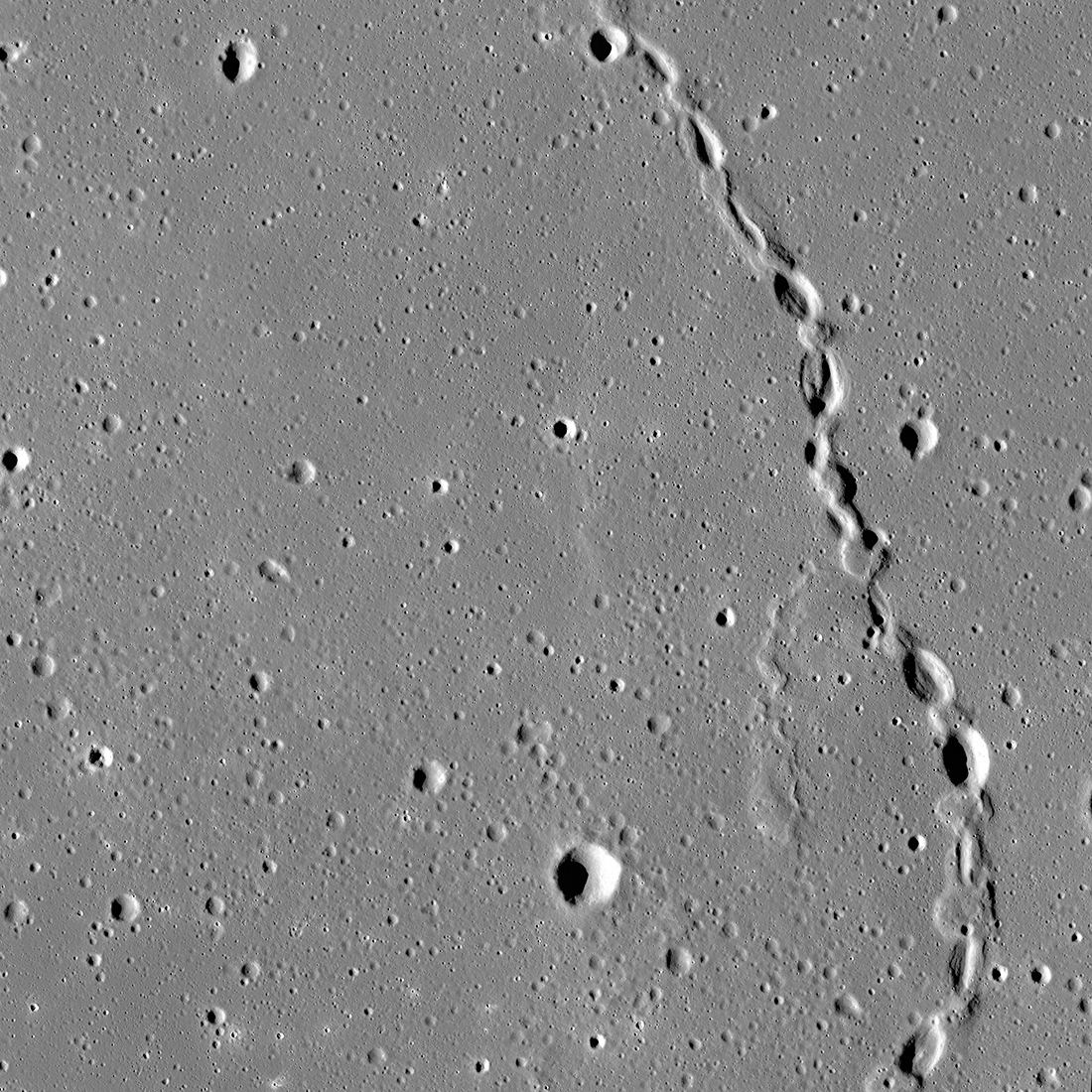
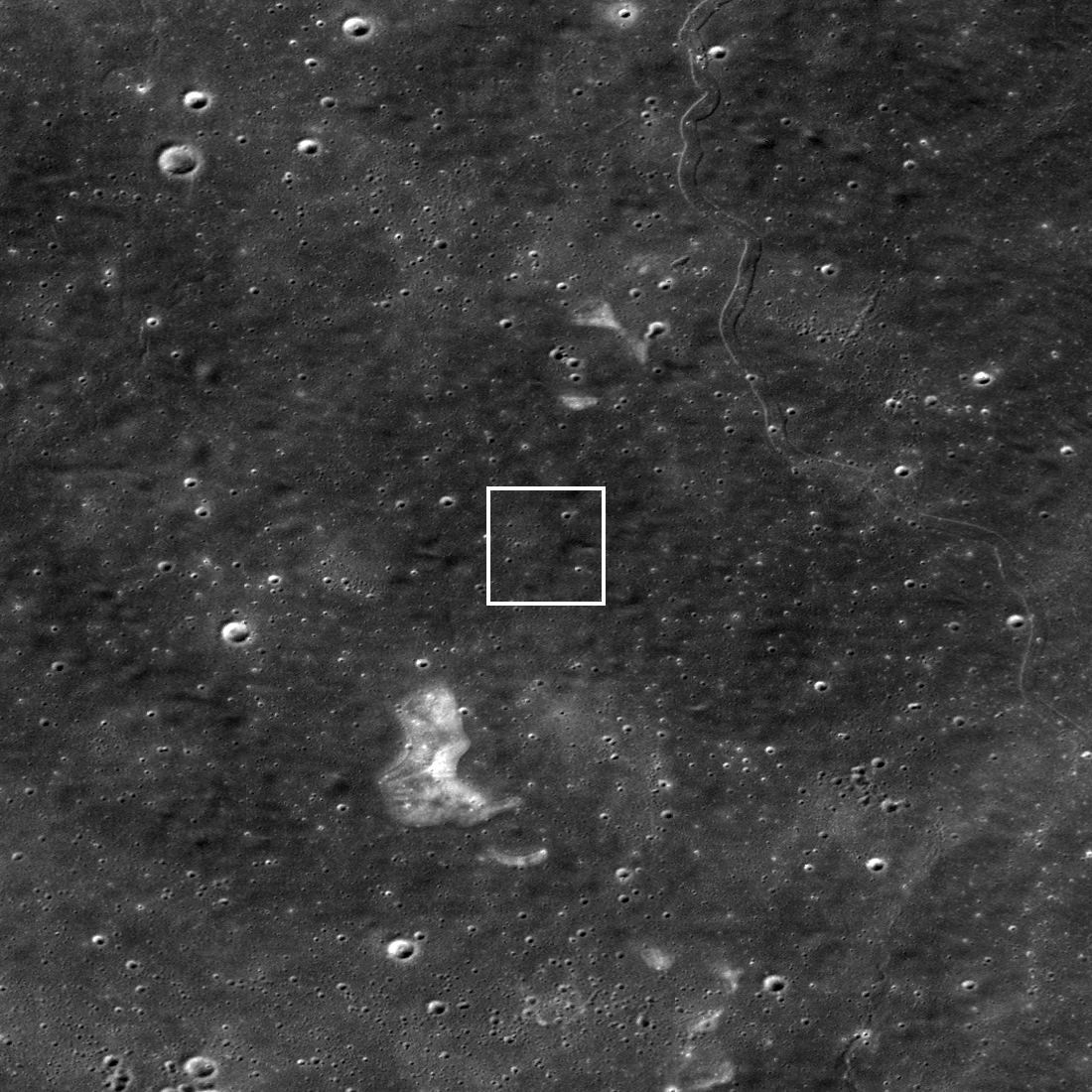
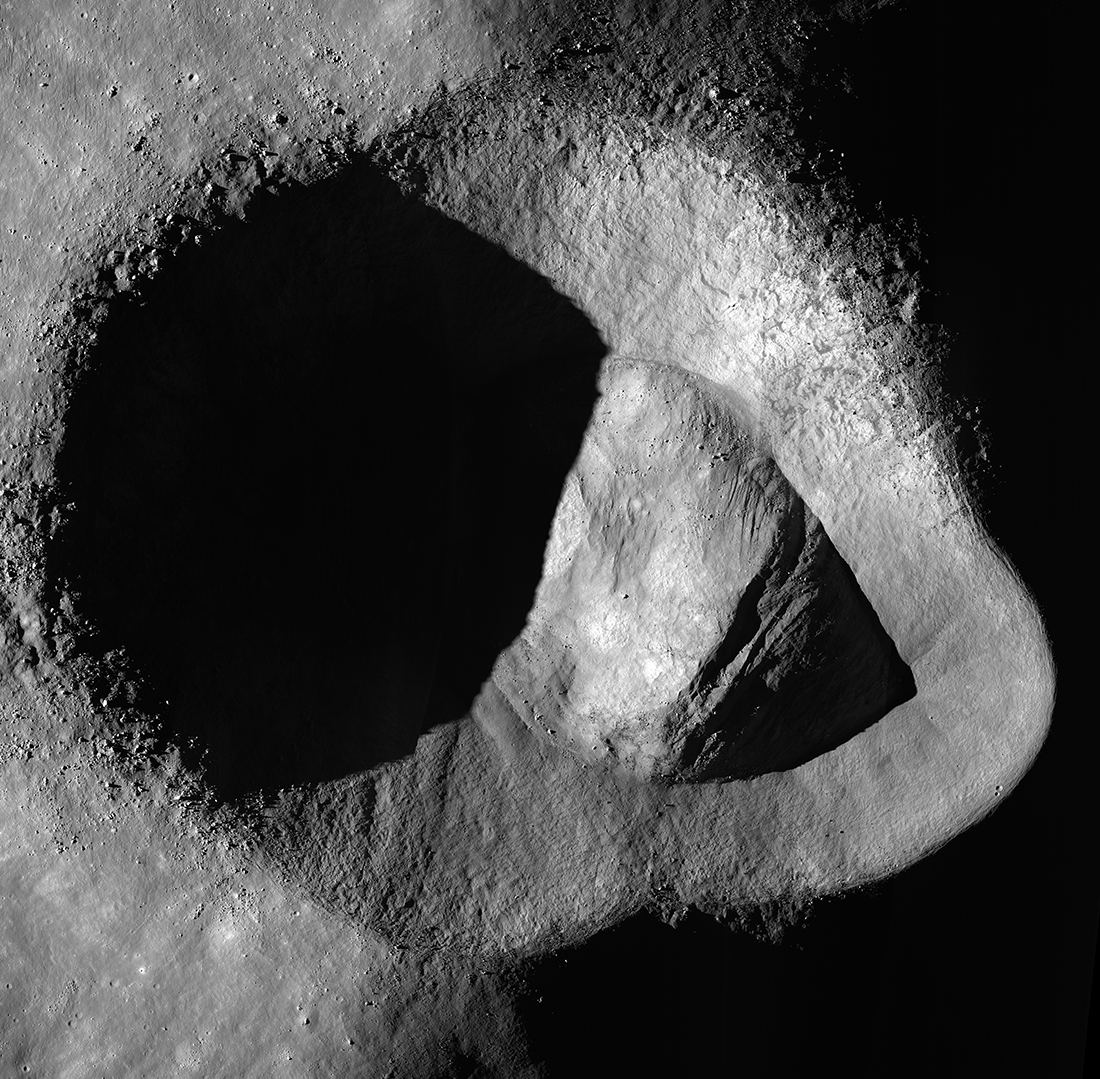
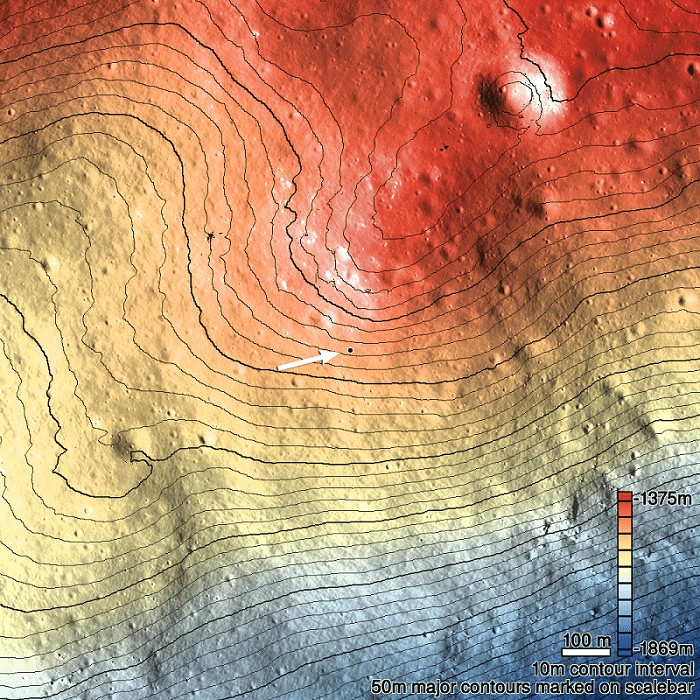
The Moon was once a geologically active place characterized by volcanoes, lava flows, and a magnetic field generated by action in its interior. The Moon’s airless environment has perfectly preserved evidence of this past and can be seen today as dark deposits, volcanic domes, and cones. But the most recognizable features are known as “sinuous rilles,” which are believed to be ancient lava tubes that have since collapsed. The Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter Camera (LROC) recently captured images of a rille that extended 48 km long (30 mi) across the northern hemisphere.
Continue reading “Is This a Collapsed Lava Tube on the Moon?”Is This a Collapsed Lava Tube on the Moon?