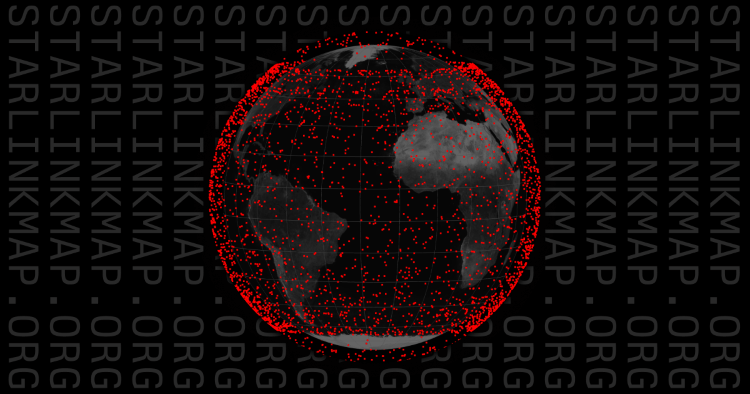
In an effort to enhance the educational outreach of their Starlink constellation, there is an interactive global map of their Starlink internet satellites, which provides live coverage of every satellite in orbit around the Earth. This interactive map and information was produced by Will DePue, who is a an OpenAI programmer and openly states he is not affiliated with SpaceX or Starlink. This interactive map comes as SpaceX continues to launch Starlink satellites into orbit on a near-weekly basis with the goal of providing customers around the world with high-speed internet while specifically targeting rural regions of the globe. In 2022, Starlink officially reached all seven continents after Starlink service became available in Antarctica. Additionally, SpaceX announced in 2023 a partnership with T-Mobile for Starlink to provide mobile coverage, as well.
Continue reading “Watch a Real-Time Map of Starlinks Orbiting Earth”Starship Reaches Orbit on SpaceX’s Third Test but Breaks Up on Re-Entry
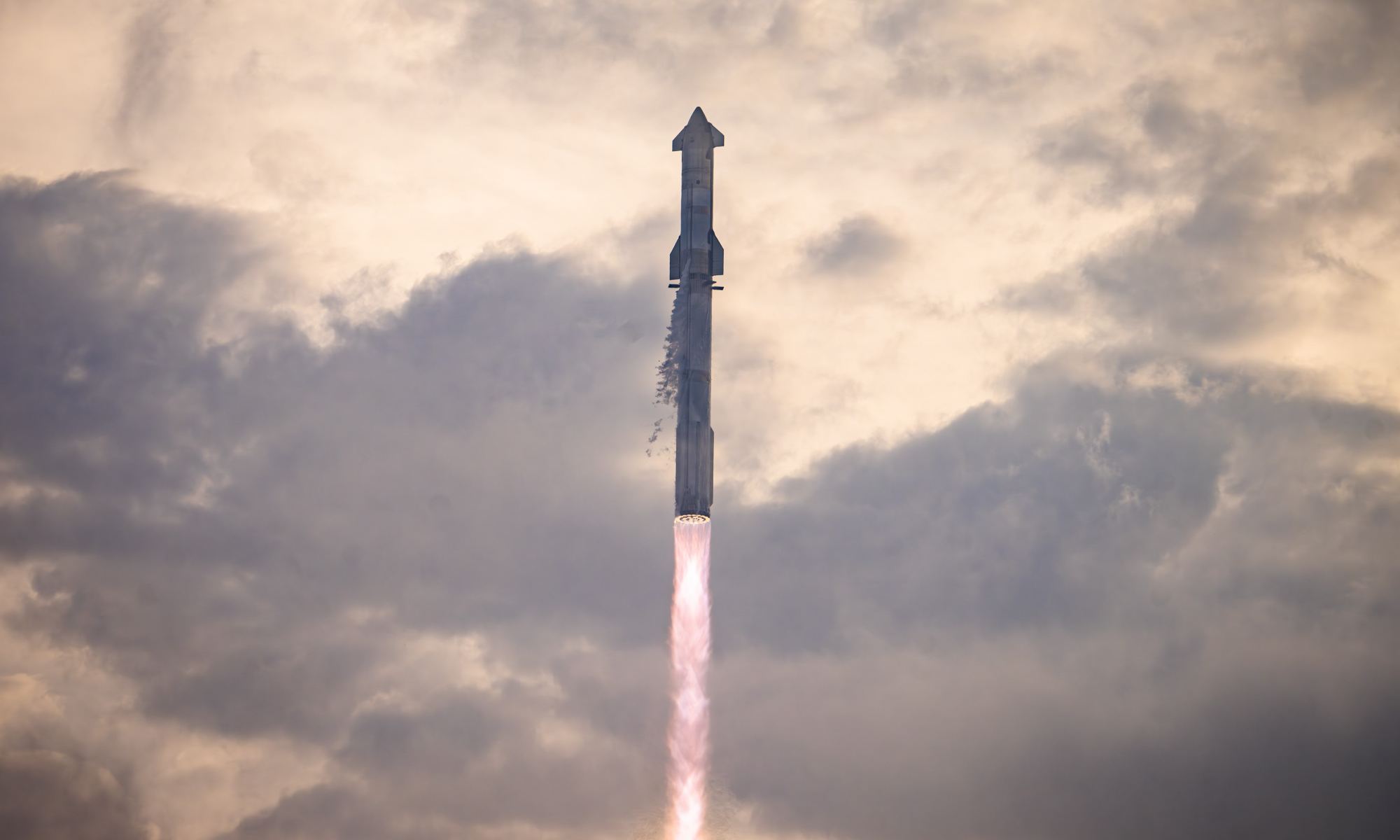
After falling short in its first two attempts, SpaceX got its Starship super-rocket to an orbital altitude today during the launch system’s third integrated flight test. Now it just has to work on the landing.
Today’s test marked a major milestone in SpaceX’s effort to develop Starship as the equivalent of a gigantic Swiss Army knife for spaceflight, with potential applications ranging from the deployment of hundreds of Starlink broadband satellites at a time to crewed odysseys to the moon, Mars and beyond.
Continue reading “Starship Reaches Orbit on SpaceX’s Third Test but Breaks Up on Re-Entry”SpaceX is Gearing Up for the Starship’s Third Orbital Test Flight
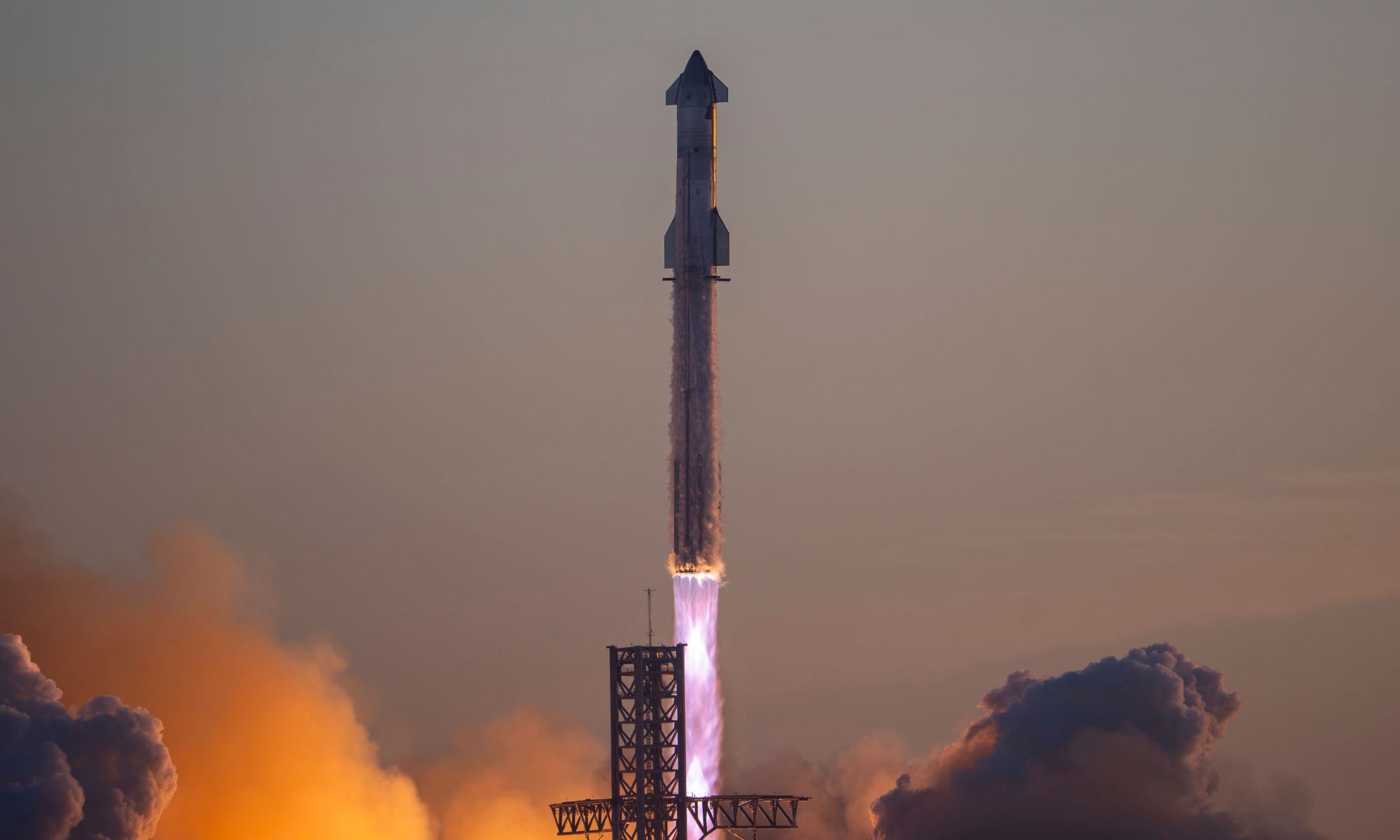

The Starship/Super Heavy is the world’s first fully reusable launch system and the most powerful rocket in history. It is also the key to fulfilling SpaceX’s long-term vision of broadband satellite internet, delivering crews and cargo to the lunar surface, and creating the first self-sustaining city on Mars. After years of development, design changes, and “hop tests” at the company’s launch facility near Boca Chica, Texas, orbital test flights finally began in April last year. The first two flights ended in the loss of both vehicles, though the second flight saw the Starship prototype reach orbit.
According to a recent statement from the company, Flight Test-3 (FT-3) could be happening as soon as Thursday, March 14th, pending approval of the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA). The event will be covered in a live webcast streaming on the company website and SpaceX’s official X (Twitter) account.
Continue reading “SpaceX is Gearing Up for the Starship’s Third Orbital Test Flight”A Capsule With Antiviral Drugs Grown in Space Returns to Earth
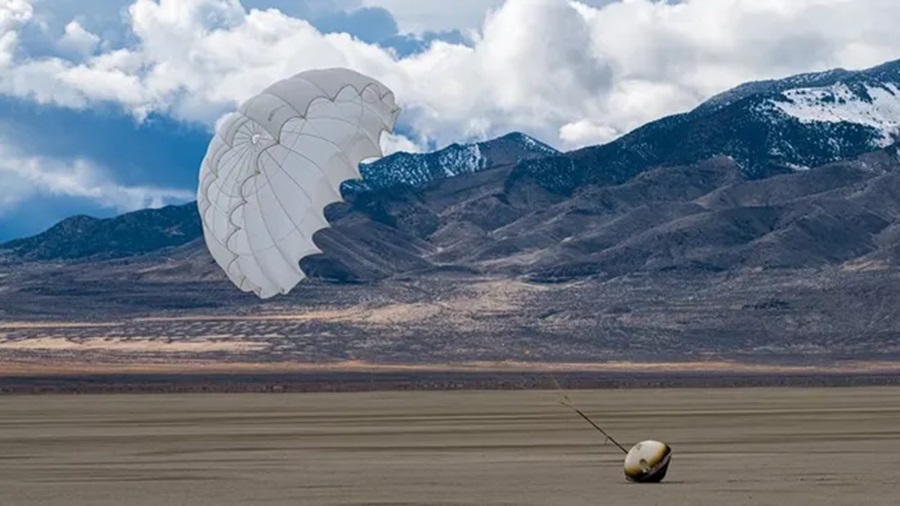
On Wednesday, February 21st, at 01:40 p.m. PST (04:40 p.m. EST), an interesting package returned to Earth from space. This was the capsule from the W-1 mission, an orbital platform manufactured by California-based Varda Space Industries, which landed at the Utah Test and Training Range (UTTR). Even more interesting was the payload, which consisted of antiviral drugs grown in the microgravity environment of Low Earth Orbit (LEO). The mission is part of the company’s goal to develop the infrastructure to make LEO more accessible to commercial industries.
Continue reading “A Capsule With Antiviral Drugs Grown in Space Returns to Earth”Intuitive Machines’ Odysseus Lander Begins Its Moon Odyssey
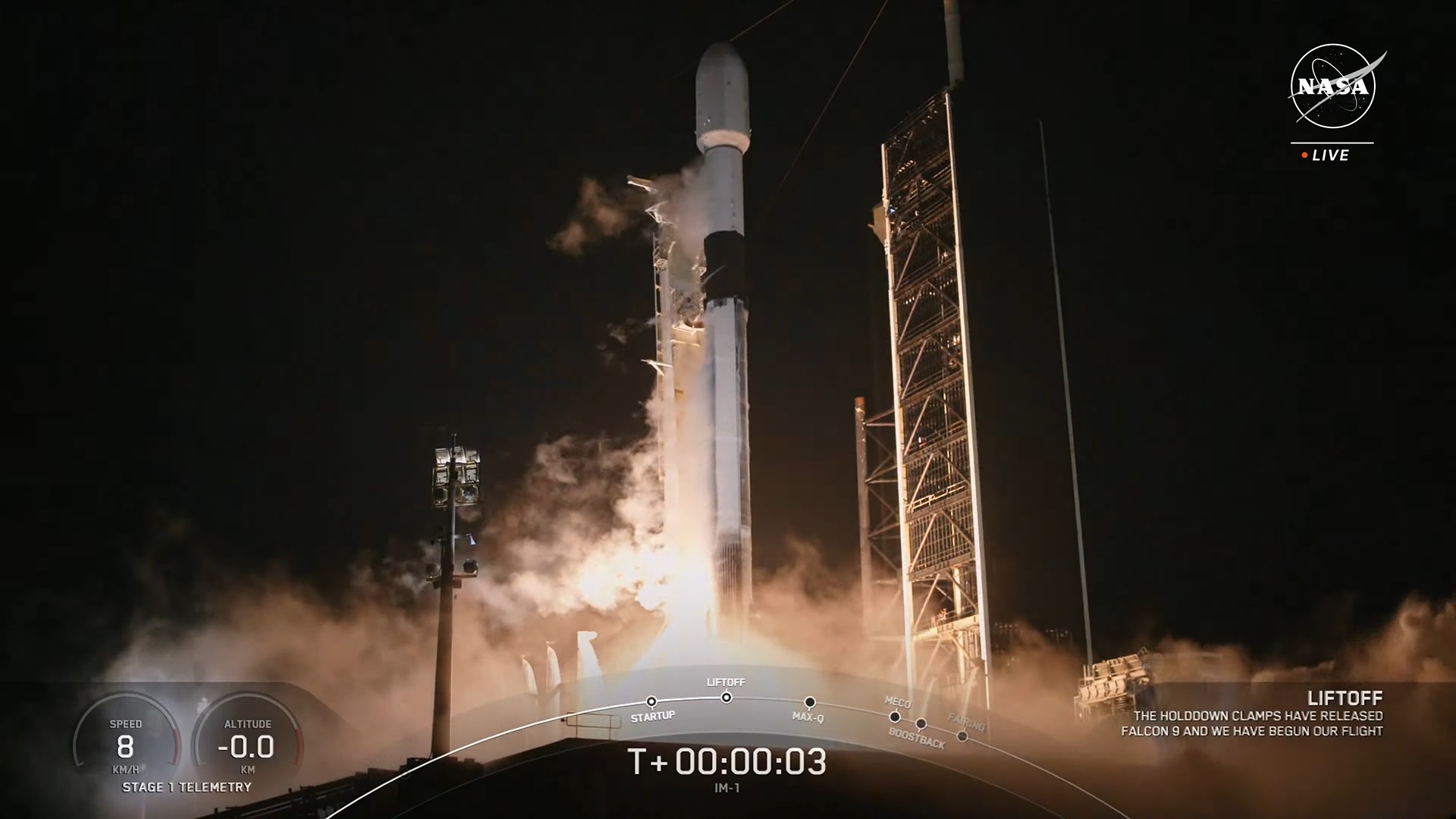

Now it’s Intuitive Machines’ turn to try making history with a robotic moon landing.
Today’s launch of the Houston-based company’s Odysseus lander marks the first step in an eight-day journey that could lead to the first-ever soft landing of a commercial spacecraft on the moon. Odysseus would also be the first U.S.-built spacecraft to touch down safely on the lunar surface since Apollo 17’s mission in 1972.
The lander — which is as big as an old-fashioned British phone booth, or the Tardis time portal from the “Doctor Who” TV series — was sent spaceward from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket at 1:05 a.m. ET (0605 UTC).
Continue reading “Intuitive Machines’ Odysseus Lander Begins Its Moon Odyssey”Space Force Chooses its First “Guardian” to go to Space
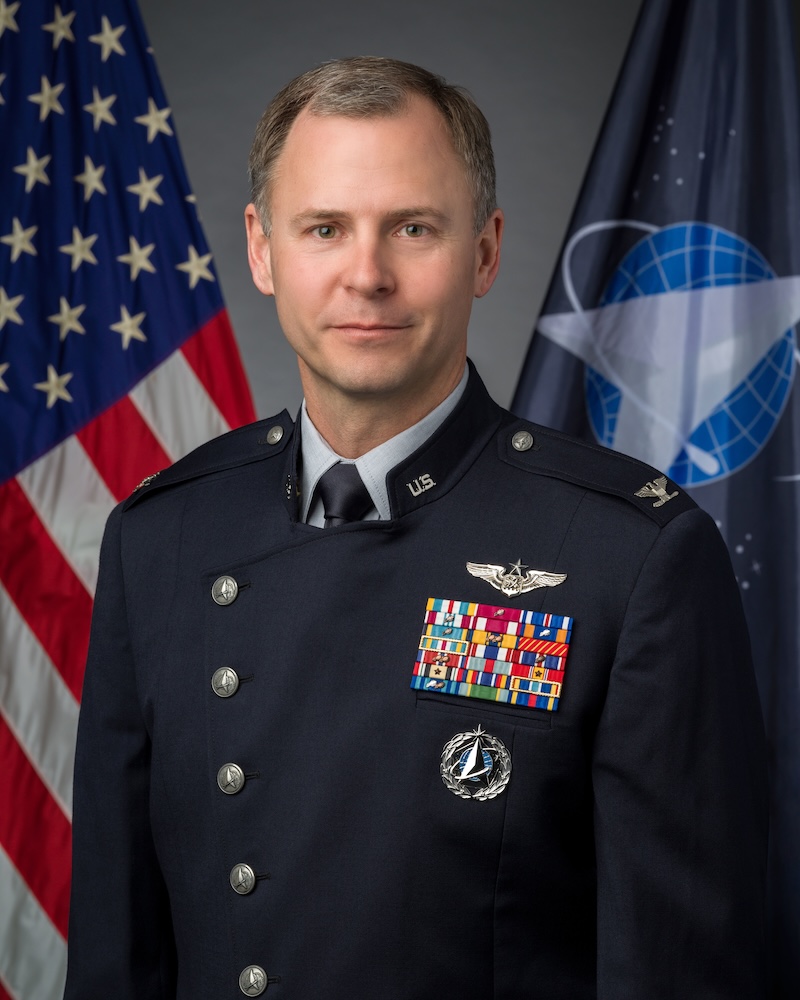

Although the U.S. Space Force is tasked with military operations in regards to space, they’ve never actually sent one of their own into orbit. This week, the agency announced that Col. Nick Hague will launch to the International Space Station in August 2024 to pilot the Crew-9 mission, as part of SpaceX’s ninth crew rotation to the ISS for NASA. He’ll join two NASA astronauts and a cosmonaut on the trip to space and then work as a flight engineer, spending six months on the station doing research and operations activities.
Continue reading “Space Force Chooses its First “Guardian” to go to Space”Now We Know Why Starship’s Second Flight Test Failed
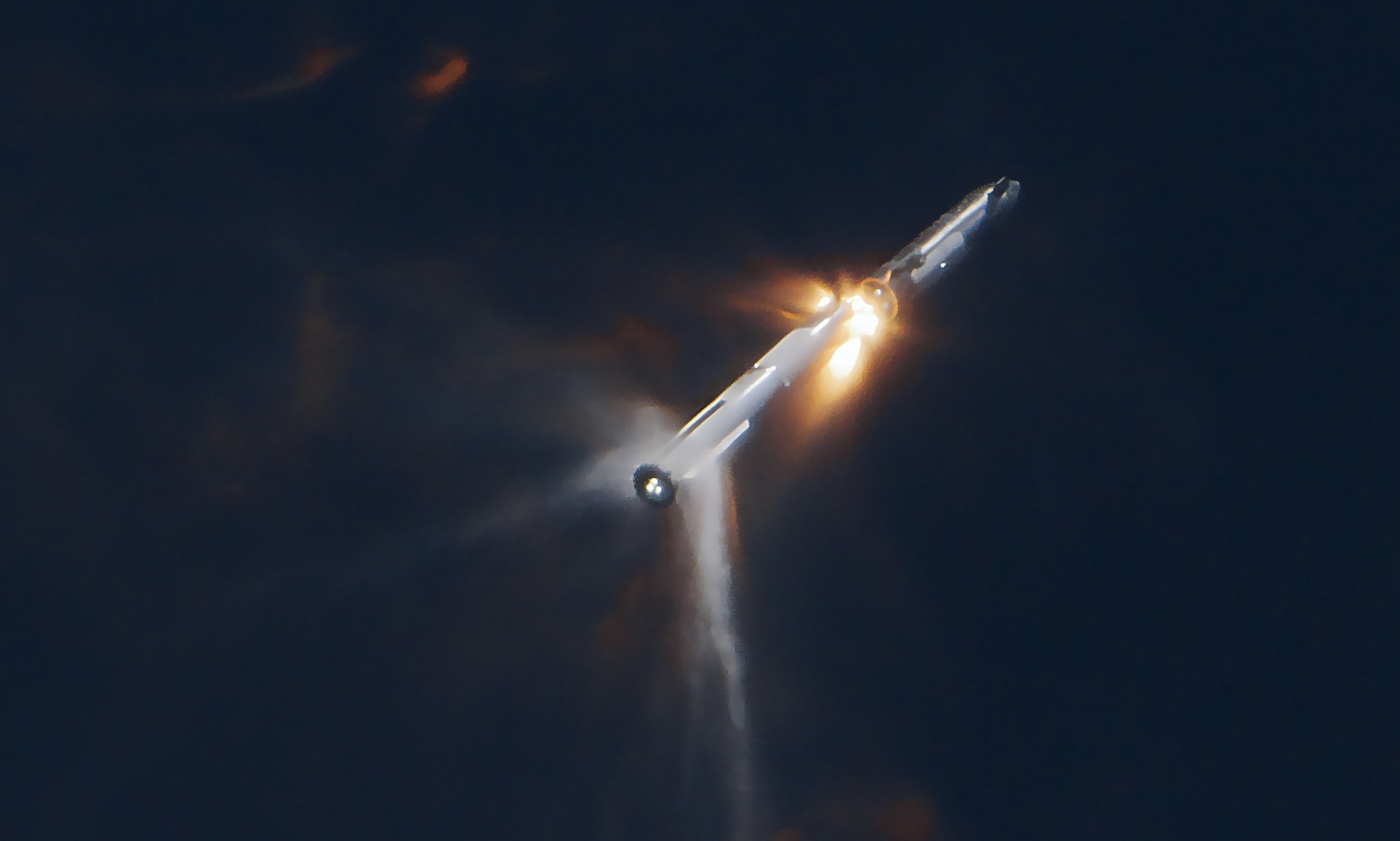
SpaceX is often in the headlines, unfortunlatey its not always good news. On 18th November we saw the second of the Starship and SuperHeavy booster get off the launchpad successfully, it failed before reaching orbit. In a recent event, Elon Musk explained how a fuel venting near the end of the burn was responbie but entirely avoidable next time!
Continue reading “Now We Know Why Starship’s Second Flight Test Failed”NASA is Pushing Back its Moon Landings to 2026
I wasn’t around for the Apollo program that took human beings to the Moon. I would have love to have seen it all unfold though. With NASAs Artemis program the opportunity will soon be with us again to watch humans set foot on another world, just not for the first time. Alas NASA announced on Tuesday that the Moon landings which form part of Artemis 3, have been pushed back one year to 2026.
Continue reading “NASA is Pushing Back its Moon Landings to 2026”SpaceX Tested Its Starship Again. Successful Launch But Both Vehicles Were Destroyed
After months of waiting, SpaceX made its second attempt at an orbital flight this past Saturday (November 18th). During their previous attempt, which occurred back in April, a fully-stacked Starship (SN24) and Super Heavy (BN7) prototypes managed to make it off the landing pad and reach an altitude of about 40 km (25 miles) above sea level. Unfortunately, the SN24 failed to separate from the BN7 booster a few minutes into the flight, causing the vehicle to fall into an uncontrolled tumble and forcing the ground teams to detonate the onboard charges.
Things went better this time as the SN25 and BN9 prototypes took off at about 7:00 AM local time (8:00 AM EDT; 05:00 AM PDT) from the Starbase launch complex. The SN25 successfully separated from its booster two minutes and fifty seconds later – at an altitude of 70 km (43 mi) – and reached an altitude of about 148 kilometers (92 miles), just shy of SpaceX’s goal of 150 km (~93 mi). However, the booster stage was lost about 30 seconds after separation, exploding over the Gulf of Mexico. The SN25 also exploded about eight minutes into the flight, reportedly because its flight termination system was activated.
Continue reading “SpaceX Tested Its Starship Again. Successful Launch But Both Vehicles Were Destroyed”Starship Could Be Ready to Launch on Friday
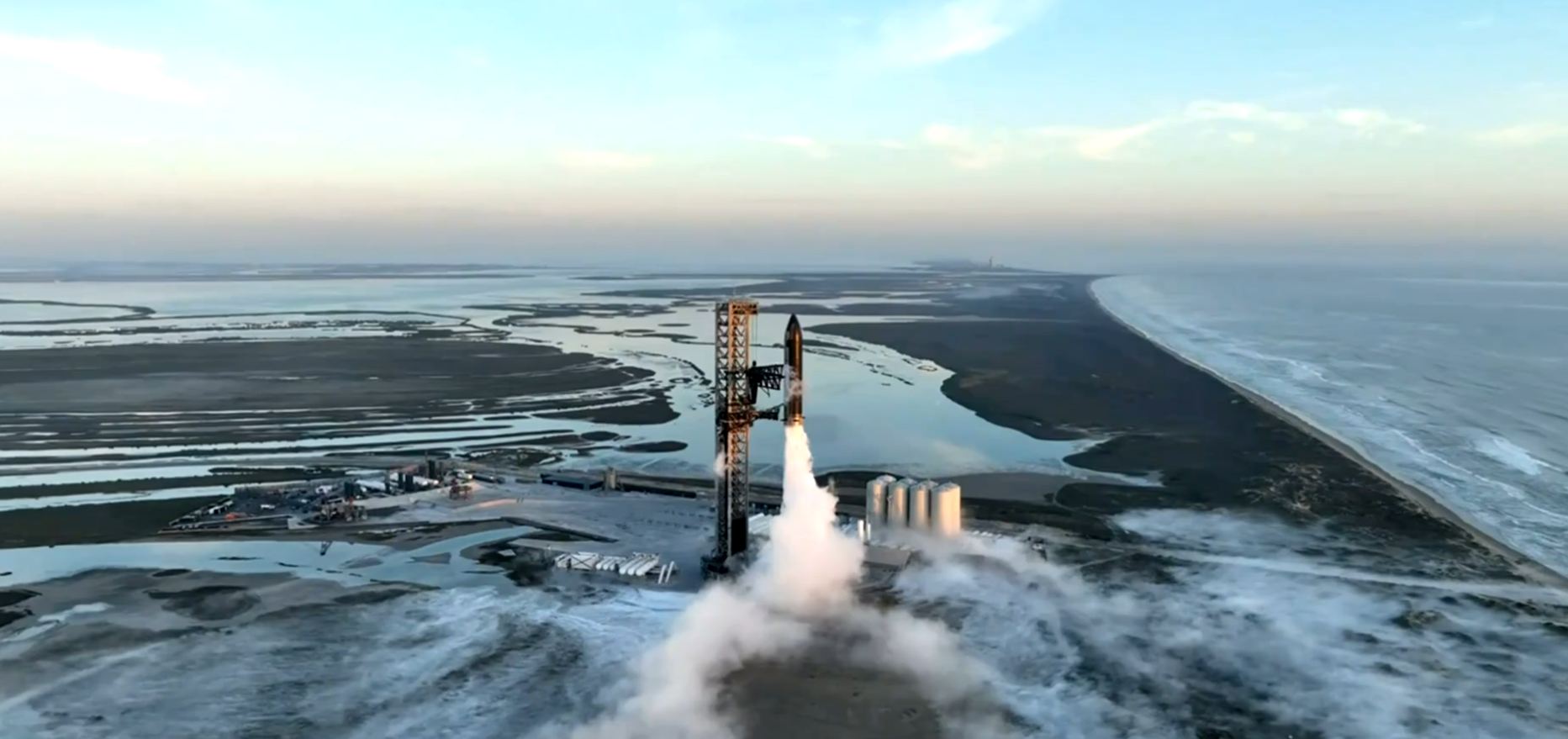
Space exploration should never be run of the mill nor something that finds itself on the back pages of the newspaper. Captain James T. Kirk was right that space really is the final frontier and making it more accessible is one of the driving forces behind SpaceX. Their mission to seek out new life and new civilisations, wait that’s wrong – that’s Starfleet. The SpaceX mission ‘to revolutionise space technology, with the ultimate goal of enabling people to live on other planets is at the forefront of the development of the enormous Starship which may make another launch attempt as soon as this Friday 17th November.
Continue reading “Starship Could Be Ready to Launch on Friday”