in Chile and the Spitzer Space Telescope – had identified a system of seven rocky exoplanets in the TRAPPIST-1 system. As if this wasn’t encouraging enough for exoplanet-enthusiasts, it was also indicated that three of the seven planets orbited within the stars’ circumstellar habitable zone (aka. “Goldilocks Zone”).
Since that time, this system has been the focus of considerable research and follow-up surveys to determine whether or not any of its planets could be habitable. Intrinsic to these studies has been the question whether or not the planets have liquid water on their surfaces. But according to a new study by a team of American astronomers, the TRAPPIST planets may actually have too much water to support life.
Continue reading “TRAPPIST-1 Planets Might Actually Have Too Much Water to be Habitable”