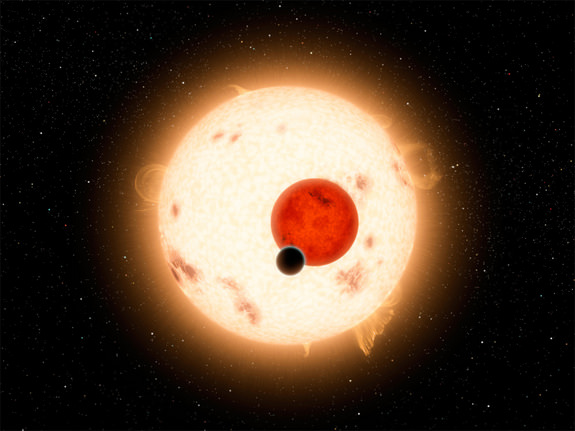
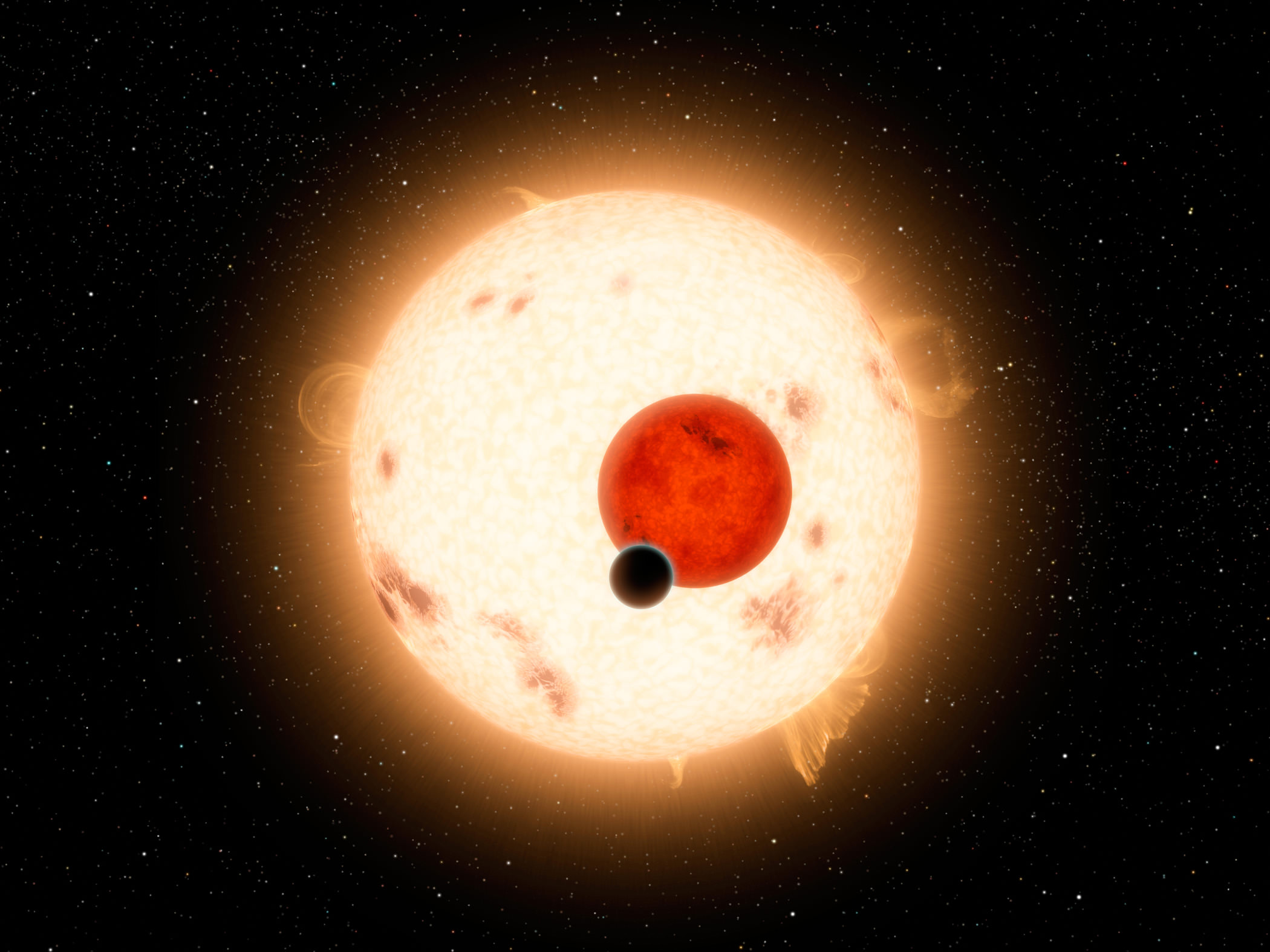
In the famous scene from the Star Wars movie “A New Hope” we recall young Luke Skywalker contemplating his future in the light of a binary sunset on the planet Tatooine. Not so many years later in 2011, astronomers using the Kepler Space Telescope discovered Kepler-16b, the first Tatooine-like planet known to orbit two suns in a binary system. Now astronomers have found a planet in a triple star system where an observer would either experience constant daylight or enjoy triple sunrises and sunsets each day, depending on the seasons, which last longer than human lifetimes.
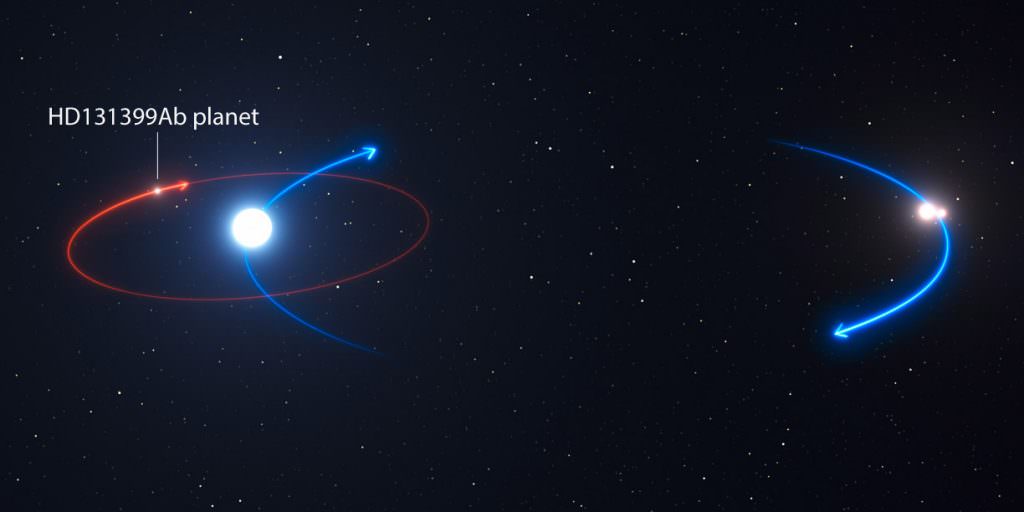
They used the SPHERE instrument on the European Southern Observatory’s Very Large Telescope to directly image the planet, the first ever found inside a triple-star system. The three stars are named HD 131399A, HD 131399B and HD 131399C in order of decreasing brightness; the planet orbits the brightest and goes by the chunky moniker HD 131399Ab.
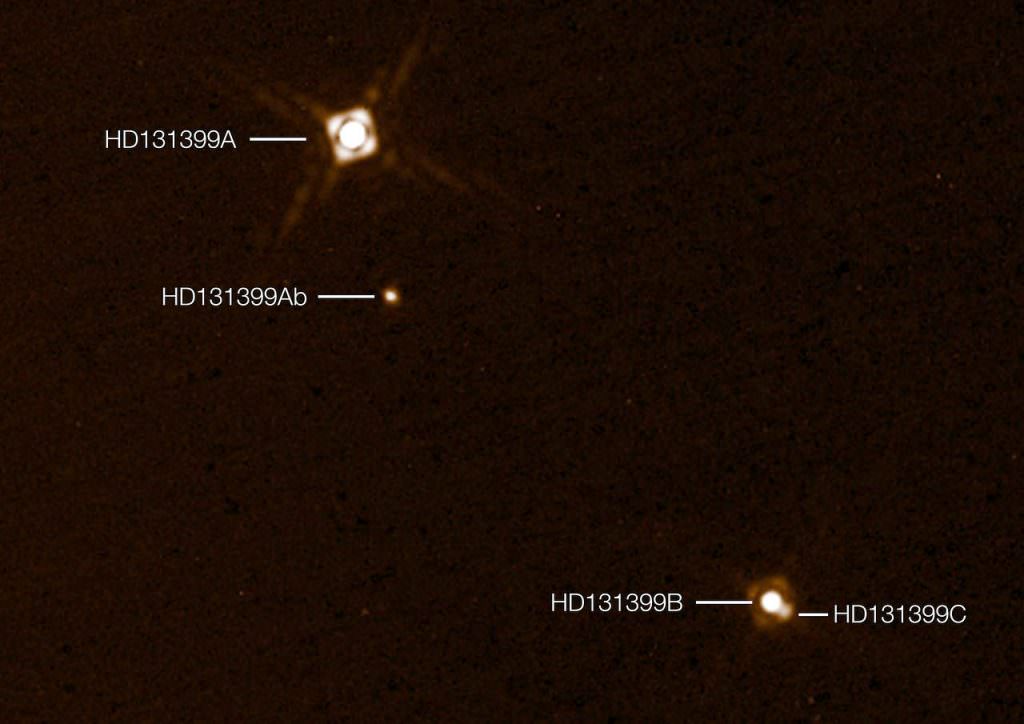

Located about 320 light-years from Earth in the constellation of Centaurus the Centaur HD 131399Ab is about 16 million years old, making it also one of the youngest exoplanets discovered to date, and one for which we have a direct image. With a temperature of around 1,075° F (580° C) and the mass about four times that of Jupiter, it’s also one of the coldest and least massive directly-imaged exoplanets.

To pry it loose from the glare of its host suns, a team of astronomers led by the University of Arizona used a state of the art adaptive optics system to give razor-sharp images coupled with SPHERE, an instrument that blocks the light from the central star(s) similar to the way a coronagraph blocks the brilliant solar disk and allows study of the Sun’s corona. Finally, the region around the star is photographed in infrared polarized light to make any putative planets stand out more clearly against the remaining glare.
The planet, HD 131399Ab, is unlike any other known world — its orbit around the brightest of the three stars is by far the widest known within a multi-star system. It was once thought that planets orbiting a multi-star system would be unstable because of the changing gravitational tugs on the planet from the other two stars. Yet this planet remains in orbit instead of getting booted out of the system, leading astronomers to think that planets orbiting multiple stars might be more common that previously thought.
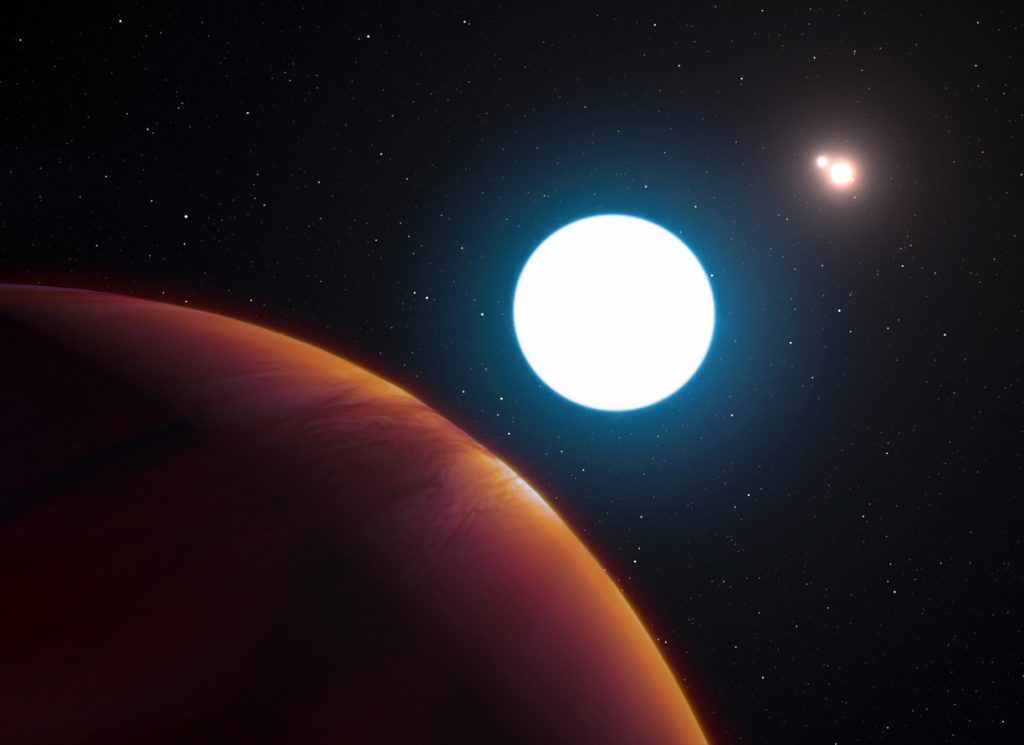

HD 131399Ab orbits HD 131399A, estimated to be 80% more massive than the Sun. Its double-star companions orbit about 300 times the Earth-Sun distance away. For much of the planet’s 550 year orbit, all three stars would appear close together in the sky and set one after the other in unique triple sunsets and sunrises each day. But when the planet reached the other side of its orbit around its host sun, that star and the pair would lie in opposite parts of the sky. As the pair set, the host would rise, bathing HD 131399Ab in near-constant daytime for about one-quarter of its orbit, or roughly 140 Earth-years.
Click to see a wonderful simulation showing how the planet orbits within the trinary system
Planets in multi-star systems are of special interest to astronomers and planetary scientists because they provide an example of how the mechanism of planetary formation functions in these more extreme scenarios. Since multi-star systems are just as common as single stars, so planets may be too.
How would our perspective of the cosmos change I wonder if Earth orbited triple suns instead of a single star? Would the sight deepen our desire for adventure like the fictional Skywalker? Or would we suffer the unlucky accident of being born at the start of a multi-decade long stretch of constant daylight? Wonderful musings for the next clear night under the stars.