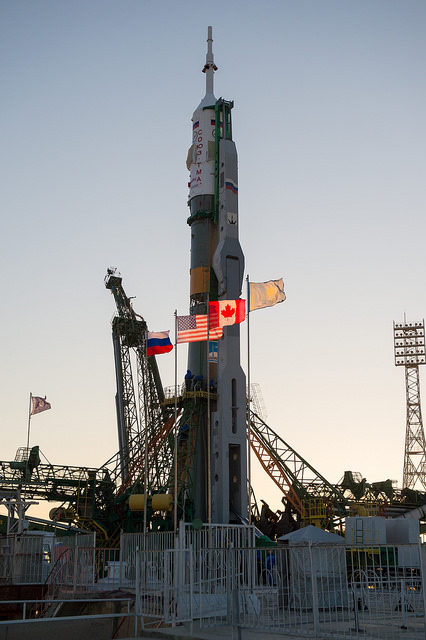
Want to know more about the Soyuz rocket? This new video from ESA is based on actual lessons for astronauts about the Soyuz rocket and describes the parts of the Soyuz, the stages and launch sequence. The info here was part of ESA Basic Training for the ESA astronaut class of 2009 (also known as the Shenanigans09).
ESA Launches ‘Albert Einstein’ Cargo Spacecraft to the Space Station

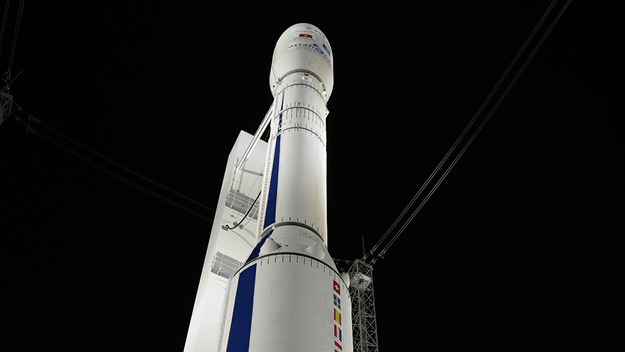
ESA used a little E=mc^2 and launched the Automated Transfer Vehicle-4 (ATV-4) resupply ship, named “Albert Einstein” in honor of the iconic physicist, famous for his handy little equation. Liftoff of the Ariane 5 rocket from Europe’s spaceport in Kourou, French Guiana occurred at 5:52 p.m. EDT (2152 GMT) on June 5, 2013. This is second-to-last of ESA’s five planned ISS resupply spacecraft; the first one launched 2008, and all have been named after scientists.
ATV-4 will take a leisurely 10 days to reach the station, with docking scheduled for June 15.
You can watch the launch video below.
The three previous ATVs were named for Jules Verne, Johannes Kepler and Edoardo Amaldi.
The 13-ton ATV-4 will deliver more than 7 tons of supplies to the station when it docks to the aft port of the Russian Zvezda service module a week from Saturday.
The cargo includes 5,465 pounds of dry cargo, experiment hardware and supplies, 1,896 pounds of propellant for transfer to the Zvezda service module, 5,688 pounds of propellant for reboost and debris avoidance maneuver capability, 1,257 pounds of water and 220 pounds of oxygen and air.
Before the ATV-4 arrives at the station, the Russian ISS Progress 51 cargo spacecraft will undock from the Zvezda port at 13:53 UTC (9:53 a.m. EDT), Tuesday, June 11.
Watch Live: Soyuz Fast-Track Launch to the Space Station
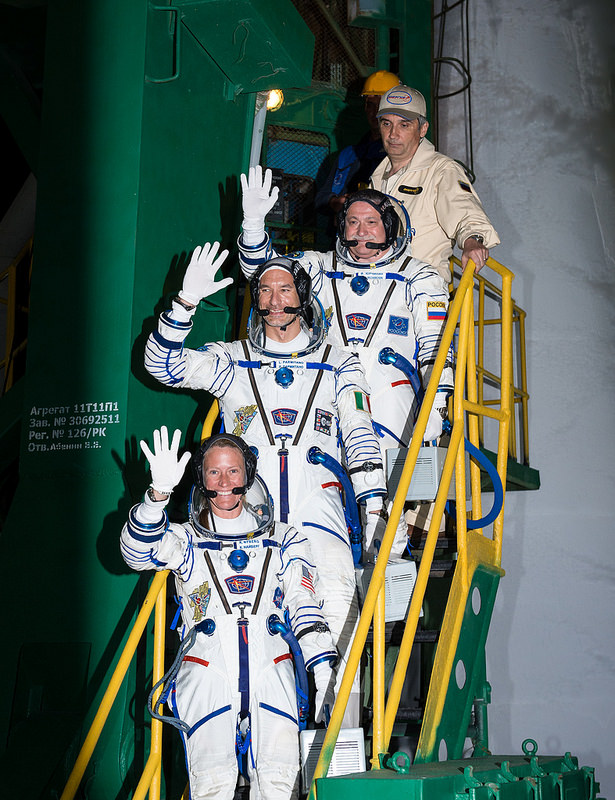

Three new International Space Station crew members are set to launch aboard the Soyuz TMA-09M spacecraft from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Launch is scheduled for is 20:31 UTC (4:31 p.m. EDT) Tuesday (2:31 a.m. May 29, Baikonur time). The new Expedition 36 crew will take an accelerated four-orbit, 6-hour journey to Space Station. They will be docking at 02:17 UTC on May 29 (10:17 pm. EDT May 28). You can watch Live NASA TV coverage below, which begins an hour before launch (19:30 UTC, 3:30 p.m. EDT), and live coverage will return about 45 minutes before docking.
The new crew includes Soyuz Commander Fyodor Yurchikhin of the Russian Federal Space Agency (Roscosmos), NASA astronaut Karen Nyberg and European Space Agency (ESA) astronaut Luca Parmitano.
UPDATE: If you missed the launch live, you can watch a replay, below.
Live Video streaming by Ustream
The crew will dock their Soyuz to the station’s Rassvet module. After the hatches open, the new trio will join Flight Engineer Chris Cassidy of NASA and Commander Pavel Vinogradov and Flight Engineer Alexander Misurkin of Roscosmos who docked with the orbital complex May 28. All six crew members will then participate in a welcome ceremony with family members and mission officials gathered at the Russian Mission Control Center in Korolev near Moscow.
In the past, Soyuz manned capsules and Progress supply ships were launched on trajectories that required about two days, or 34 orbits, to reach the ISS. The new fast-track trajectory has the rocket launching shortly after the ISS passes overhead. Then, additional firings of the vehicle’s thrusters early in its mission expedites the time required for a Russian vehicle to reach the Station.
This is the second Soyuz crew vehicle to make the accelerated trip, and three Progress resupply ships have also taken the fast track to the ISS.

You can see more images from the Expedition 36 launch and pre-launch activities at NASA HQ’s Flickr page.
ESA’s Vega Rocket Launches Three Satellites to Space
The second flight of ESA’s newest launch vehicle has successfully sent three different satellites to space. Launching at 02:06 GMT on 7 May from Europe’s Spaceport in Kourou, French Guiana, the Vega rocket carried two Earth observation satellites — ESA’s Proba-V, Vietnam’s VNREDSat-1A — and Estonia’s first satellite, the ESTCube-1 technology demonstrator were released into different orbits. The complex mission required five upper-stage boosts, with the flight lasting about twice as long as its first launch, in February 2012.
ESA officials said the success demonstrates the Vega rocket’s versatility.
Watch the launch video below.
“It is another great day for ESA, for its Member States and for Europe,” said Jean-Jacques Dordain, Director General of ESA. “Thanks to decisions taken by Member States, ESA and European industry are demonstrating once again their capabilities of innovation. Among the Member States, special mention goes to Italy which has led the Vega Programme, Belgium which has led the Proba projects at ESA, and France which has led the development and maintenance of the European spaceport here in Kourou. We are also proud to have made possible the launch of the first satellite from Estonia.”
The three solid-propellant stages performed flawlessly and after two burns of the liquid-propellant upper stage, the Proba?V was released into a circular orbit at an altitude of 820 km, over the western coast of Australia, some 55 minutes into flight.
After releasing Proba-V, the upper stage performed a third burn and the top half of the egg-shaped Vega Secondary Payload Adapter was ejected. After a fourth burn to circularize the orbit at an altitude of 704 km, VNREDSat-1A was released 1 hour 57 minutes into flight. ESTCube?1 was ejected from its dispenser three minutes later.
The fifth and last burn put the spent upper stage on a trajectory that ensures a safe reentry that complies with new debris mitigation regulations.
Source: ESA
Antares Rocket Launches Successfully
Orbital Sciences Antares rocket successfully launched on its maiden voyage at 5 pm EDT (21:00 UTC) on Sunday, April 21 from the Mid-Atlantic Regional Spaceport at NASA’s Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia. The test flight is serving as the precursor for a demonstration flight of its Cygnus resupply ship to the International Space Station later this year. About 10 minutes after launch, it placed a mass simulator payload to orbit designed to mimic the Cygnus spacecraft’s weight and characteristics. It is in orbit at 250 km (155 miles) in altitude and moving at27,350 km/hr (17,000 mph).
Watch Live: First Launch of Antares Rocket
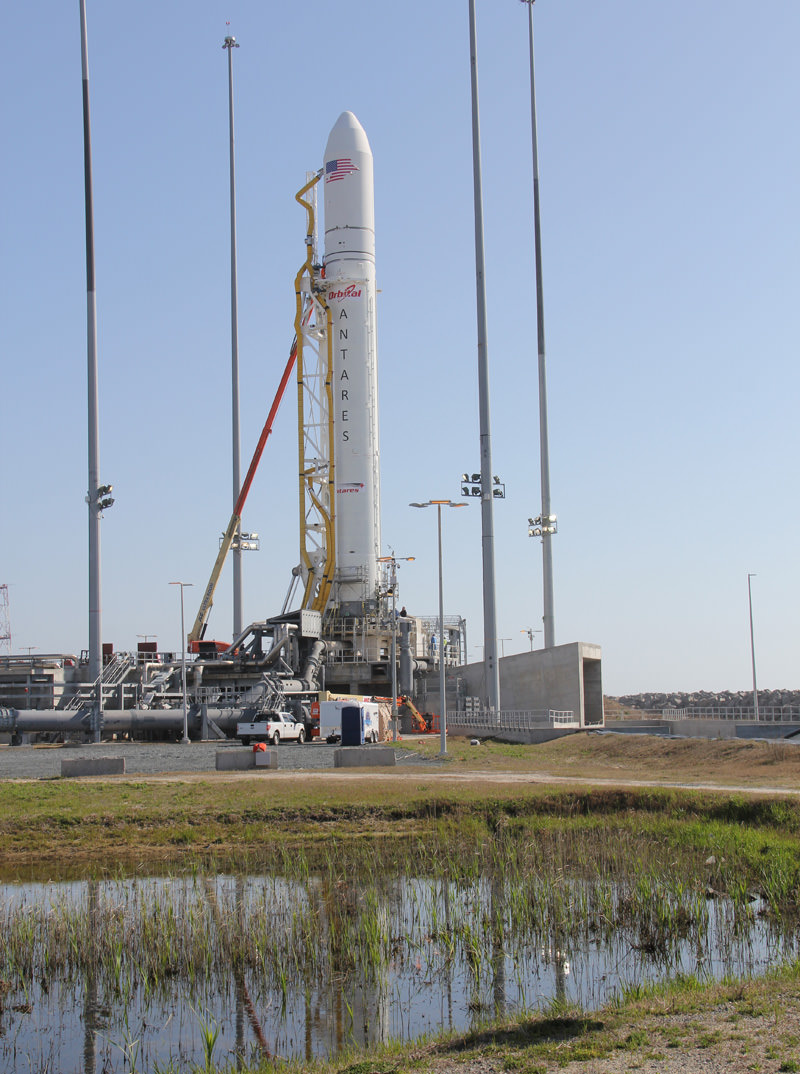

UPDATE: Wednesday’s test launch for Orbital Science Corporation’s Antares rocket was aborted due to the premature disconnection of a second-stage umbilical about 12 minutes before launch was scheduled. The earliest the flight can be rescheduled is Friday, April 19.
“We are still examining all of the data, but it appears that the issue is fairly straightforward,” said Frank Culbertson, Orbital’s executive vice president and mission director for the Antares test flight, in a statement released by the company. “With this being the first launch of the new system from a new launch facility we have taken prudent steps to ensure a safe and successful outcome. Today, our scrub procedures were exercised and worked as planned. We are looking forward to a successful launch on Friday.”
[end of update]
It’s been billed as “the biggest, loudest and brightest rocket ever to launch from NASA’s Wallops Flight Facility” in Virginia, and the commercial company Orbital Sciences Corporation is ready to send their Antares rocket on its maiden test flight. Orbital is testing Antares under NASA’s Commercial Orbital Transportation Services (COTS) program, and the rocket will send a dummy module into orbit that has the same mass as Orbital’s Cygnus cargo spacecraft, as well as a few smaller satellites, testing the rocket’s capabilities.
You can watch live here via NASA TV’s Ustream. There is a press briefing at 2 pm EDT (18:00 UTC), and launch coverage starts at 4:00 pm EDT (20:00 UTC), with the launch window open between 5 and 8 pm EDT (21:00 and midnight UTC).
This will mark not only the first launch of Antares, but the first orbital launch of a liquid-fueled rocket from Wallops. If all goes well with this flight, Orbital will carry out a full flight demonstration of Antares and the Cygnus cargo delivery system to the International Space Station around mid-2013.
If you live along the Eastern Seaboard of the US, here’s great information on how you might be able to see the launch, and here’s our article with more info on the flight.
Watch “Fast-Track” Launch of Soyuz Live
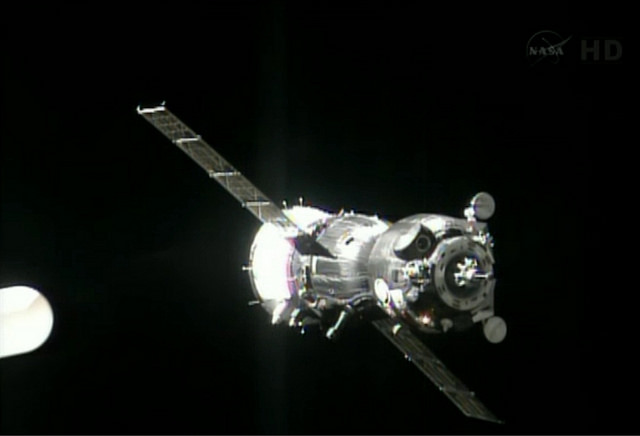

Watch live the first “fast-track” human Soyuz flight to the International Space Station. The Soyuz TMA-08M crew will arrive at the ISS just five hours and 49 minutes after launch instead of the usual two days. Commander Pavel Vinogradov, flight engineer Alexander Misurkin and NASA astronaut Christopher Cassidy are scheduled for liftoff from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan at 20:43 UTC (4:43:20 p.m. EDT) on Thursday, March 28, 2013. (If you missed the launch live, watch the video of it below:)
Continue reading “Watch “Fast-Track” Launch of Soyuz Live”
Next Soyuz Crew Will Take 6-Hour Fast-Track to Space Station
The next Soyuz crew will be the first to try out the new abbreviated four-orbit rendezvous with the International Space Station. This relatively new, modified launch and docking profile for the Russian ships has been tried successfully with three Progress resupply vehicles, and now Roscosmos and NASA have agreed to try it on a human flight.
“We tried this approach on the cargo vehicles, and now we will try to do it on the manned vehicles,” said Sergei Krikalev, former cosmonaut, who now leads the Gagarin Cosmonaut Training Center near Moscow, speaking through an interpreter on NASA TV. “Now we have onboard new machinery and new software, so the vehicle is more autonomous, so it’s possible to do a lot onboard the vehicle and to calculate the burns so they don’t consume a lot of fuel.”
In the past, Soyuz manned capsules and Progress supply ships were launched on trajectories that required about two days, or 34 orbits, to reach the ISS. The new fast-track trajectory has the rocket launching shortly after the ISS passes overhead. Then, additional firings of the vehicle’s thrusters early in its mission expedites the time required for a Russian vehicle to reach the Station.
Liftoff of the Soyuz TMA-08M spacecraft is scheduled for 4:43 p.m. EDT (20:43 UTC) on March 28 from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Docking is set for 10:31 p.m. EDT (02:31 UTC).
“The Soyuz is not the most comfortable vehicle to be in for an extended period of time,” said NASA astronaut Chris Cassidy who is part of the Expedition 35/36 crew who will make the first fast-track flight. “The toilet is right next to where you sleep which are right next to your buddy and eating and all; it’s like living for a day in a smart car or a Volkswagen Beetle….So the benefit to us is we get to the space station faster with the facilities that it offers, much more comfortable type of environment to be in and it also demonstrates some technology that’s useful in getting to the space station on that same day.”
One of the reasons given in the past for having the two-day or even three-day flight in the Soyuz was to allow the crew members time to get acclimated to being in a weightless environment. This new fast approach doesn’t allow for that, but Cassidy said he doesn’t think that thinking is really applicable, since the cramped Soyuz is so different from the voluminous space station.
“The adaptation of that I think is a little bit different,” he said. “You’re really not truly adapting in that day and a half. Two days on the Soyuz, that same adaptation that you’ll have once you get to the space station just because it’s a different perspective for your brain to get its arms around.”
The Soyuz took the first crew to the International Space Station in November 2000, and since that time, at least one Soyuz has always been at the Station, generally to bring the crews back and forth, but also to serve as a lifeboat should the crew have to return to Earth unexpectedly. Now that the space shuttles have been retired, the Soyuz is currently the only way for ISS crews to go to and from the Station. When there is a full crew of six on board, that means two Soyuz are docked at the ISS.
SpaceX is shooting for sometime in 2015 for the first crew flights of the Dragon to the ISS.
Indian Rocket Launches Swarm of International Mini Satellites

A Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) successfully launched from India today, sending seven different international satellites into orbit. Launch was at 7:31 a.m. EST (12:31 UTC) and on board were three Canadian-built spacecraft including a small asteroid-hunting satellite (weighing in at just 74 kg) called NEOSSat, other small satellites from the UK, Austria and Denmark and an India-France joint effort called SARAL, an Earth observation satellite, the primary payload for the launch.
Reports indicate all seven satellites were placed in their proper orbits and after their initial check-outs will being their missions.
NEOSSat (Near-Earth Object Surveillance Satellite)will track large asteroids that may come close to Earth and also track space debris in orbit. The suitcase-sized NEOSSat will orbit approximately 800 kilometers above the Earth, searching for objects that are difficult to spot using ground-based telescopes. Because of its location, NEOSSat will not be limited by the day-night cycle and will operate continuously.
“NEOSSat will discover many asteroids much faster than can be done from the ground alone,” said Alan Hildebrand of the University of Calgary. “Its most exciting result, however, will probably be discovering new targets for exploration by both manned and unmanned space missions.”
SARAL will be monitoring climate on Earth; CanX-3 BRITE (BRIght Target Explorer) is billed as the smallest astronomical telescope looking for faint objects; Sapphire is a military satellite that will keep track of objects orbiting between 3,800 and 25,000 miles (6,000 and 40,000 kilometers) from Earth; TUGSat-1 BRITE from Austria will monitor changes in brightness in stars; AAUSat 3 from Denmark will moniter ship traffic on Earth’s oceans, and STRaND-1 is a nanosatellite carrying a smartphone, has unique “screaming in space” experiment.
See more information on each satellite on our preview article.
Continuing the Landsat Mission: New Satellite Launches to Space
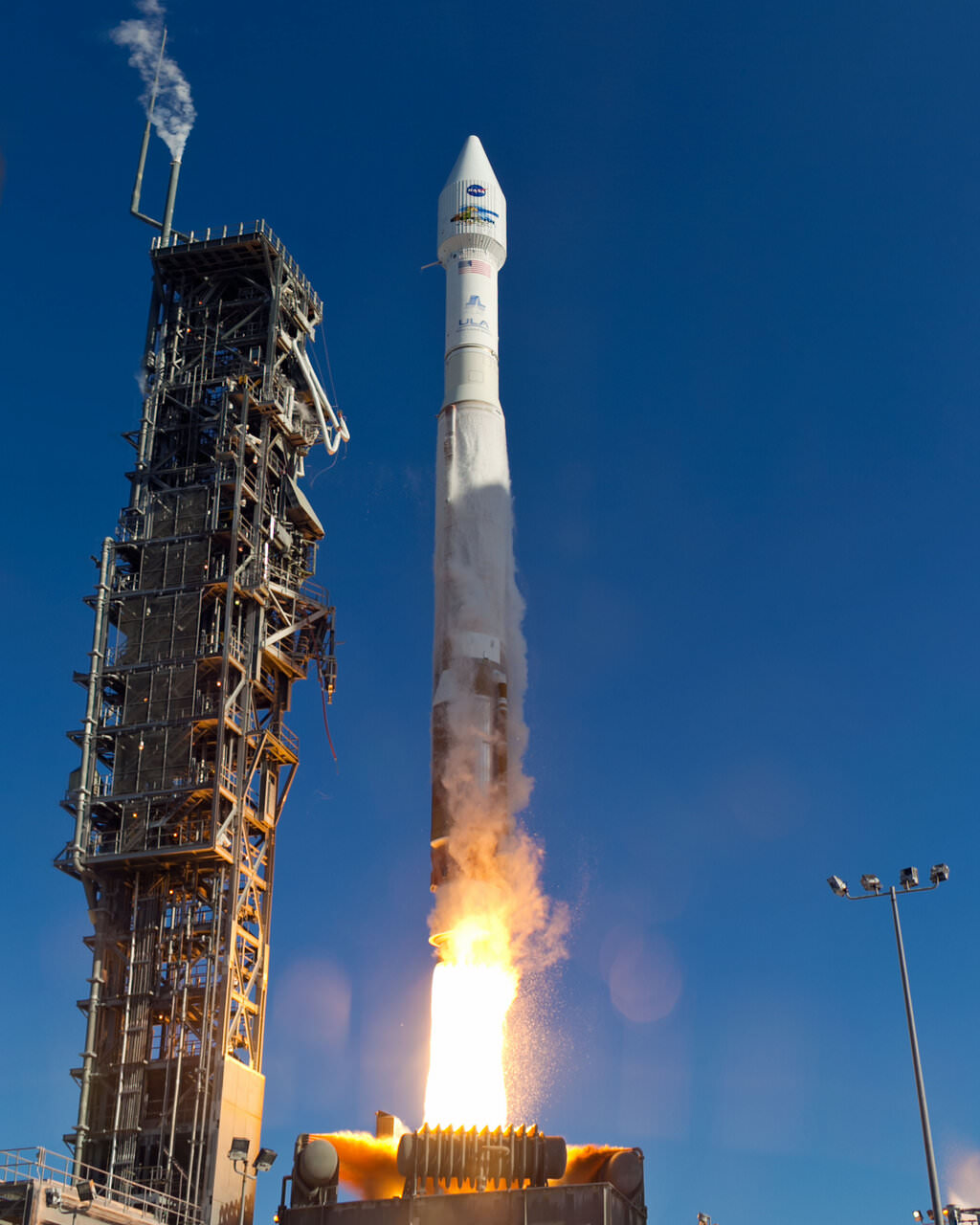

NASA launched a successor to the long-time Landsat satellite Earth-observing program today, sending the Landsat Data Continuity Mission satellite to orbit via an Atlas V rocket from Vandenberg Air Force Base at 1:02 EST (10:02 PST, 18:02 UTC). The new LDCM carries two new instruments, the Operational Land Imager and the Thermal Infrared Sensor, which will collect data that are compatible with data from previous Landsat mission, 5 and 7, and improve upon it with advanced instrument designs that are more sensitive to changes to the land surface, NASA said. This is the eighth Landsat satellite, and after extensive on-orbit testing and certified for its mission, it will be renamed Landsat 8.
See the launch video, below:
LDCM will continue the Landsat program’s 40-year data record of monitoring Earth from space, making critical observations to help with energy and water management, forest monitoring, human and environmental health, urban planning, disaster recovery and agriculture.
The new satellite is about the size of a large SUV, weighing 2,780 kg (6,133-pounds). The two instruments will monitor Earth’s surface in visible and multiple infrared wavelengths, resolving large-scale surface features and collecting some 400 images per day. The satellite is equipped with a 3.14-terabyte solid-state recorder to store data between downlink sessions.
“This will be the best Landsat satellite launched to date,” said Jim Irons, LDCM project scientist at Goddard Spaceflight Center, “the best Landsat satellite ever in terms of the quality and quantity of the data collected by the LDCM sensors.”

Irons said the Landsat program is a critical and extremely valuable national asset.
“Since the launch of Landsat 1, we have seen — and we have caused — dramatic changes to the global land surface that continue today at rates unprecedented in human history,” he said. “These changes are due to an increasing population, advancing technologies and climate change. LDCM will extend and improve upon the Landsat record of landscape change. The resulting observations and information will be critical to managing increasing demands on land resources and preparing for inevitable changes to the global land surface.”
Recently, Landsat 5 successfully set the new Guinness World Records title for ‘Longest-operating Earth observation satellite.’ It was launched on March 1, 1984, and outlived its three-year design life. It delivered high-quality, global data of Earth’s land surface for 28 years and 10 months, completing over 150,000 orbits and sending back more than 2.5 million images of Earth’s surface. On Dec. 21, 2012 the USGS announced Landsat 5 would be decommissioned in the coming months after the failure of a redundant gyroscope. The satellite carries three gyroscopes for attitude control and needs two to maintain control.
The Landsat Program is managed by the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS).
Read more about the Landsat Program here.
This timeline shows the continuing Landsat Program:

This video shows the separation of the spacecraft as it prepares to go into orbit: