Shortly after Einstein published his Theory of General Relativity in 1915, physicists began to speculate about the existence of black holes. These regions of space-time from which nothing (not even light) can escape are what naturally occur at the end of most massive stars’ life cycle. While black holes are generally thought to be voracious eaters, some physicists have wondered if they could also support planetary systems of their own.
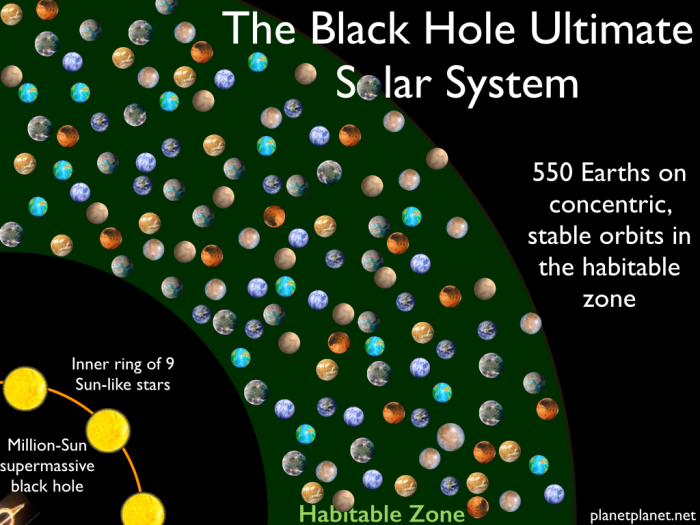
Looking to address this question, Dr. Sean Raymond – an American physicist currently at the University of Bourdeaux – created a hypothetical planetary system where a black hole lies at the center. Based on a series of gravitational calculations, he determined that a black hole would be capable of keeping nine individual Suns in a stable orbit around it, which would be able to support 550 planets within a habitable zone.
He named this hypothetical system “The Black Hole Ultimate Solar System“, which consists of a non-spinning black hole that is 1 million times as massive as the Sun. That is roughly one-quarter the mass of Sagittarius A*, the super-massive black hole (SMBH) that resides at the center of the Milky Way Galaxy (which contains 4.31 million Solar Masses).

As Raymond indicates, one of the immediate advantages of having this black hole at the center of a system is that it can support a large number of Suns. For the sake of his system, Raymond chose 9, thought he indicates that many more could be sustained thanks to the sheer gravitational influence of the central black hole. As he wrote on his website:
“Given how massive the black hole is, one ring could hold up to 75 Suns! But that would move the habitable zone outward pretty far and I don’t want the system to get too spread out. So I’ll use 9 Suns in the ring, which moves everything out by a factor of 3. Let’s put the ring at 0.5 AU, well outside the innermost stable circular orbit (at about 0.02 AU) but well inside the habitable zone (from about 2.7 to 5.4 AU).”
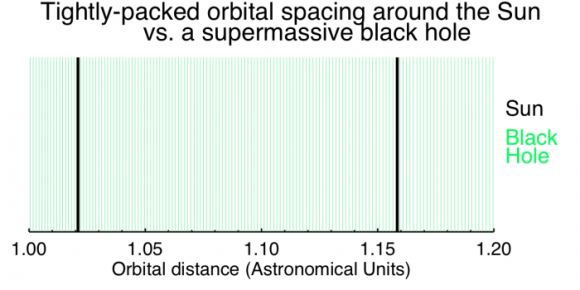
Another major advantage of having a black hole at the center of a system is that it shrinks what is known as the “Hill radius” (aka. Hill sphere, or Roche sphere). This is essentially the region around a planet where its gravity is dominant over that of the star it orbits, and can therefore attract satellites. According to Raymond, a planet’s Hill radius would be 100 times smaller around a million-sun black hole than around the Sun.
This means that a given region of space could stably fit 100 times more planets if they orbited a black hole instead of the Sun. As he explained:
“Planets can be super close to each other because the black hole’s gravity is so strong! If planets are little toy Hot wheels cars, most planetary systems are laid out like normal highways (side note: I love Hot wheels). Each car stays in its own lane, but the cars are much much smaller than the distance between them. Around a black hole, planetary systems can be shrunk way down to Hot wheels-sized tracks. The Hot wheels cars — our planets — don’t change at all, but they can remain stable while being much closer together. They don’t touch (that would not be stable), they are just closer together.”
This is what allows for many planets to be placed with the system’s habitable zone. Based on the Earth’s Hill radius, Raymond estimates that about six Earth-mass planets could fit into stable orbits within the same zone around our Sun. This is based on the fact that Earth-mass planets could be spaced roughly 0.1 AU from each other and maintain a stable orbit.
Given that the Sun’s habitable zone corresponds roughly to the distances between Venus and Mars – which are 0.3 and 0.5 AU away, respectively – this means there is 0.8 AUs of room to work with. However, around a black hole with 1 million Solar Masses, the closest neighboring planet could be just 1/1000th (0.001) of an AU away and still have a stable orbit.
Doing the math, this means that roughly 550 Earths could fit in the same region orbiting the black hole and its nine Suns. There is one minor drawback to this whole scenario, which is that the black hole would have to remain at its current mass. If it were to become any larger, it would cause the Hill radii of its 550 planets to shrink down further and further.
Once the Hill radius got down to the point where it was the same size as any of the Earth-mass planets, the black hole would begin to tear them apart. But at 1 million Solar masses, the black hole is capable of supporting a massive system of planets comfortably. “With our million-Sun black hole the Earth’s Hill radius (on its current orbit) would already be down to the limit, just a bit more than twice Earth’s actual radius,” he says.
Lastly, Raymond considers the implications that living in such a system would have. For one, a year on any planet within the system’s habitable zone would be much shorter, owing to the fact their orbital periods would be much faster. Basically, a year would last roughly 1.6 days for planets at the inner edge of the habitable zone and 4.6 days for planets at the outer edge of the habitable zone.
In addition, on the surface of any planet in the system, the sky would be a lot more crowded! With so many planets in close orbit together, they would pass very close to one another. That essentially means that from the surface of any individual Earth, people would be able to see nearby Earths as clear as we see the Moon on some days. As Raymond illustrated:
“At closest approach (conjunction) the distance between planets is about twice the Earth-Moon distance. These planets are all Earth-sized, about 4 times larger than the Moon. This means that at conjunction each planet’s closest neighbor appears about twice the size of the full Moon in the sky. And there are two nearest neighbors, the inner and outer one. Plus, the next-nearest neighbors are twice as far away so they are still as big as the full Moon during conjunction. And four more planets that would be at least half the full Moon in size during conjunction.”
He also indicates that conjunctions would occur almost once per orbit, which would mean that every few days, there would be no shortage of giant objects passing across the sky. And of course, there would be the Sun’s themselves. Recall that scene in Star Wars where a young Luke Skywalker is watching two suns set in the desert? Well, it would a little like that, except way more cool!
According to Raymond’s calculations, the nine Suns would complete an orbit around the black hole every three hours. Every twenty minutes, one of these Suns would pass behind the black hole, taking just 49 seconds to do so. At this point, gravitational lensing would occur, where the black hole would focus the Sun’s light toward the planet and distort the apparent shape of the Sun.
To illustrate what this would look like, he provides an animation (shown above) created by @GregroxMun – a planet modeller who develops space graphics for Kerbal and other programs – using Space Engine.
While such a system may never occur in nature, it is interesting to know that such a system would be physically possible. And who knows? Perhaps a sufficiently advanced species, with the ability to tow stars and planets from one system and place them in orbit around a black hole, could fashion this Ultimate Solar System. Something for SETI researchers to be on the lookout for, perhaps?
This hypothetical exercise was the second installment in two-part series by Raymond, titled “Black holes and planets”. In the first installment, “The Black Hole Solar System“, Raymond considered what it would be like if our system orbited around a black hole-Sun binary. As he indicated, the consequences for Earth and the other Solar planets would be interesting, to say the least!
Raymond also recently expanded on the Ultimate Solar System by proposing The Million Earth Solar System. Check them all out at his website, PlanetPlanet.net.
Further Reading: PlanetPlanet