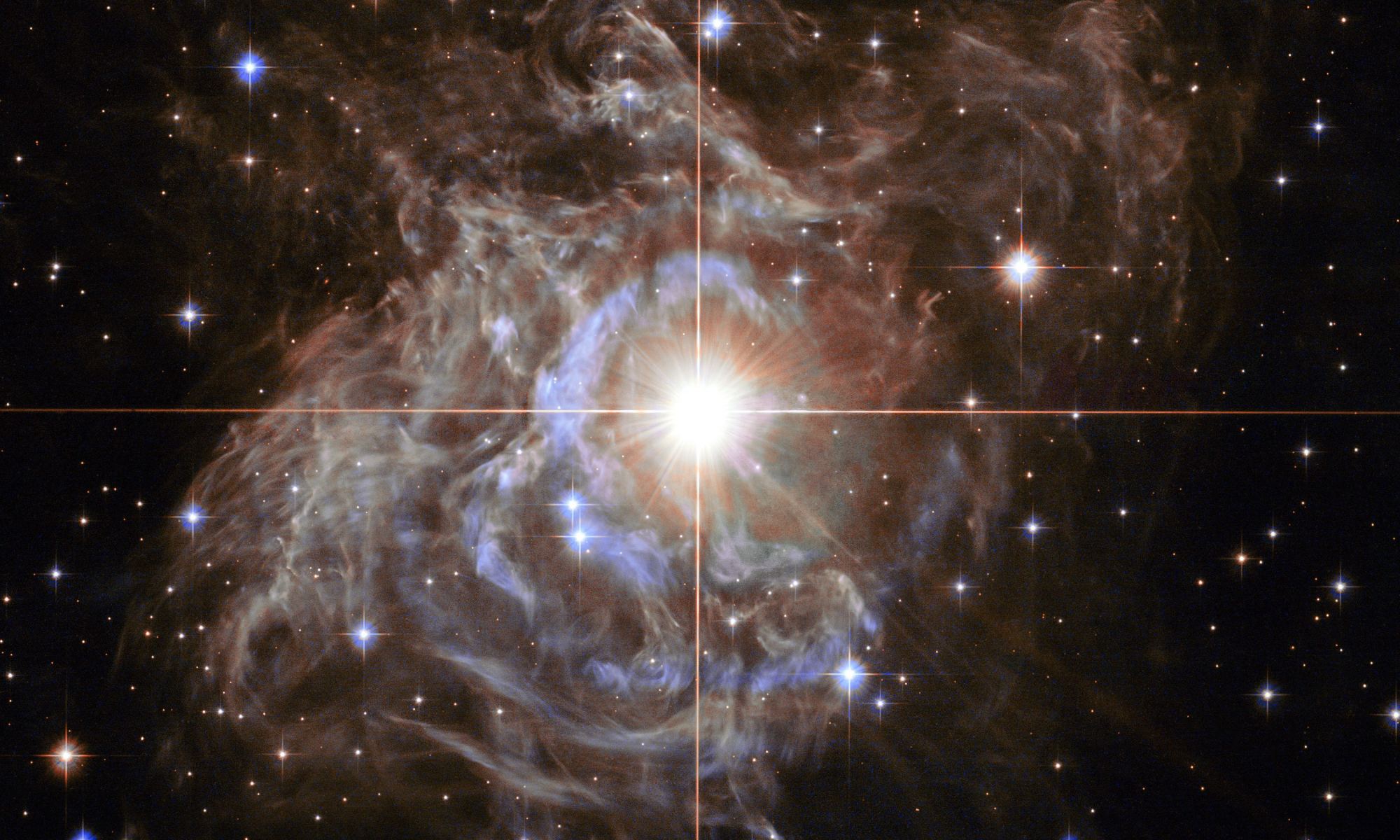
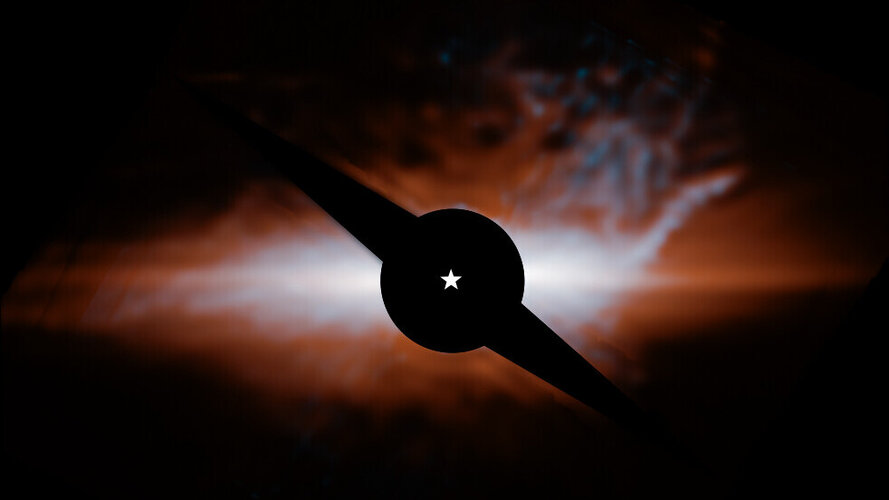
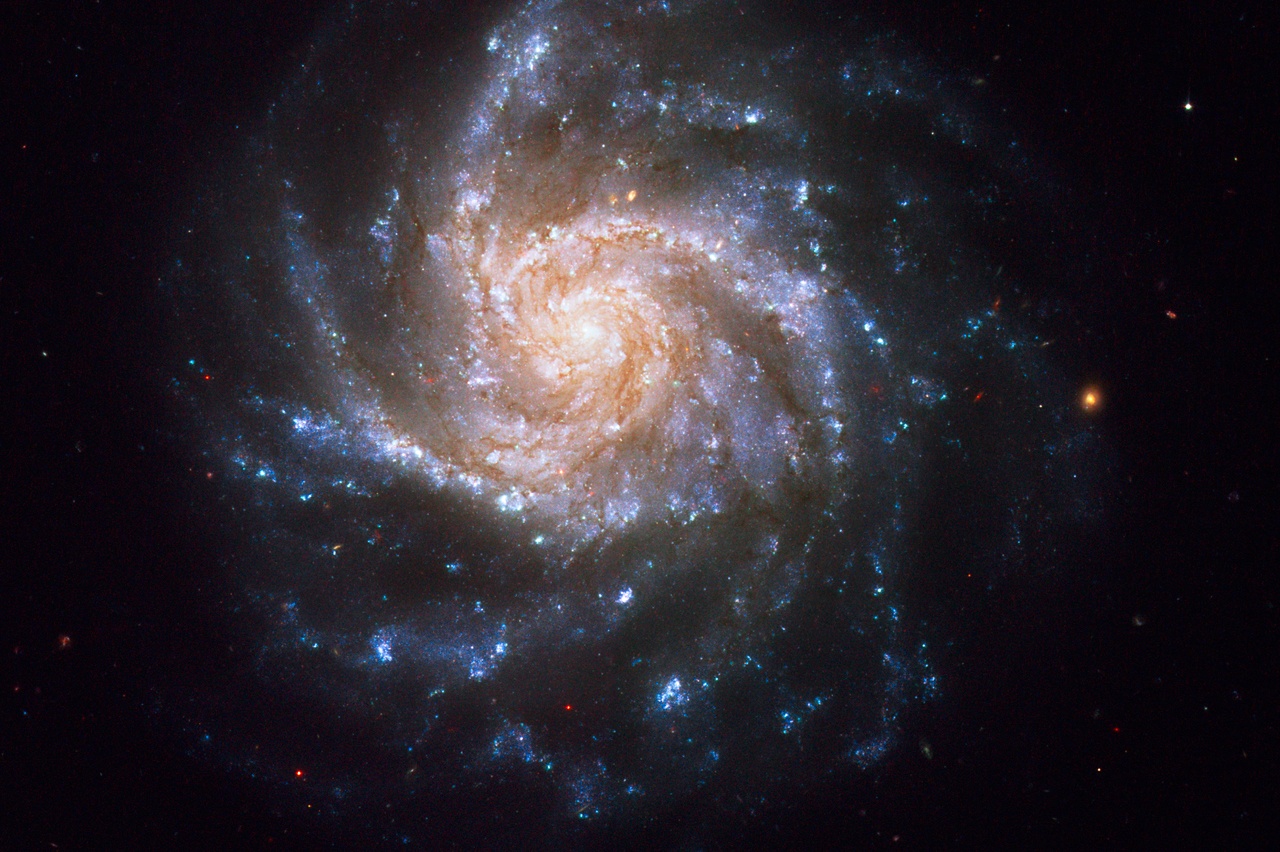
Perhaps the greatest and most frustrating mystery in cosmology is the Hubble tension problem. Put simply, all the observational evidence we have points to a Universe that began in a hot, dense state, and then expanded at an ever-increasing rate to become the Universe we see today. Every measurement of that expansion agrees with this, but where they don’t agree is on what that rate exactly is. We can measure expansion in lots of different ways, and while they are in the same general ballpark, their uncertainties are so small now that they don’t overlap. There is no value for the Hubble parameter that falls within the uncertainty of all measurements, hence the problem.
Continue reading “Astronomers Rule Out One Explanation for the Hubble Tension”Astronomers Rule Out One Explanation for the Hubble Tension