At this moment the mega rover Curiosity is barely 48 hours from Mars and transformation into a “priceless asset” on the Red Planet’s surface where she’ll initiate the search for evidence for habitats of Martian microbial life – past or present.
NASA JPL engineers have guided the Curiosity Mars Science Lab (MSL) so precisely on her 352-million-mile (567-million-kilometer) interplanetary journey through space that they decided to cancel today’s planned course adjusting thruster firing, known as Trajectory Correction Maneuver 5 (TCM-5). If needed, they have one last chance for a course correction burn (TCM-6) this weekend on Sunday.
“We are now about 1000 yards from the entry target that will bring us to the touchdown point on the North side of Gale Crater,” said Tomas Martin-Mur, MSL Navigation team chief of NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif., at an Aug. 2 MSL news briefing.
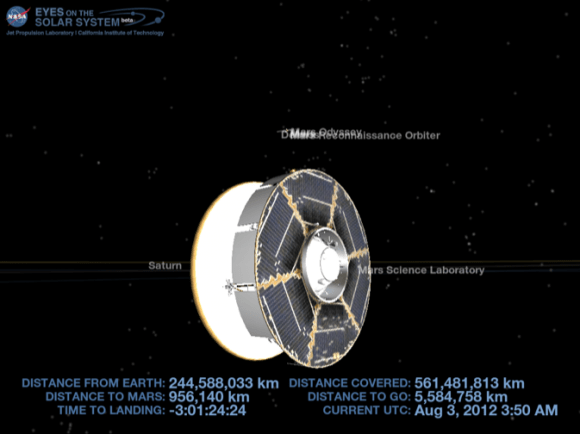
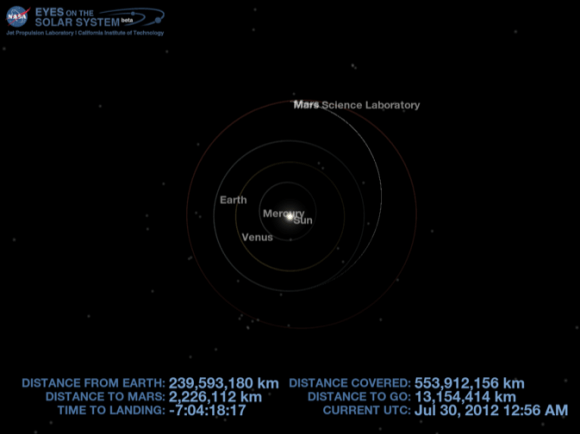
Curiosity is now less than 450,000 miles away from Mars, careening through space at over 8000 MPH (3576 m/s) and accelerating moment by moment due to the ever increasing pull of Mars gravity.
To put that in perspective, that’s less than twice the distance from the Earth to the Moon.
By the time Curiosity hits the Martian atmosphere on Sunday night/Monday early morning (Aug 5/6) she’ll be blazing through space at more than 13,200 MPH (5,900 m/s).
“I’m less than 500,000 miles from Mars & the Red Planet looks about the size as a full moon seen from Earth. 2 days to landing!” Curiosity tweeted a short while ago.
She remains healthy, with all systems operating nominally. And she is brave!
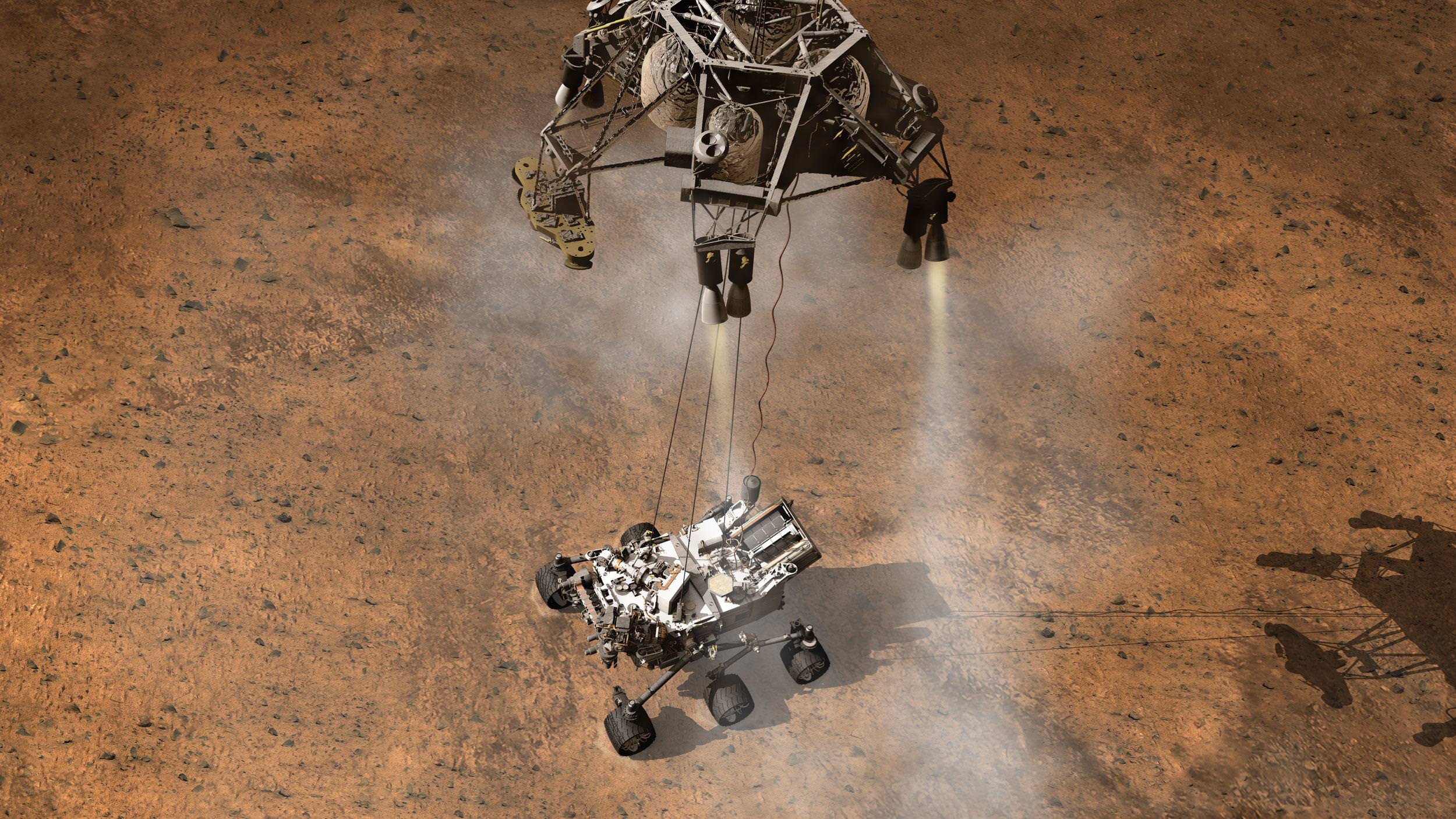
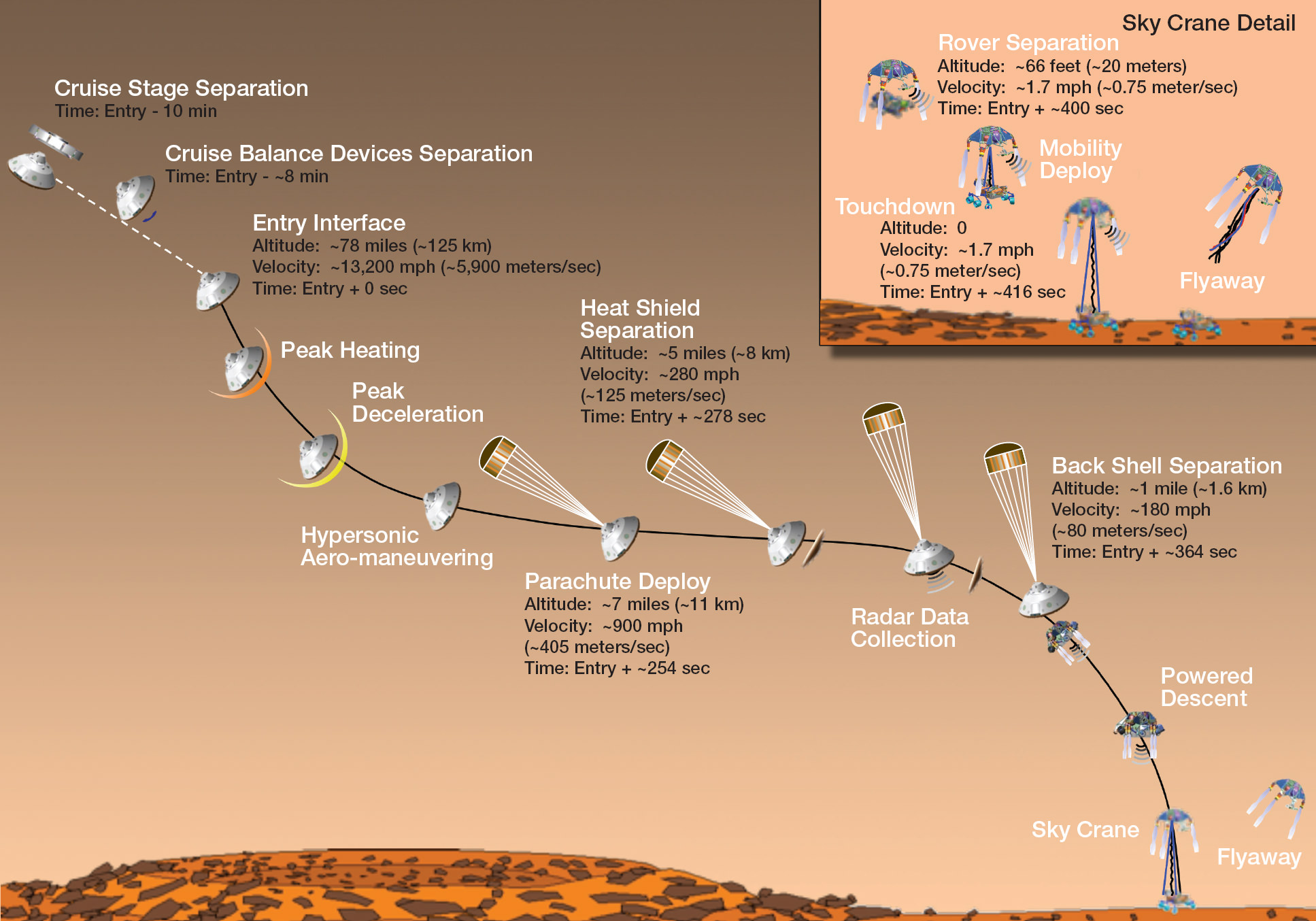
Curiosity will not flinch knowing she must endure the “7 Minutes of Terror” and the fiery entry,descent and landing to touchdown inside the 96 mile wide Gale Crater just 2 days from now.
Watch the harrowing landing animation – here.
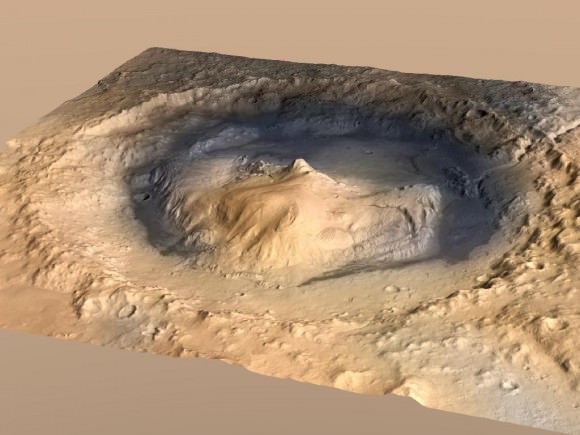

Image Caption: Gale Crater Landing site for Curiosity. Credit: NASA
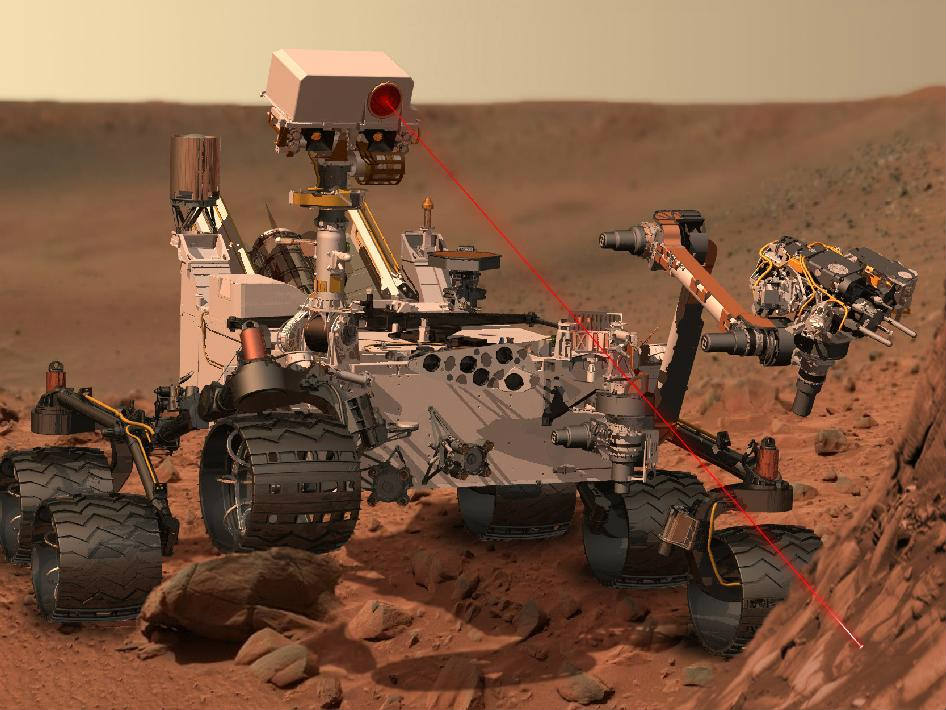
Absolutely staggering photos and science discoveries are expected from Curiosity – the boldest, most daring and by far the most scientifically complex and capable robotic emissary ever dispatched by humans to another world.
But after landing, the team needs to first test the rover’s components and unfurl the robots camera mast and instruments.
“We must recognize that on Sunday night at 10:32 PM PST(1:32 AM EST, 532 GMT) we will have a ‘priceless asset’ that we placed on the surface of another planet that could last for a long time IF we operate it correctly,” said Pete Theisinger, MSL project manager, JPL, at the Aug. 2 news briefing.
“So we will be cautious as hell about what we do with it !”
“This is a very complicated beast, so we all need to exercise caution. It’s much, much more complicated than Spirit and Opportunity in terms of the interactions amongst the various pieces and the things we need to keep track of in order to operate it successfully.”
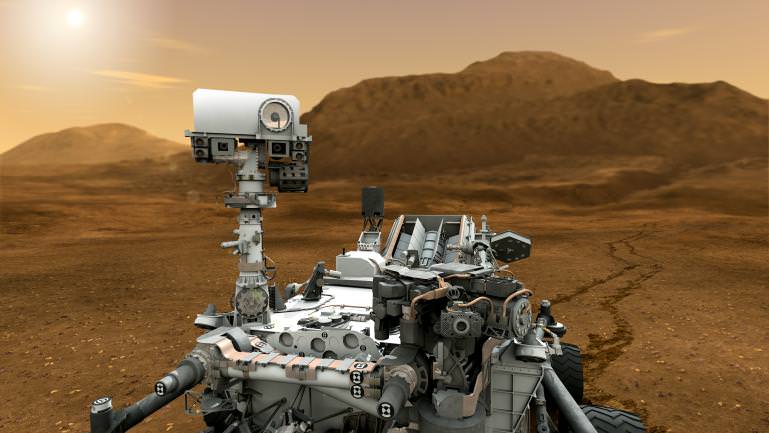
A few hours after touchdown, Curiosity will send back the first images from the Gale crater landing site beside a towering 3 mile (5 km) high layered Martian mountain, named Mount Sharp.
“We will start doing science right away. Very roughly, the contact science will begin in 2 to 4 weeks. Sampling science will begin 1 to 2 months after we land,” explained Theisinger.
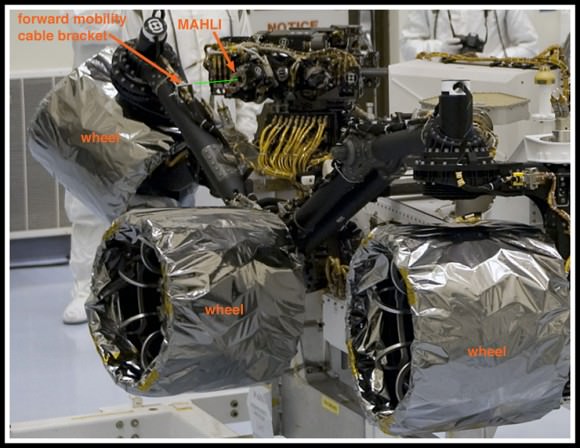
The car-sized Curiosity is 10 feet (3 meters) long and packed with 10 state-of-the-art science experiments that will search for organic molecules – the building blocks of life – and clay minerals, potential markers for signs of Martian microbial life and habitable zones.
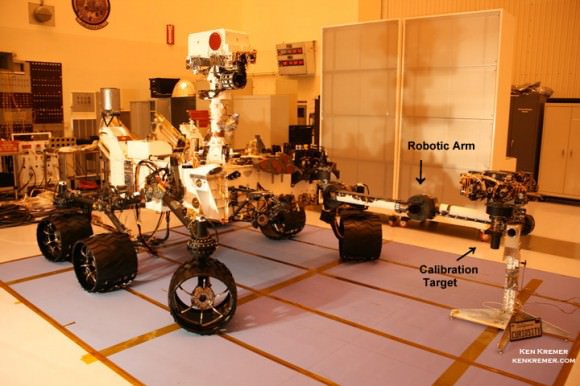
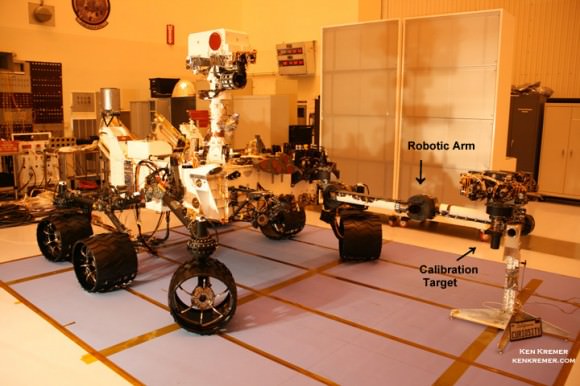
Image Caption:Curiosity Mars Science Laboratory Rover – inside the Cleanroom at KSC, with robotic arm extended prior to encapsulation and Nov. 26, 2011 liftoff. Credit: Ken Kremer/kenkremer.com
Watch NASA TV online for live coverage of the Curiosity landing on Aug 5/6 starting at 11:30 pm EDT:
www.mars.jpl.nasa.gov or www.nasa.gov
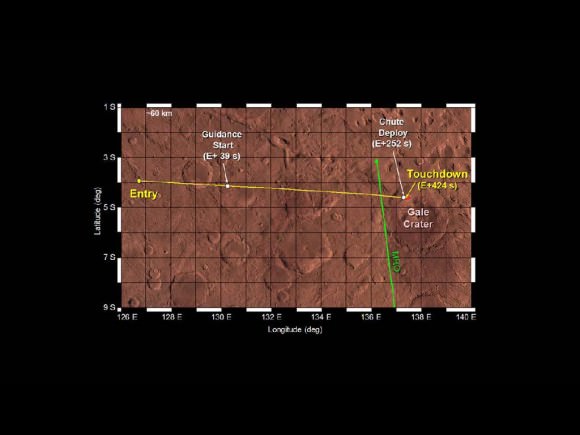
Image Caption: MSL entry track to Gale Crater. Credit: NASA
Read continuing recent features about Curiosity by Ken Kremer starting here:
4 Days to Mars: Curiosity activates Entry, Descent and Landing Timeline – EDL Infographic
Curiosity’s Grand Entrance with Star Trek’s William Shatner and Wil Wheaton – Video Duet
Curiosity Completes Crucial Course Correction – 1 Week from Mars !
T Minus 9 Days – Mars Orbiters Now in Place to Relay Critical Curiosity Landing Signals