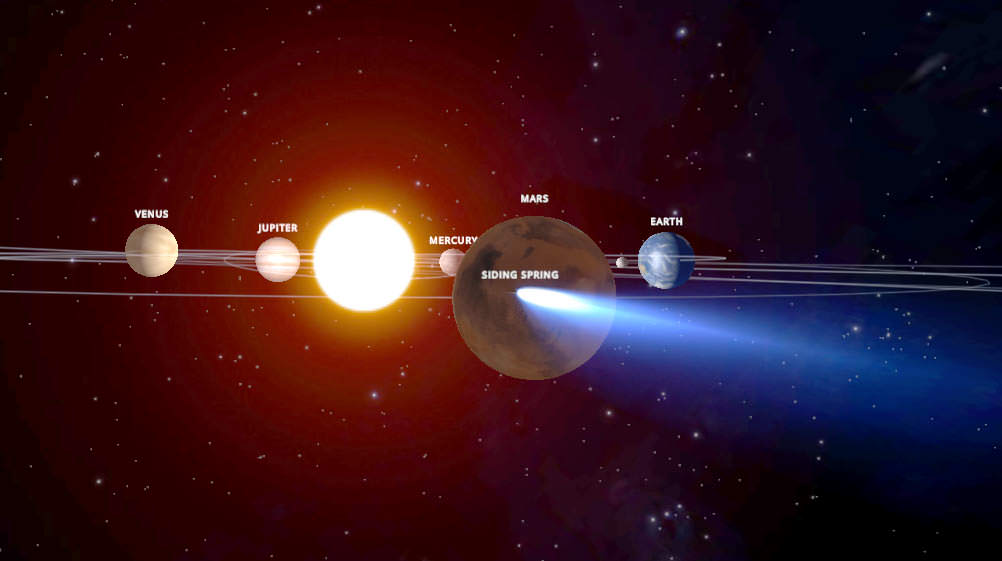
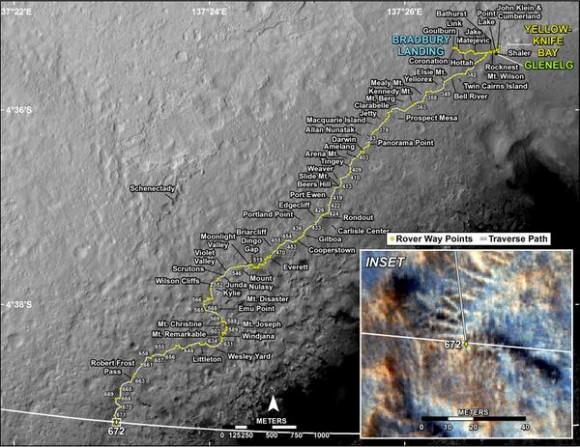
As Comet C/2013 A1 Siding Spring inches closer to the Red Planet, NASA’s taking steps to protect its fleet of orbiting Mars spacecraft. On October 19, the comet’s icy nucleus will miss the planet by just 82,000 miles (132,000 km). That’s 17 times closer than the closest recorded Earth-approaching comet, Lexell’s Comet in 1770.

No one’s worried about the tiny nucleus doing any damage. It’ll zip right by. Rather it’s dust particles embedded in vaporizing ice that concern NASA planners. Dust spreads into a broad tail that could potentially brush Mars’ upper atmosphere and strike an orbiter. A single particle of debris half a millimeter across may not seem like your mortal enemy, but when it’s traveling at 35 miles (56 km) per second relative to the spacecraft, one hit could spell trouble.
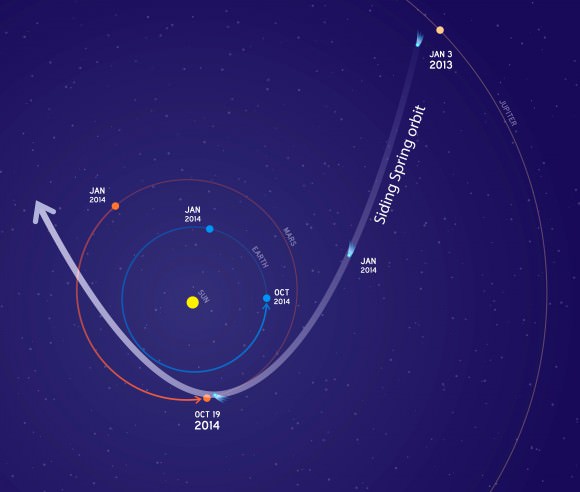
“Three expert teams have modeled this comet for NASA and provided forecasts for its flyby of Mars,” explained Rich Zurek, chief scientist for the Mars Exploration Program at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. “The hazard is not an impact of the comet nucleus, but the trail of debris coming from it. Using constraints provided by Earth-based observations, the modeling results indicate that the hazard is not as great as first anticipated. Mars will be right at the edge of the debris cloud, so it might encounter some of the particles — or it might not.”
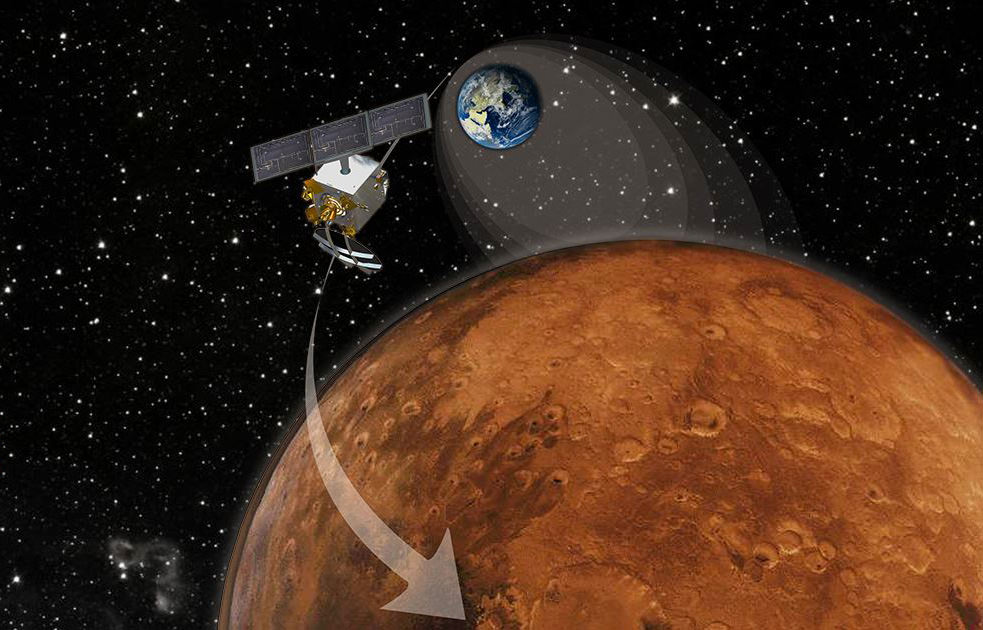
The agency’s taking a prudent approach. NASA currently operates the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) and Mars Odyssey spacecraft with a third orbiter, MAVEN, currently on its way to the planet and expected to settle into orbit a month before the comet flyby. Teams operating the orbiters plan to have all spacecraft positioned on the opposite side of Mars when the comet is most likely to pass by.
Already, mission planners tweaked MRO’s orbit on July 2 to move it toward a safe position with a second maneuver to follow on August 27. A similar adjustment is planned for Mars Odyssey on August 5 and October 9 for the Mars Atmosphere and Volatile Evolution (MAVEN) probe. The time of greatest risk to the spacecraft is brief – about 20 minutes – when the widest part of the comet’s tail passes closest to the planet.

One question I’m always asked is whether the Mars rovers are in any danger of dust-producing meteors in the comet’s wake. While the planet might get peppered with a meteor shower, its atmosphere is thick enough to incinerate cometary dust particles before they reach the surface, not unlike what happens during a typical meteor shower here on Earth. Rover cameras may be used to photograph the comet before the flyby and to capture meteors during the comet’s closest approach.
Despite concerns about dust, NASA knows a good opportunity when it sees one. In the days before and after the flyby, all three orbiters will conduct studies on the comet.
According to a recent NASA press release, instruments on MRO and Odyssey will examine the nucleus, coma and tail and possible effects on the Martian atmosphere:

“Odyssey will study thermal and spectral properties of the comet’s coma and tail. MRO will monitor Mars’ atmosphere for possible temperature increases and cloud formation, as well as changes in electron density at high altitudes and MAVEN will study gases coming off the comet’s nucleus as it’s warmed by the sun. The team anticipates this event will yield detailed views of the comet’s nucleus and potentially reveal its rotation rate and surface features.”
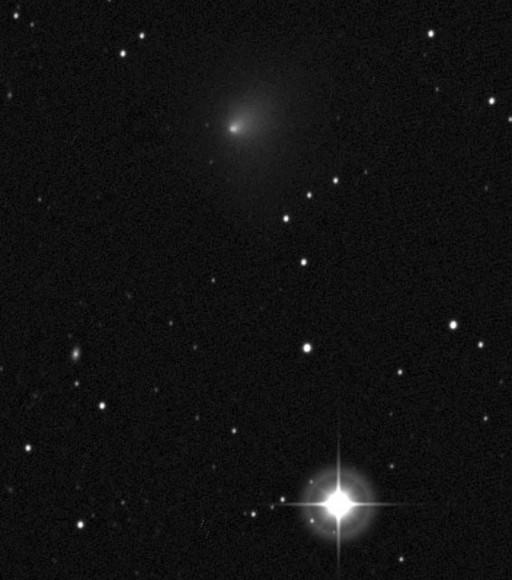
This is Comet Siding Spring’s first trip to the inner solar system. Expect exciting news as we peer up close at pristine ices and dust that have been locked in deep freeze since the time the planets formed.
For more information on the event, check out this NASA website devoted to the comet.