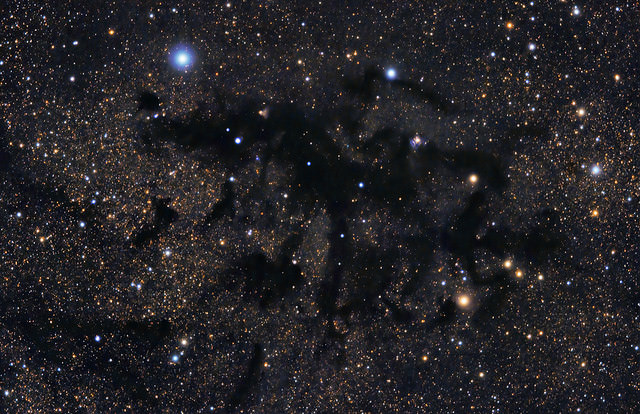
What a stunning view of this dark region of space! This image, by astrophotographer Callum Hayton shows LDN 673, a molecular cloud complex that lies in the constellation Aquila. This region is massive — around 67 trillion kilometers (42 trillion miles across), and it is between 300-600 light years from Earth. Observers in the northern hemisphere can find this region in the summer skies near the bright star Altair and the Summer Triangle.
Because the cloud lies on the galactic plane, the dark dust is back-lit by millions of stars in the Milky Way galaxy. This dusty cloud likely contains enough raw material to form hundreds of thousands of stars. Hayton explained on Flickr how the dust gets “eroded” away by stellar formation:
“When some of these clouds reach a certain mass they begin to collapse and fragment creating protostars,” Hayton wrote. “As the temperature and pressure at the centre of the protostar rises, sometimes it becomes so great that nuclear fusion begins and a star is born. In this image you can see where at least two young stars have eroded the dust around them and are now above the clouds casting light down on to the dust below.”
Gorgeous!
Want to get your astrophoto featured on Universe Today? Join our Flickr group or send us your images by email (this means you’re giving us permission to post them). Please explain what’s in the picture, when you took it, the equipment you used, etc.