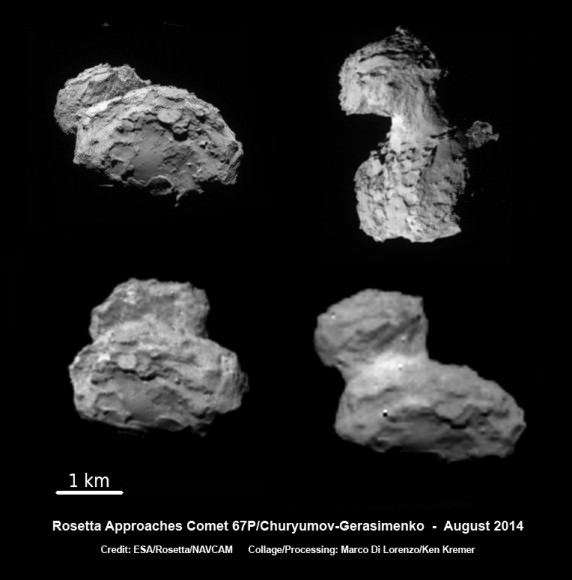
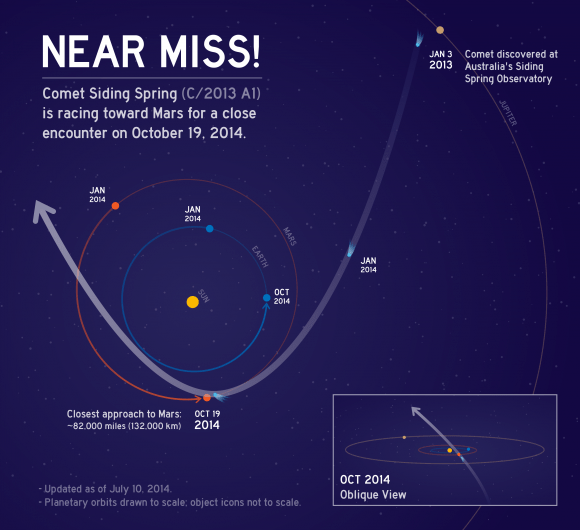
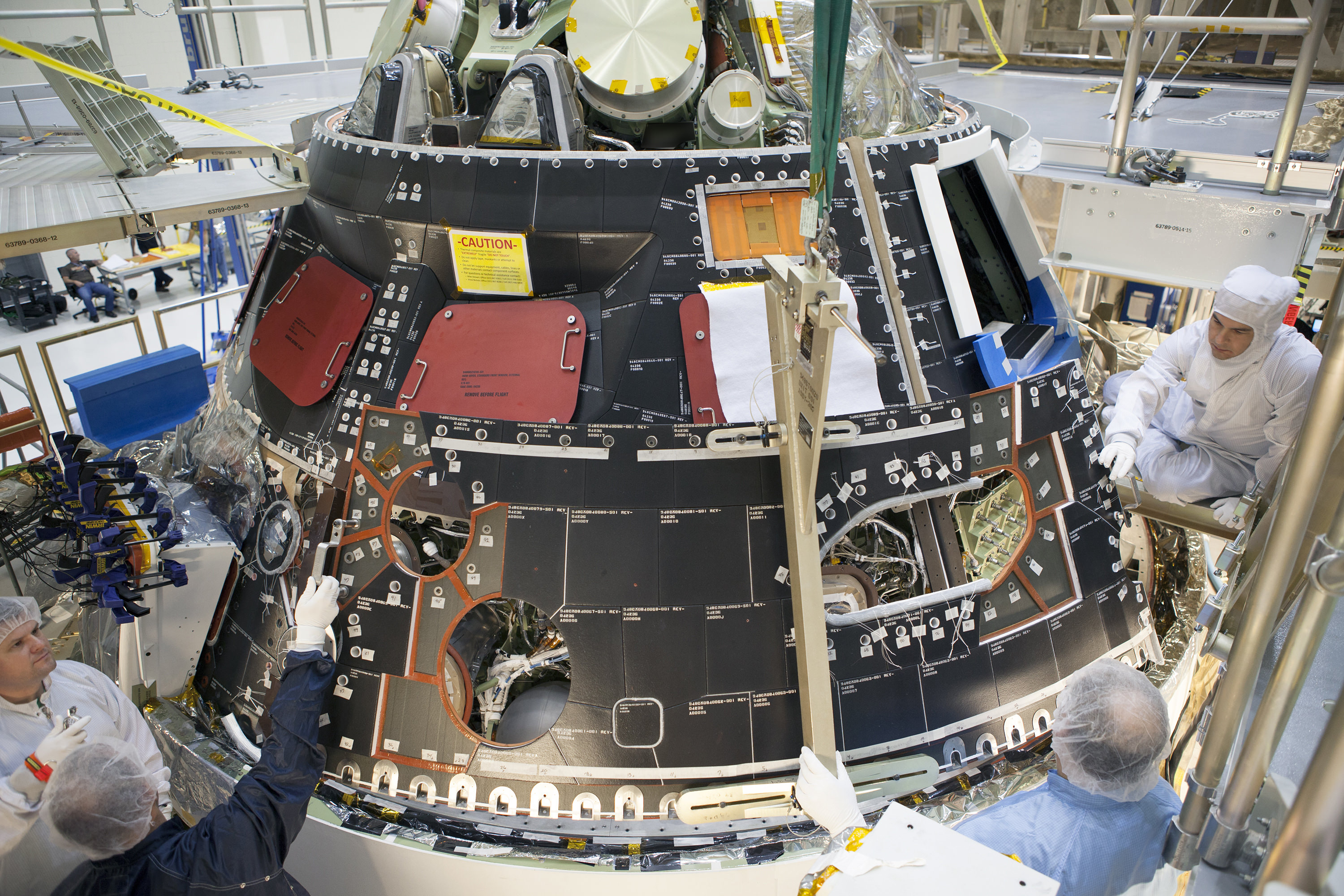
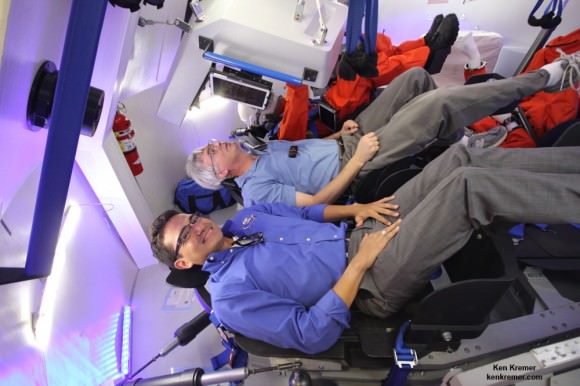
NASA’s Orion EFT 1 crew module departs Neil Armstrong Operation and Checkout Building on Sept. 11, 2014 at the Kennedy Space Center, FL, beginning the long journey to the launch pad and planned liftoff on Dec. 4, 2014. Credit: Ken Kremer – kenkremer.com
Story updated[/caption]
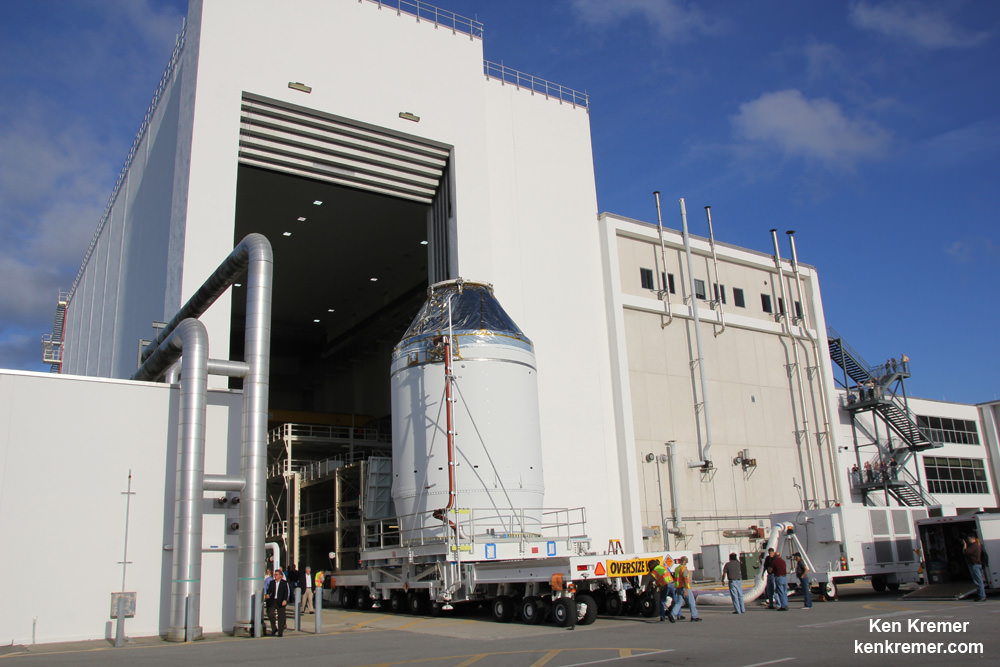
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER – NASA’s first space worthy Orion crew module rolled out of its assembly facility at the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) on Thursday, Sept. 11, taking the first step on its nearly two month journey to the launch pad and planned blastoff this coming December.
The Orion spacecraft is NASA’s next generation human rated vehicle and is scheduled to launch on its maiden uncrewed mission dubbed Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) in December 2014.
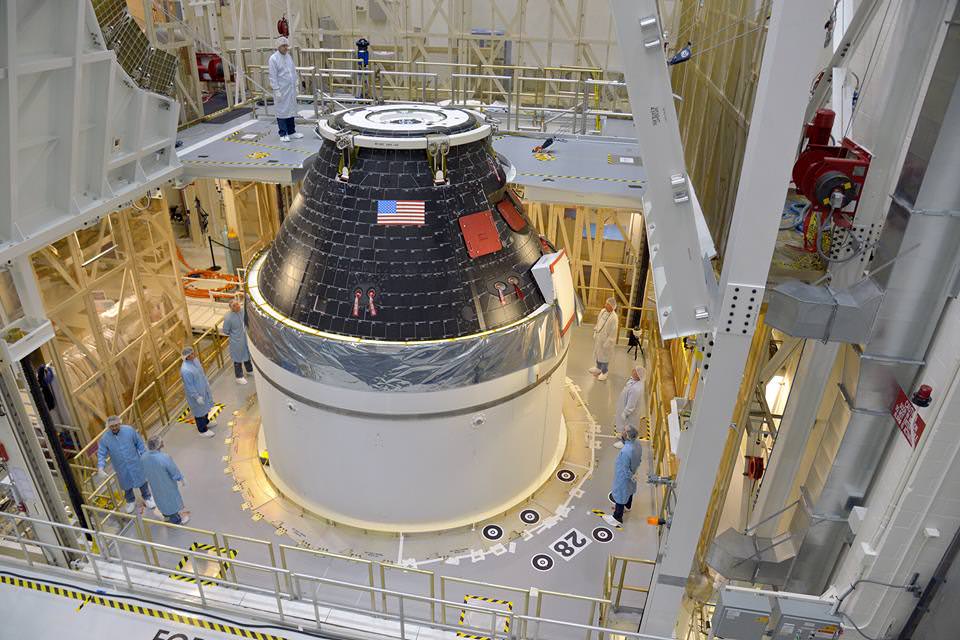
Orion’s assembly was just completed this past weekend by technicians and engineers from prime contractor Lockheed Martin inside the agency’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout (O & C) Facility. They have been working 24/7 to manufacture the capsule and prepare it for launch.
“I’m excited as can be,” said Scott Wilson, NASA’s Orion Manager of Production Operations at KSC during the move. “For some of us this has been ten years in the making.”
The black tiled Orion crew module (CM) was stacked atop an inert white colored service module (SM) in the O & C high bay in June. The CM/SM stack was placed on top of the Orion-to-stage adapter ring that will mate them to the booster rocket. Altogether the capsule, service module and adapter ring stack stands 40 feet tall and 16 feet in diameter.
“This is awesome,” Bob Cabana, Kennedy Space Center director and former shuttle commander, told the media during the rollout.

Workers subsequently covered the crew module and its thermal insulating tiles with a see through foil to shield the capsule and blanket it under a protective climate controlled atmosphere to guard against humidity.
The CM/SM stack was then lifted and placed onto a 36-wheeled transporter and moved about 1 mile to a KSC facility named the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHFS) for fueling. The move took about an hour.
“Orion will stay at the PHFS for about a month,” Wilson told me in a KSC interview during the move.
Orion will be fueled with ammonia and hyper-propellants for its flight test, said Wilson.

The fueled Orion will then move yet again to the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) for the installation of the launch abort system (LAS).
The full Orion stack will rollout to Space Launch Complex 37 in early November.
“Nothing about building the first of a brand new space transportation system is easy,” said Mark Geyer, Orion Program manager.
“But the crew module is undoubtedly the most complex component that will fly in December. The pressure vessel, the heat shield, parachute system, avionics — piecing all of that together into a working spacecraft is an accomplishment. Seeing it fly in three months is going to be amazing.”
The Orion EFT-1 test flight is slated to soar to space atop the mammoth, triple barreled United Launch Alliance (ULA) Delta IV Heavy rocket from Cape Canaveral, Florida, on Dec. 4, 2014.
The state-of-the-art Orion spacecraft will carry America’s astronauts on voyages venturing farther into deep space than ever before – past the Moon to Asteroids, Mars and Beyond!
The two-orbit, four and a half hour EFT-1 flight will lift the Orion spacecraft and its attached second stage to an orbital altitude of 3,600 miles, about 15 times higher than the International Space Station (ISS) – and farther than any human spacecraft has journeyed in 40 years.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Orion, SLS, Boeing, Sierra Nevada, Orbital Sciences, SpaceX, commercial space, Curiosity, Mars rover, MAVEN, MOM and more Earth and planetary science and human spaceflight news.