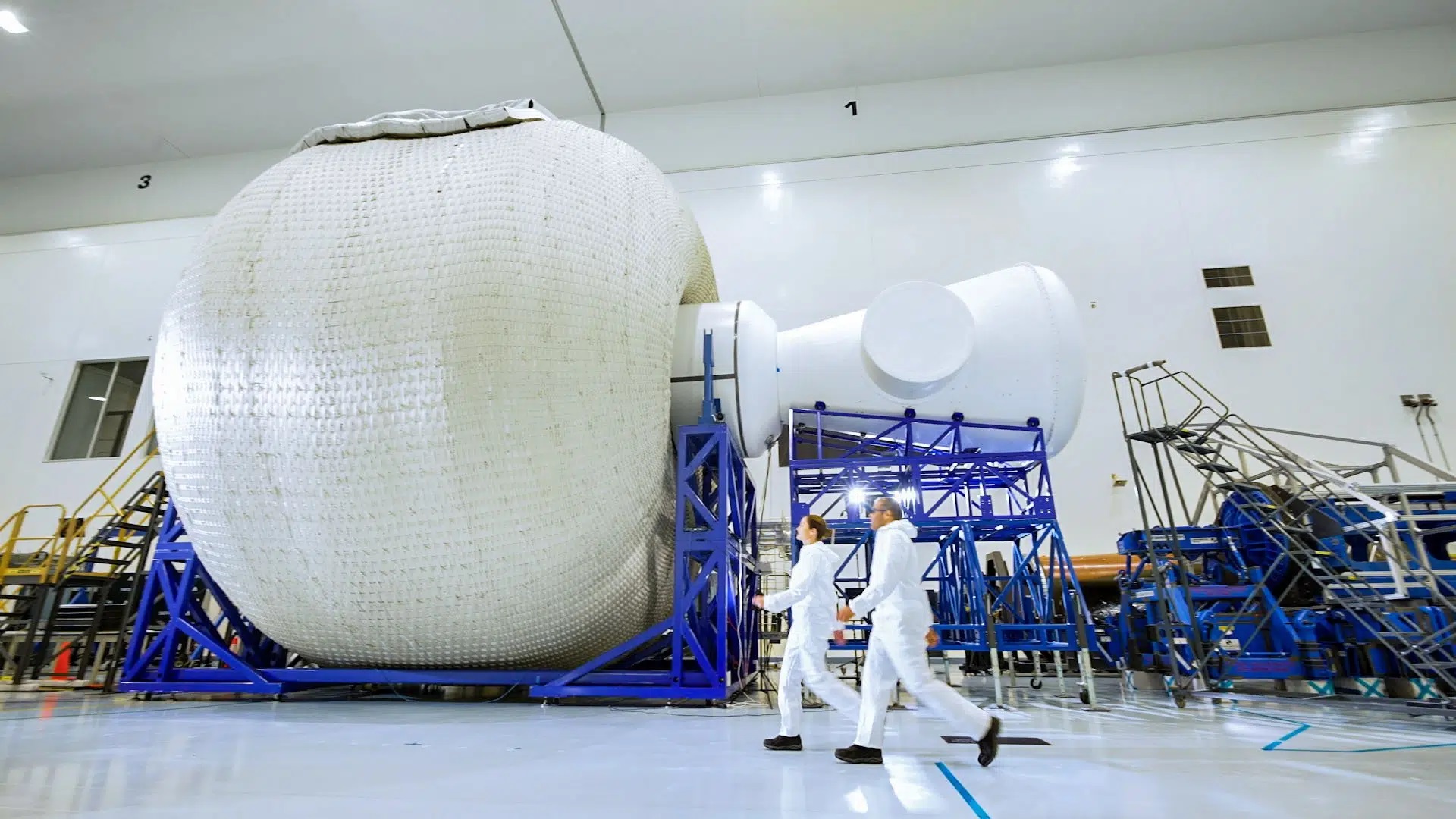
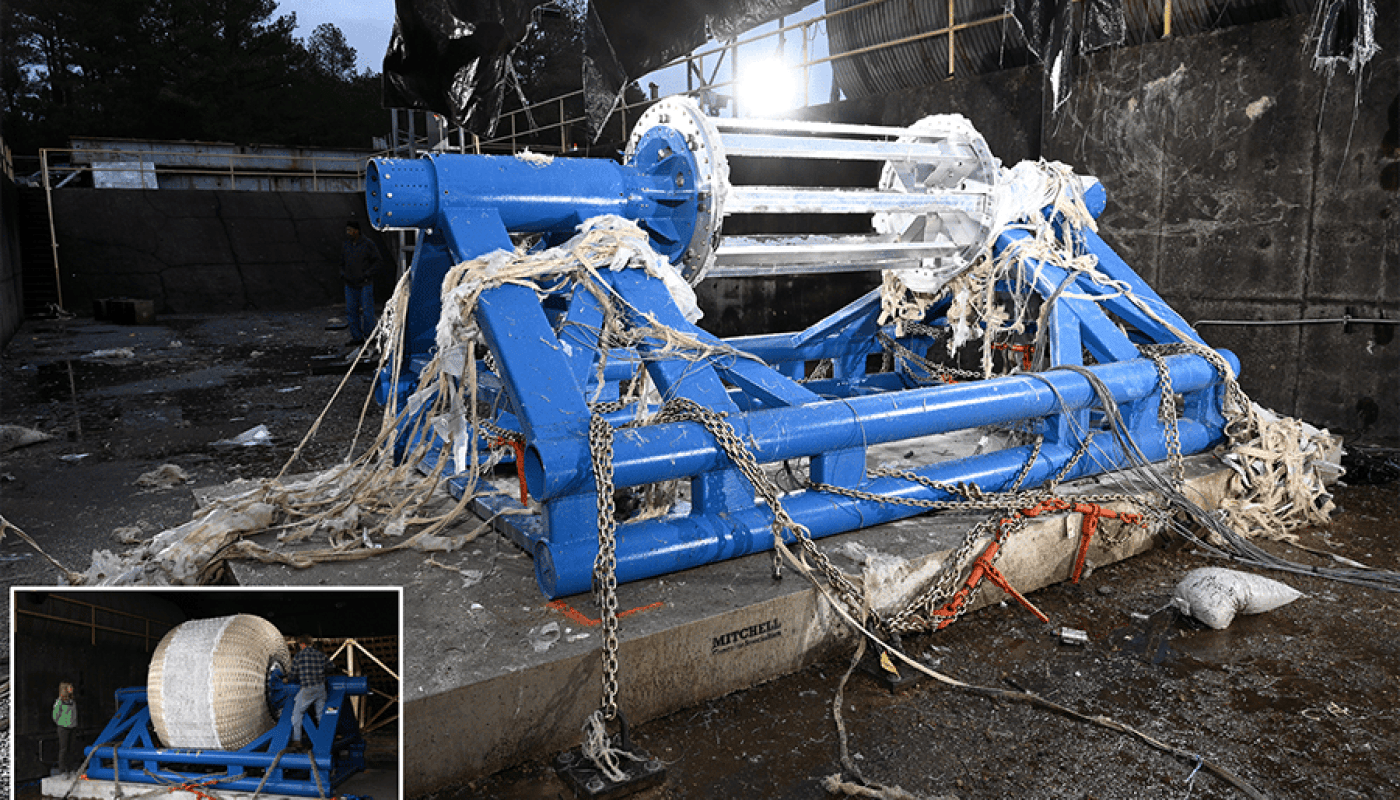
Ae inflatable habitats the future of human space exploration? This is what the space-tech company, Sierra Space, hopes to achieve as they recently conducted a successful Ultimate Burst Pressure test on June 18 with its Large Integrated Flexible Environment (LIFE®) technology at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center. The goal of these tests is to inflate the test article until it explodes while ascertaining if the maximum pressure falls within NASA’s strict safety guidelines regarding a recommended operating pressure of 60.8 psi (maximum operating pressure of 15.2 psi times four as a safety factor). Upon explosion, Sierra Space engineers immediately found the recent test achieved 74 psi, thus exceeding NASA’s safety standards by 22 percent.
Continue reading “Watch an Inflatable Habitat Burst in Super Slo-Mo”Watch an Inflatable Habitat Burst in Super Slo-Mo