The longest living Martian rover ever – Opportunity – has just surpassed another unfathomable milestone – 4500 Sols (or days) exploring the Red Planet !! That’s 50 times beyond her “warrantied” life expectancy of merely 90 Sols.
And as we are fond of reporting – the best is yet to come. After experiencing 4500 Martian sunsets, Opportunity has been granted another mission extension and she is being targeted to drive to an ancient gully where life giving liquid water almost certainly once flowed on our solar systems most Earth-like planet.
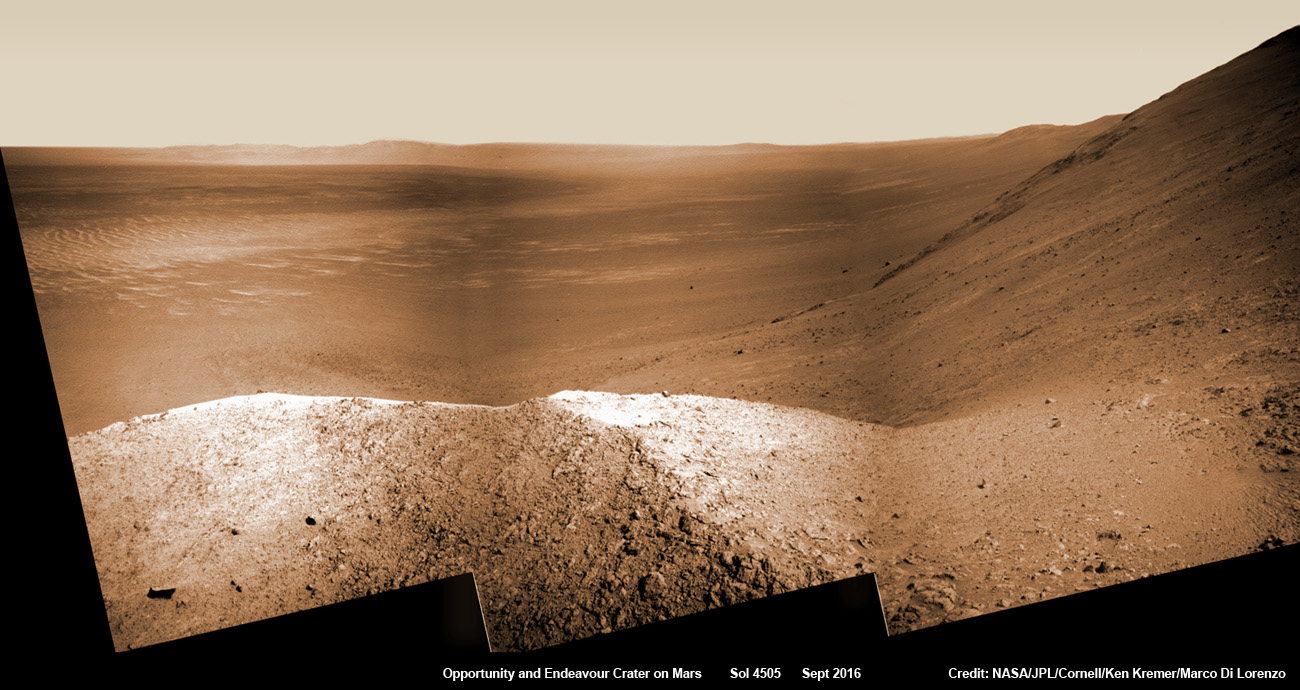
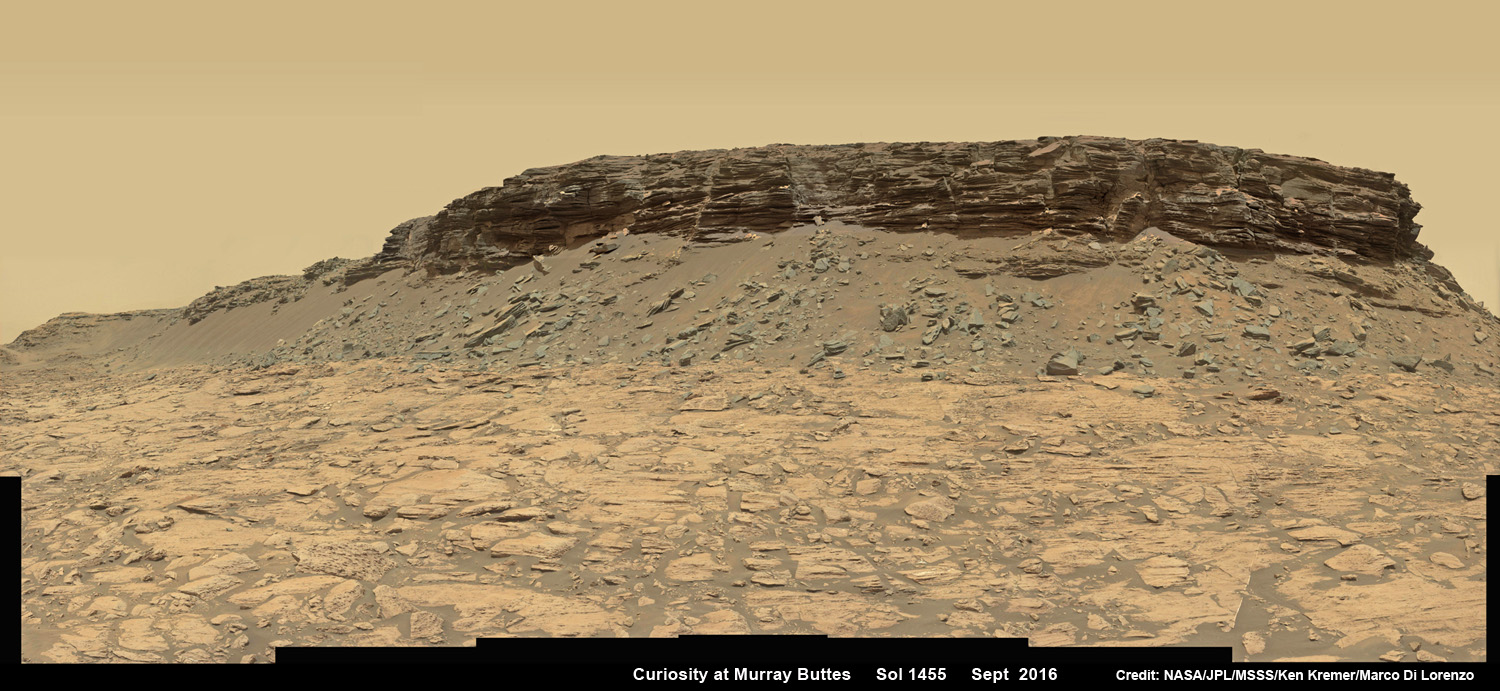
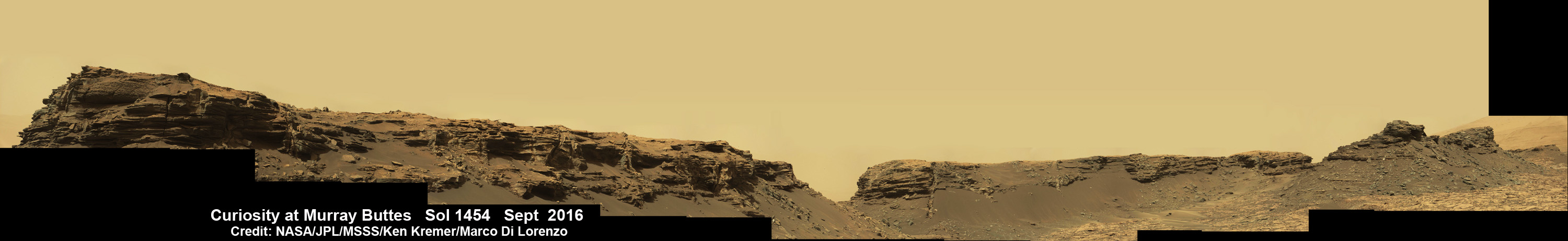
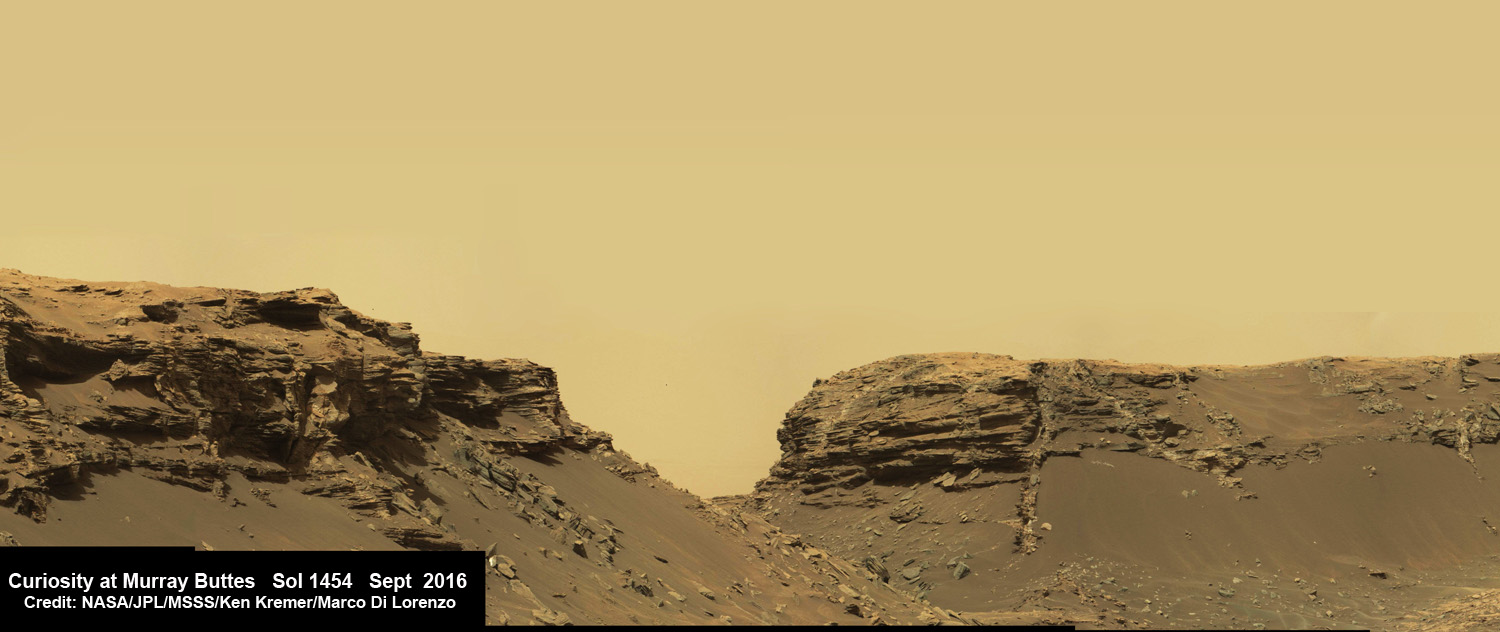
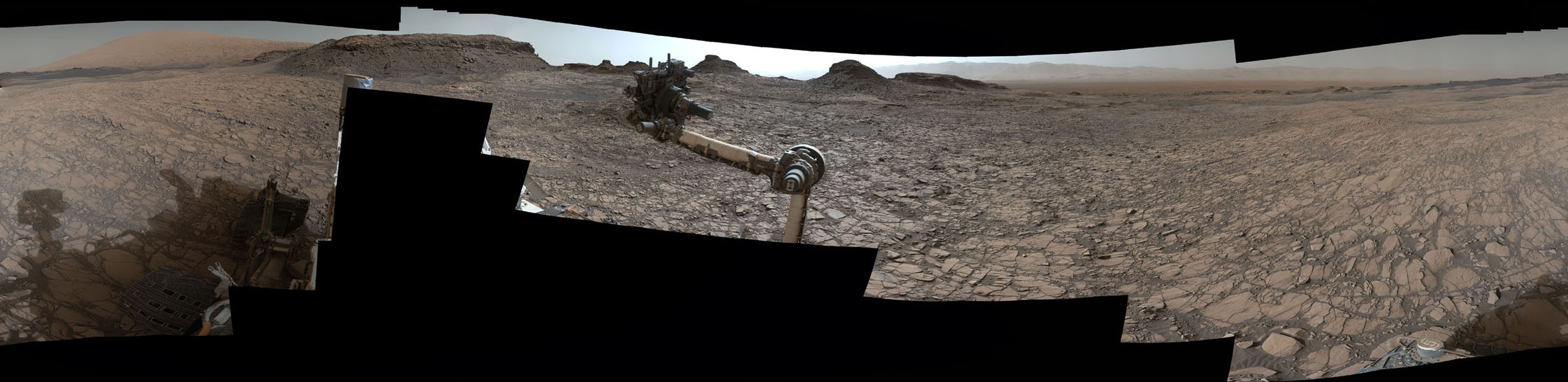
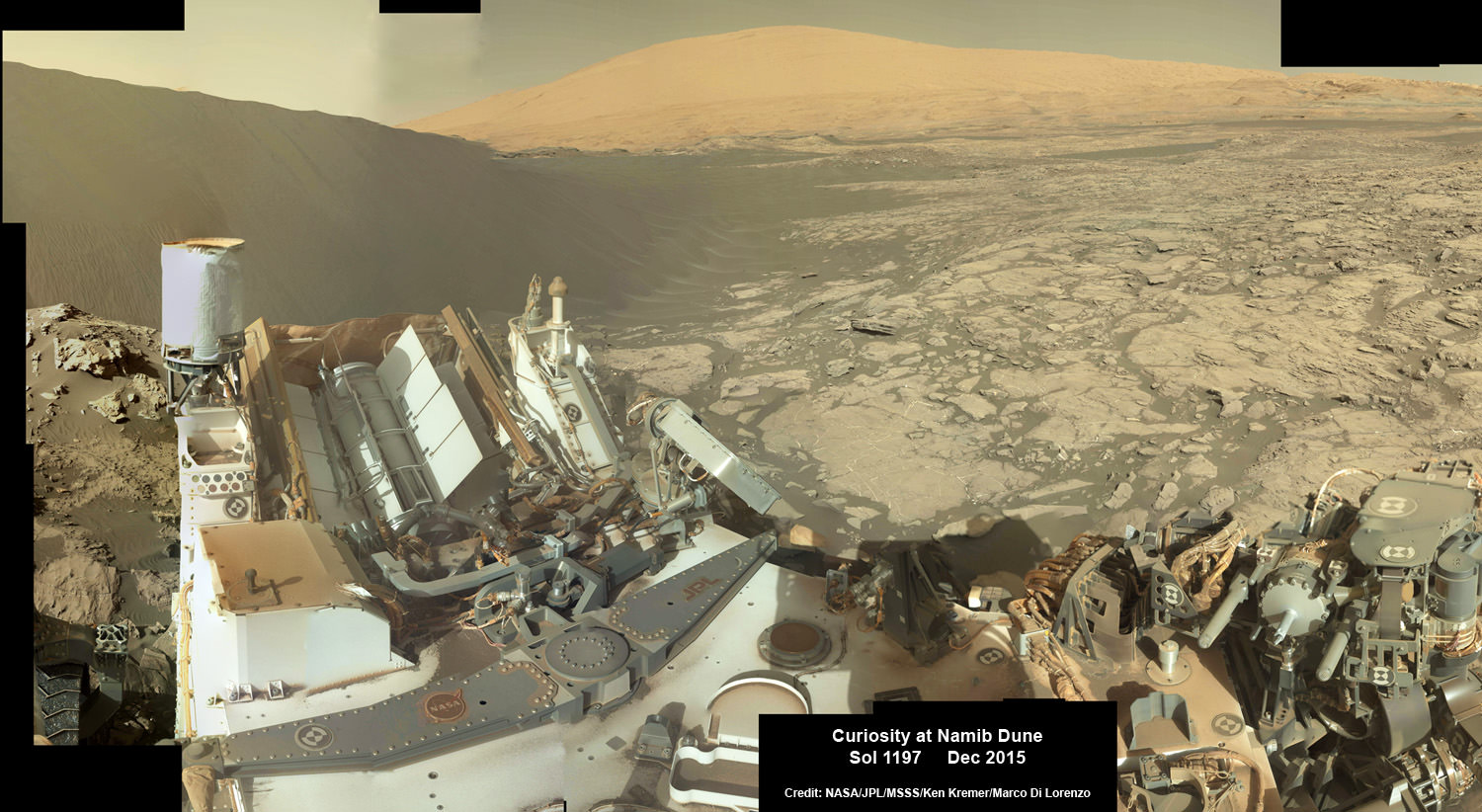
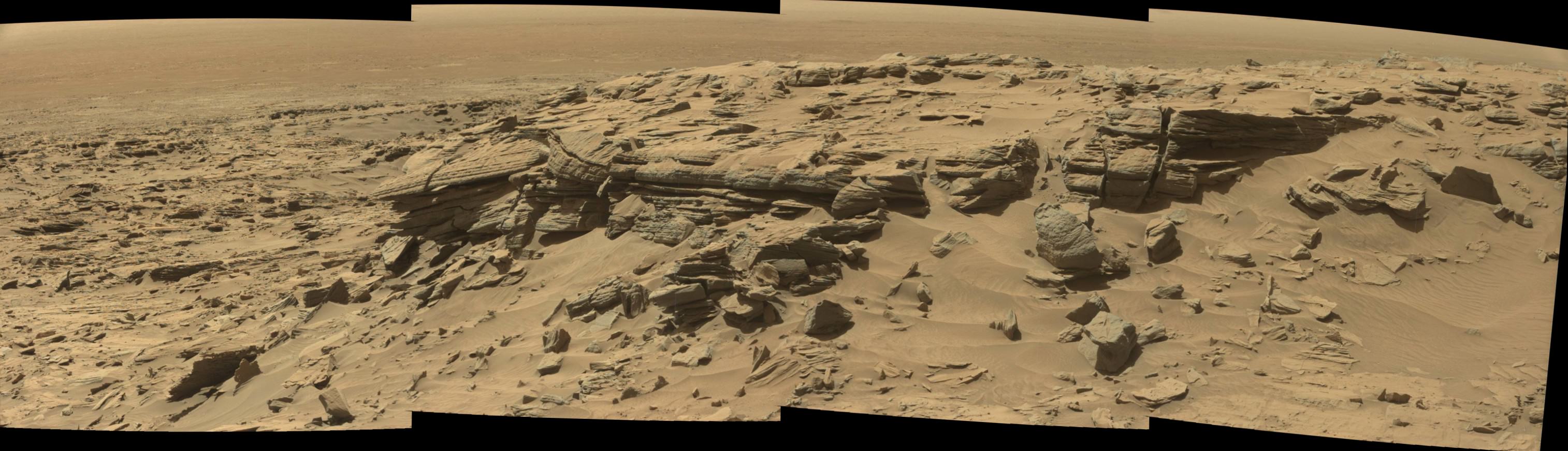
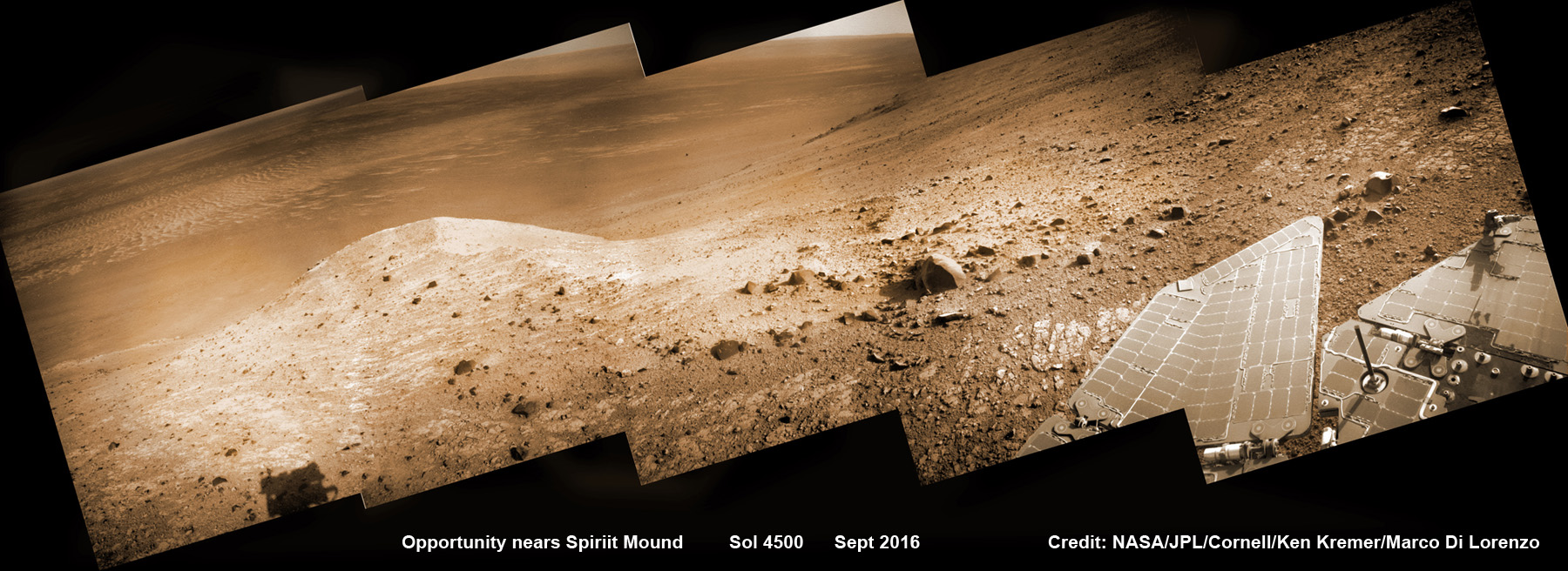
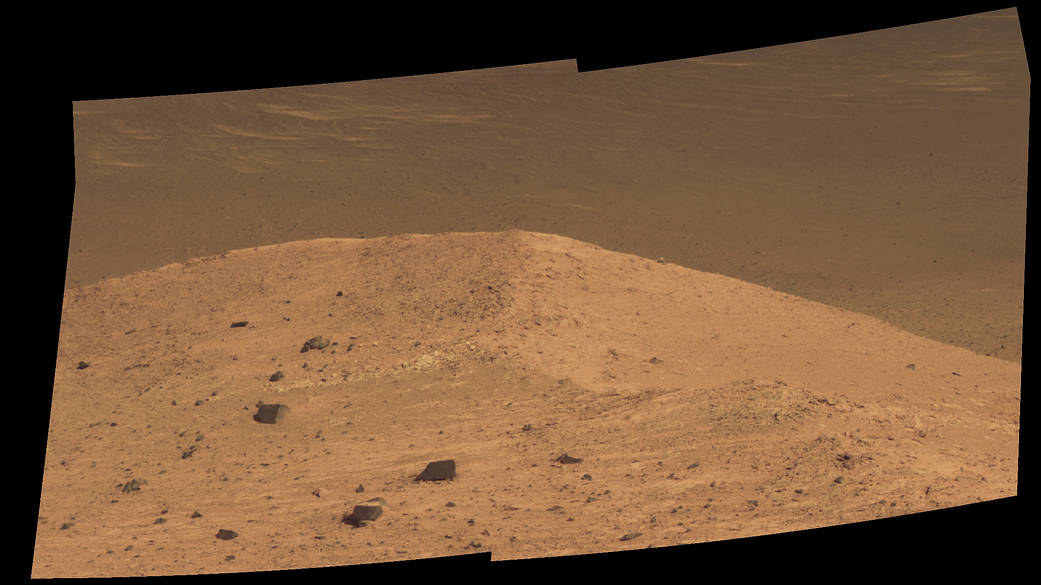
See Opportunity’s current location around ‘Spirit Mound” – illustrated in our new photo mosaic panoramas above and below.

After a scorching ‘6 minutes of Terror’ plummet through the thin Martian atmosphere, Opportunity bounced to an airbag cushioned landing on the plains of Meridiani Planum on January 24, 2004 – nearly 13 years ago!
Opportunity was launched on a Delta II rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on July 7, 2003.
“We have now exceeded the prime-mission duration by a factor of 50,” noted Opportunity Project Manager John Callas of NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, California.
“Milestones like this are reminders of the historic achievements made possible by the dedicated people entrusted to build and operate this national asset for exploring Mars.”
The newest 2 year extended mission phase just began on Oct. 1 as the rover was stationed at the western rim of Endeavour crater at the bottom of Marathon Valley at a spot called “Bitterroot Valley.”
And at this moment, as Opportunity reached and surpassed the 4500 Sol milestone, she is investing an majestic spot dubbed “Spirit Mound” – and named after her twin sister “Spirit” – who landed 3 weeks earlier!

Endeavour crater spans some 22 kilometers (14 miles) in diameter. Opportunity has been exploring Endeavour since arriving at the humongous crater in 2011.
Endeavour crater was formed when it was carved out of the Red Planet by a huge meteor impact billions of years ago.
But now for the first time she will explore the craters interior, after spending 5 years investigating the exterior and climbing to a summit on the rim and spending several year exploring the top before finally descending down the Marathon Valley feature to investigate clay minerals formed in water.
“The longest-active rover on Mars also will, for the first time, visit the interior of the crater it has worked beside for the last five years,” said NASA officials.
Marathon Valley measures about 300 yards or meters long. It cuts downhill through the west rim of Endeavour crater from west to east – the same direction in which Opportunity drove downhill from a mountain summit area atop the crater rim. See our route map below showing the context of the rovers over dozen year long traverse spanning more than the 26 mile distance of a Marathon runners race.
Opportunity is now being targeted to explore a gully carved out by water.
“We are confident this is a fluid-carved gully, and that water was involved,” said Opportunity Principal Investigator Steve Squyres of Cornell University, Ithaca, New York.
“Fluid-carved gullies on Mars have been seen from orbit since the 1970s, but none had been examined up close on the surface before. One of the three main objectives of our new mission extension is to investigate this gully. We hope to learn whether the fluid was a debris flow, with lots of rubble lubricated by water, or a flow with mostly water and less other material.”
Furthermore, in what’s a very exciting announcement the team “intends to drive Opportunity down the full length of the gully, onto the crater floor” – if the rover continues to function well during the two year extended mission which will have to include enduring her 8th frigid Martian winter in 2017.
And as is always the case, scientists will compare these interior crater rocks to those on the exterior for clues into the evolution, environmental and climatic history of Mars over billions of years.
“We may find that the sulfate-rich rocks we’ve seen outside the crater are not the same inside,” Squyres said. “We believe these sulfate-rich rocks formed from a water-related process, and water flows downhill. The watery environment deep inside the crater may have been different from outside on the plain — maybe different timing, maybe different chemistry.”

As of today, Sol 4522, Oct 12, 2016, Opportunity has taken over 214,400 images and traversed over 26.99 miles (43.44 kilometers) – more than a marathon.
The power output from solar array energy production is currently 472 watt-hours, before heading into another southern hemisphere Martian winter in 2017.
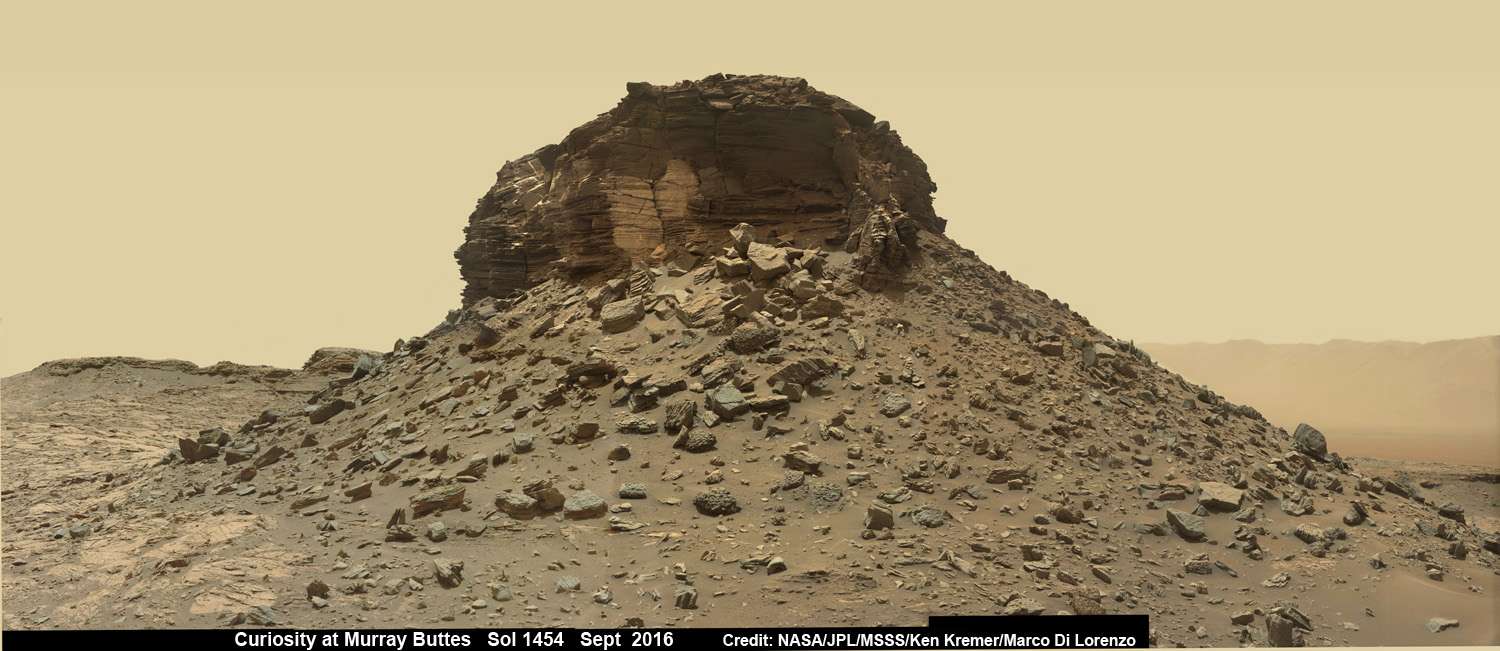
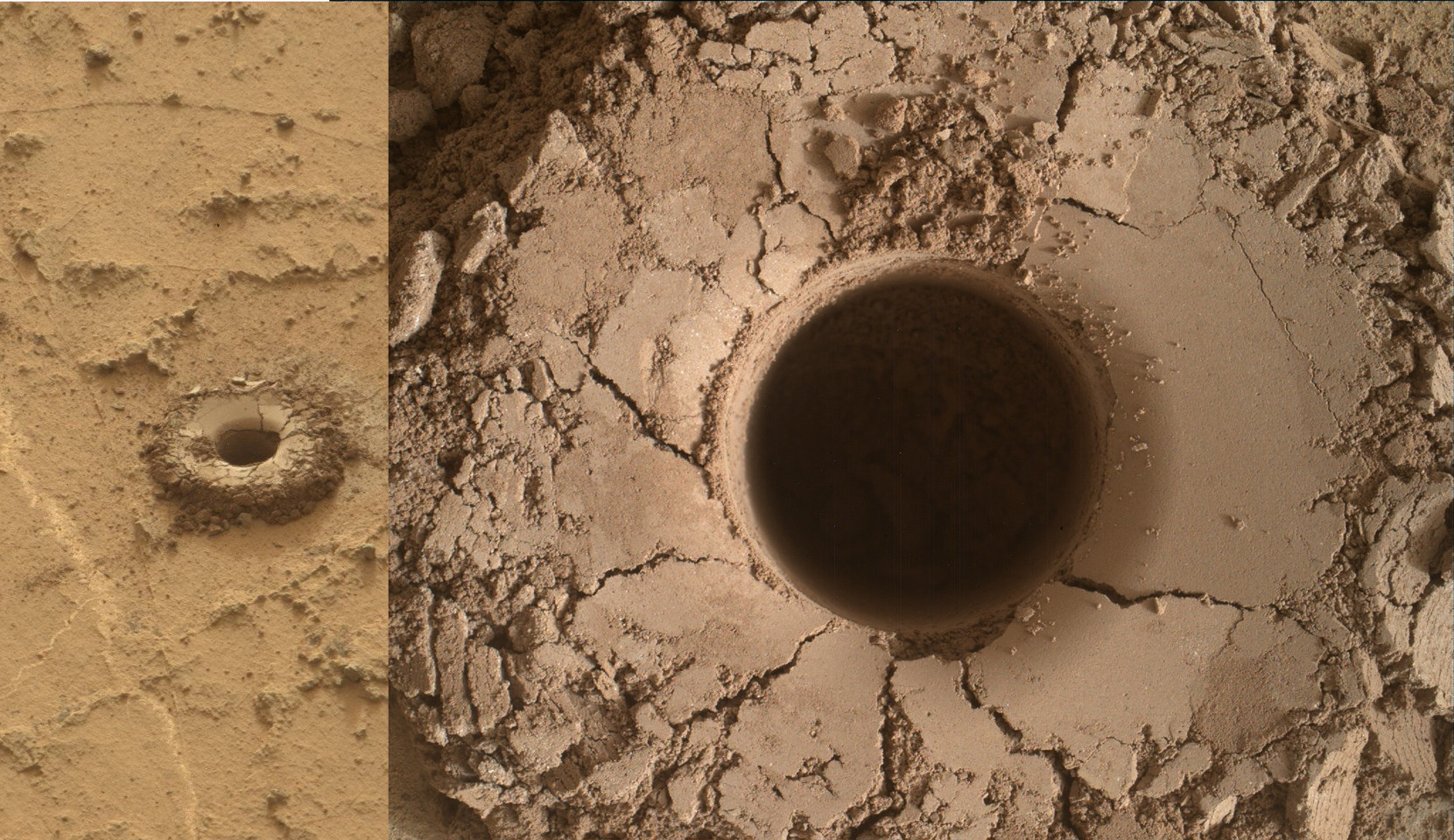
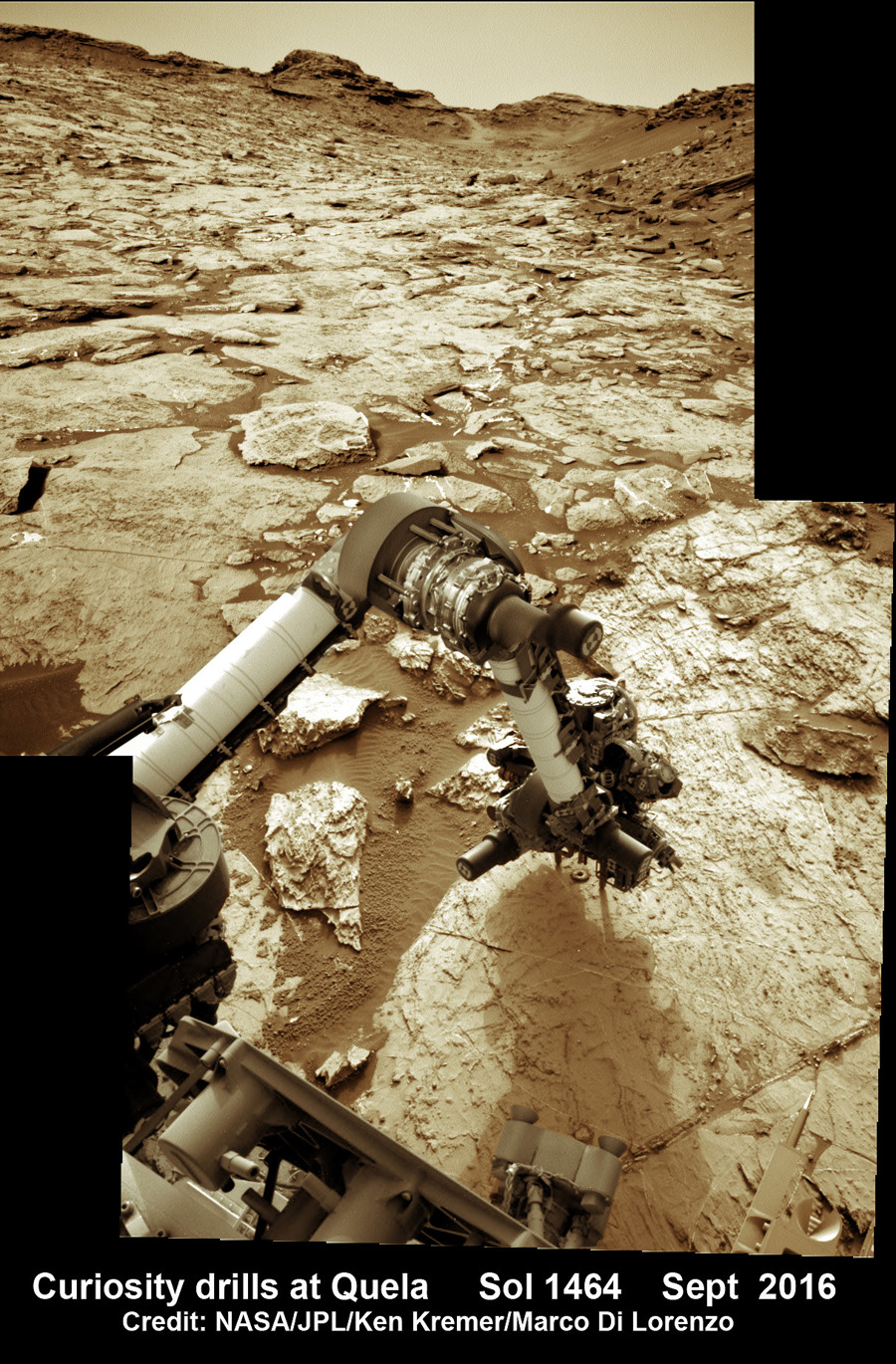
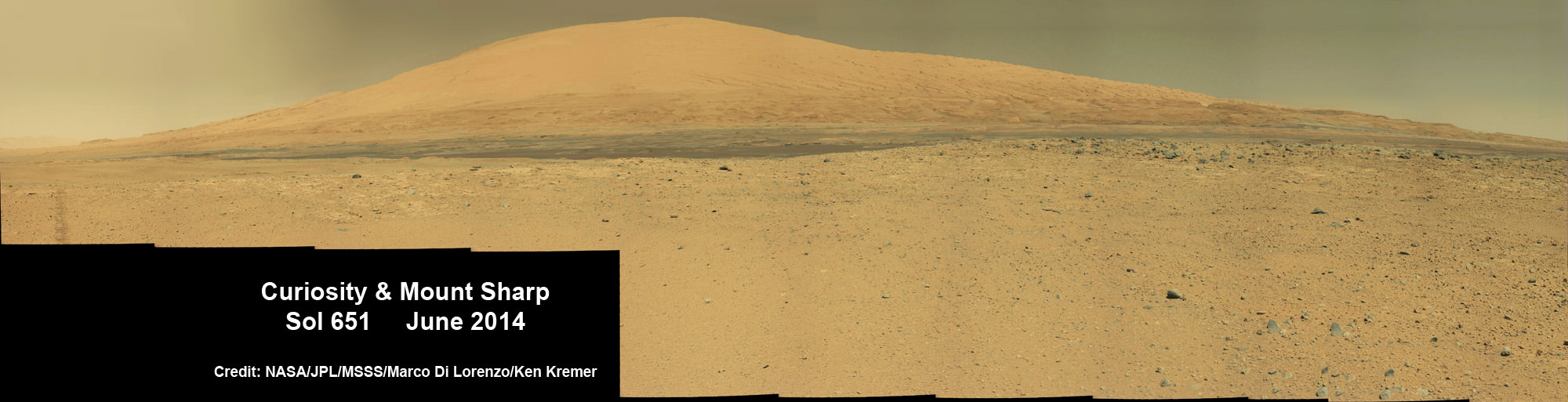
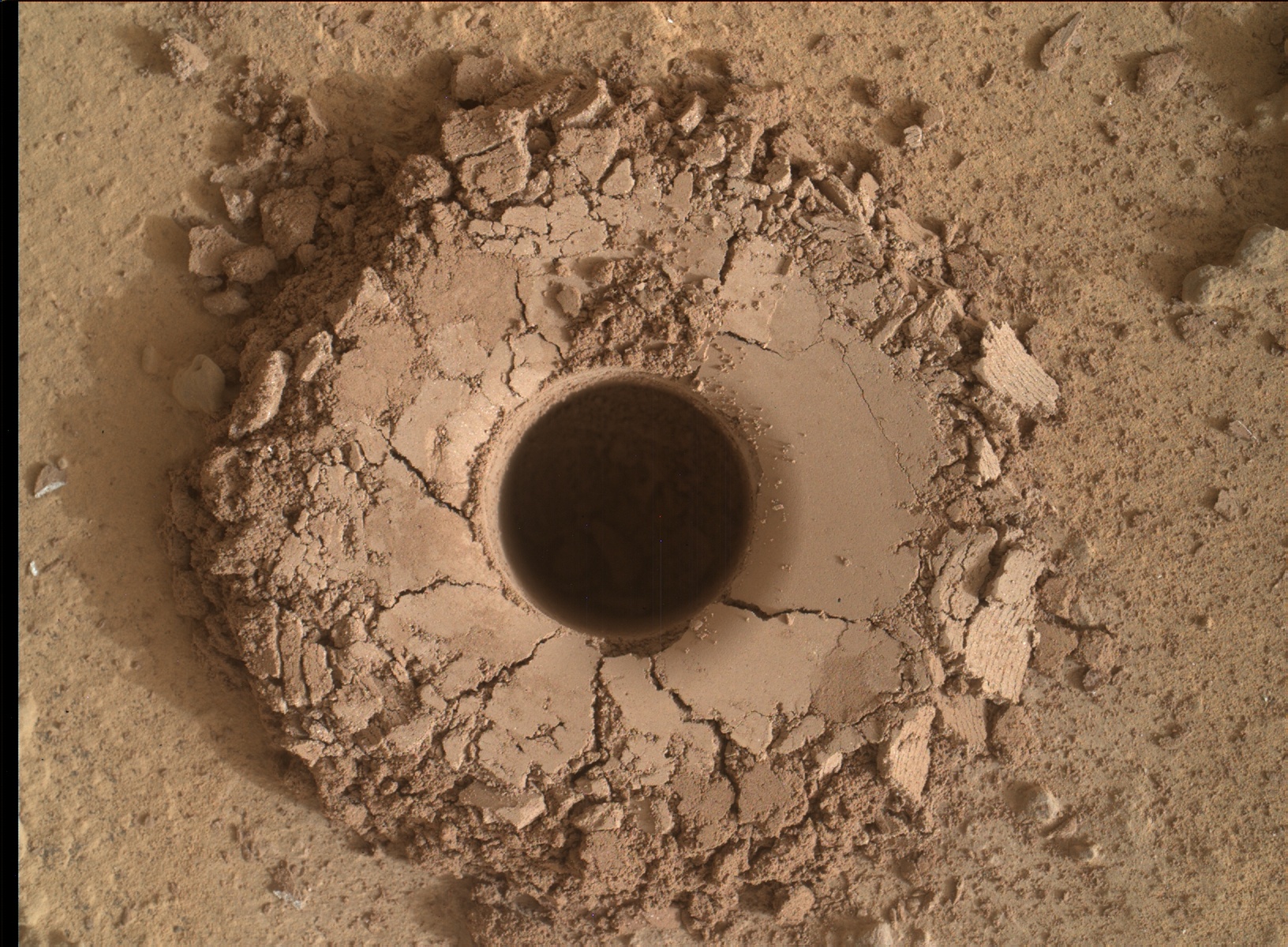
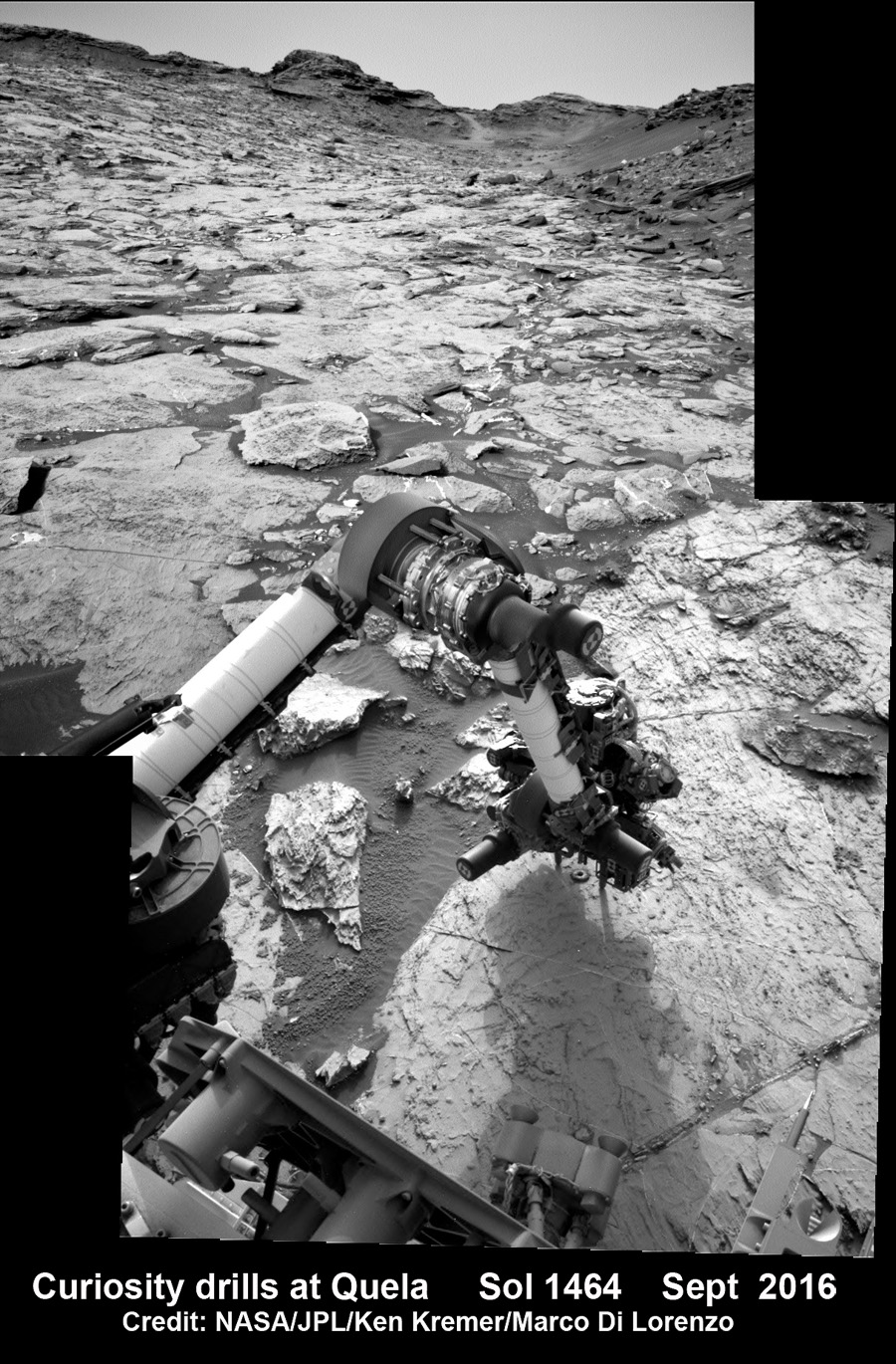
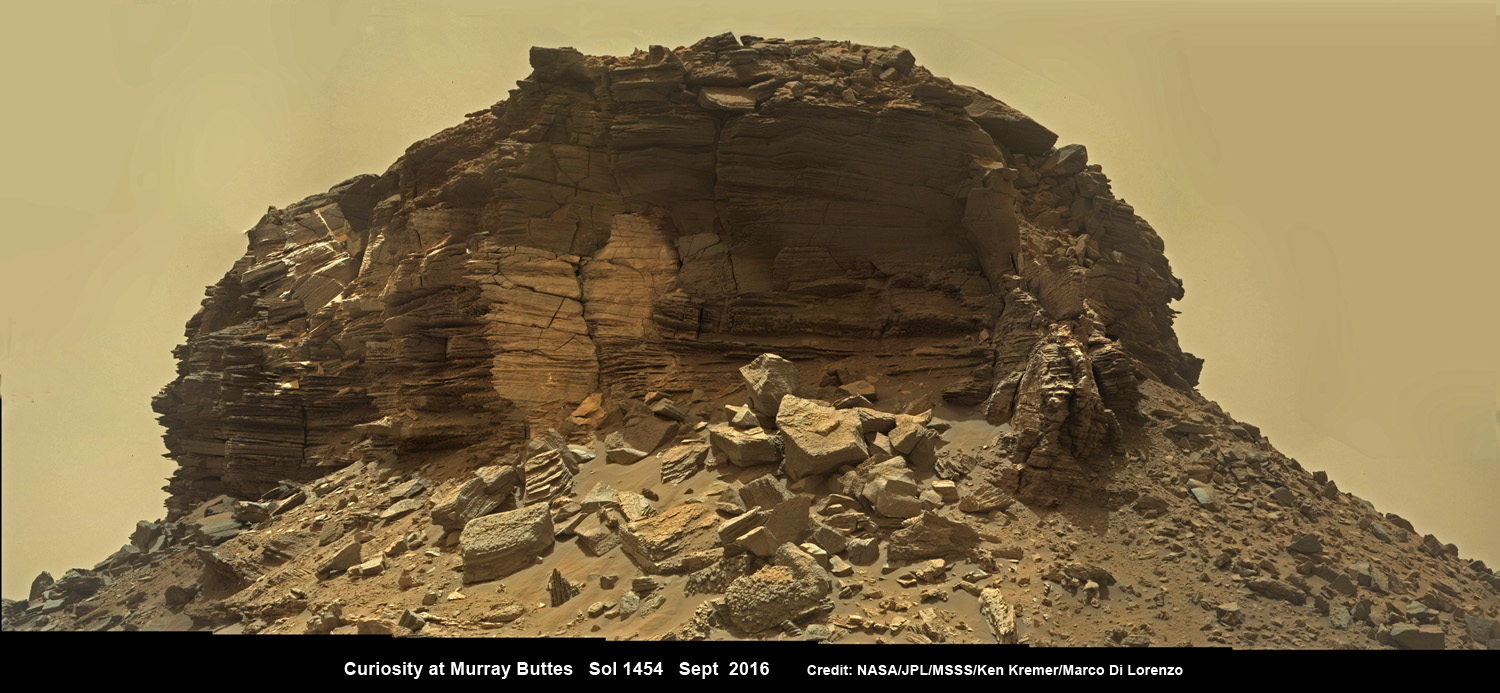
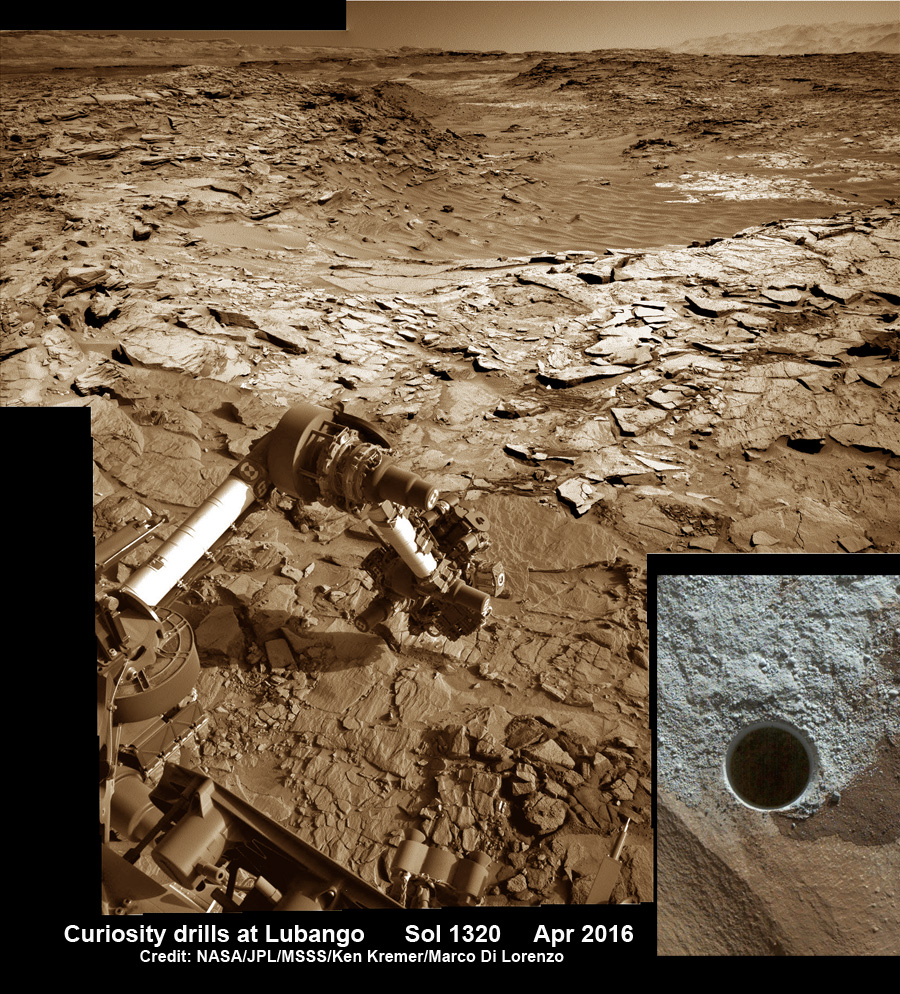
Meanwhile Opportunity’s younger sister rover Curiosity traverses and drills into the basal layers at the base of Mount Sharp.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and planetary science and human spaceflight news.