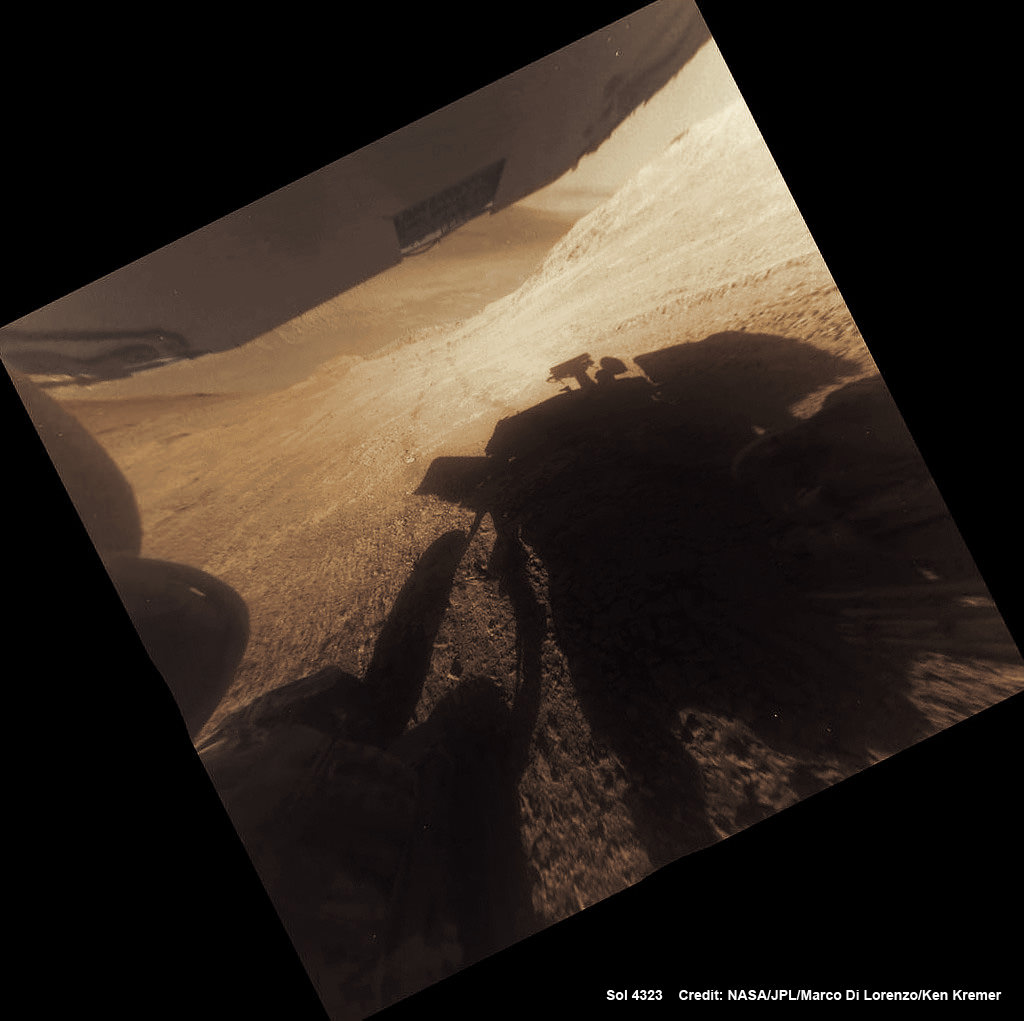
A “beautiful dust devil” was just discovered today, April 1, on the Red Planet by NASA’s long lived Opportunity rover as she is simultaneously exploring water altered rock outcrops at the steepest slopes ever targeted during her 13 year long expedition across the Martian surface. Opportunity is searching for minerals formed in ancient flows of water that will provide critical insight into establishing whether life ever existed on the fourth rock from the sun.
“Yes a beautiful dust devil on the floor of Endeavour Crater,” Ray Arvidson, Opportunity Deputy Principal Investigator of Washington University in St. Louis, confirmed to Universe Today. Spied from where “Opportunity is located on the southwest part of Knudsen Ridge” in Marathon Valley.
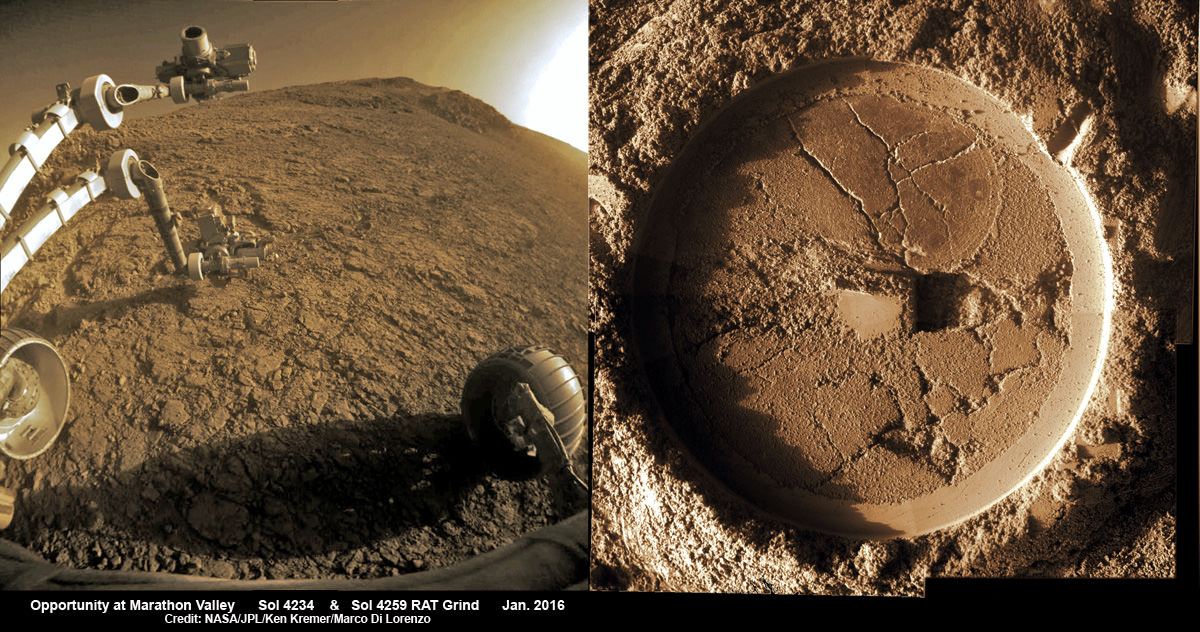
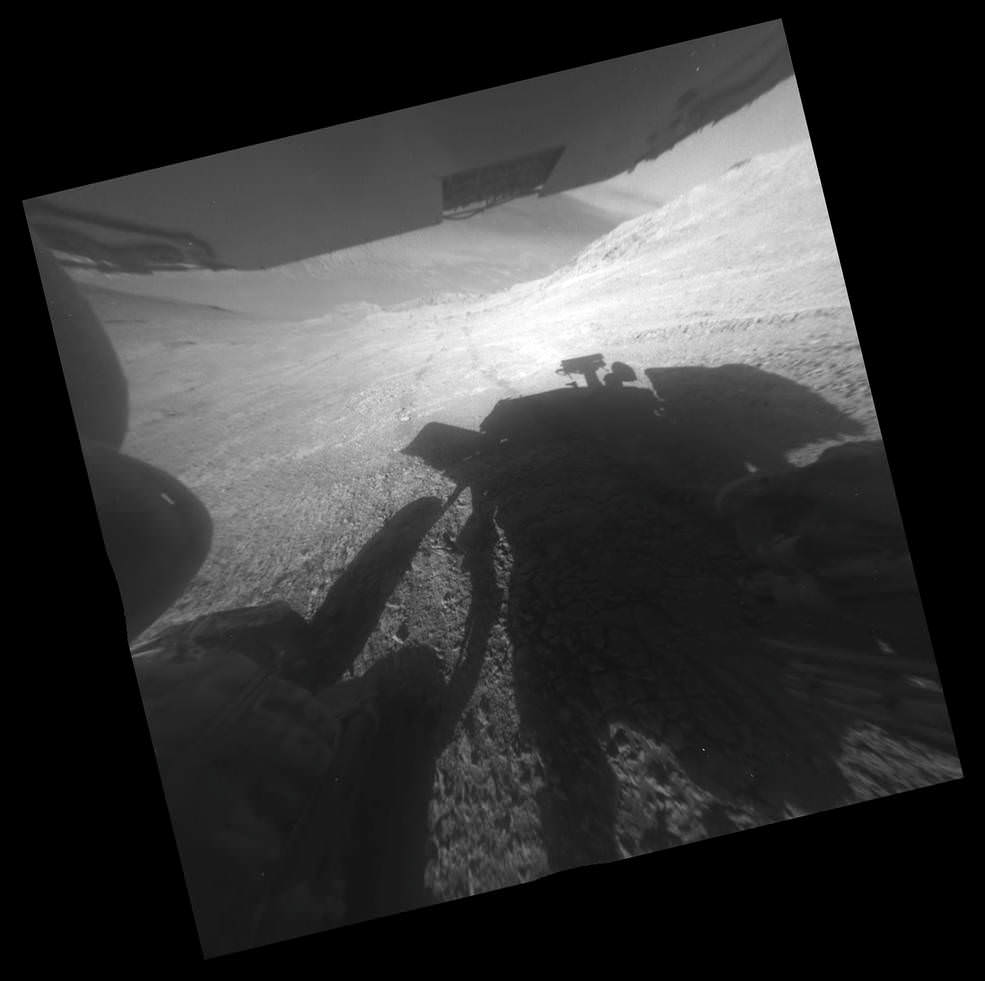
The new dust devil – a mini tornado like feature – is seen scooting across the ever fascinating Martian landscape in our new photo mosaic illustrating the steep walled terrain inside Marathon Valley and overlooking the crater floor as Opportunity makes wheel tracks at the current worksite on a crest at Knudsen Ridge. The colorized navcam camera mosaic combines raw images taken today on Sol 4332 (1 April 2016) and stitched by the imaging team of Ken Kremer and Marco Di Lorenzo.
“The dust devils have been kind to this rover,” Jim Green, Director of NASA Planetary Sciences at NASA HQ, said in an exclusive interview with Universe Today. They are associated with prior periods of solar array cleansing power boosts that contributed decisively to her longevity.
“Oppy’s best friend is on its way!”
Spotting dust devils has been relatively rare for Opportunity since landing on Mars on Jan. 24, 2004.
“There are 7 candidates, 6 of which are likely or certain,” Mark Lemmon, rover science team member from Texas A & M University, told Universe Today. “Most were seen in, on the rim of, or adjacent to Endeavour.”
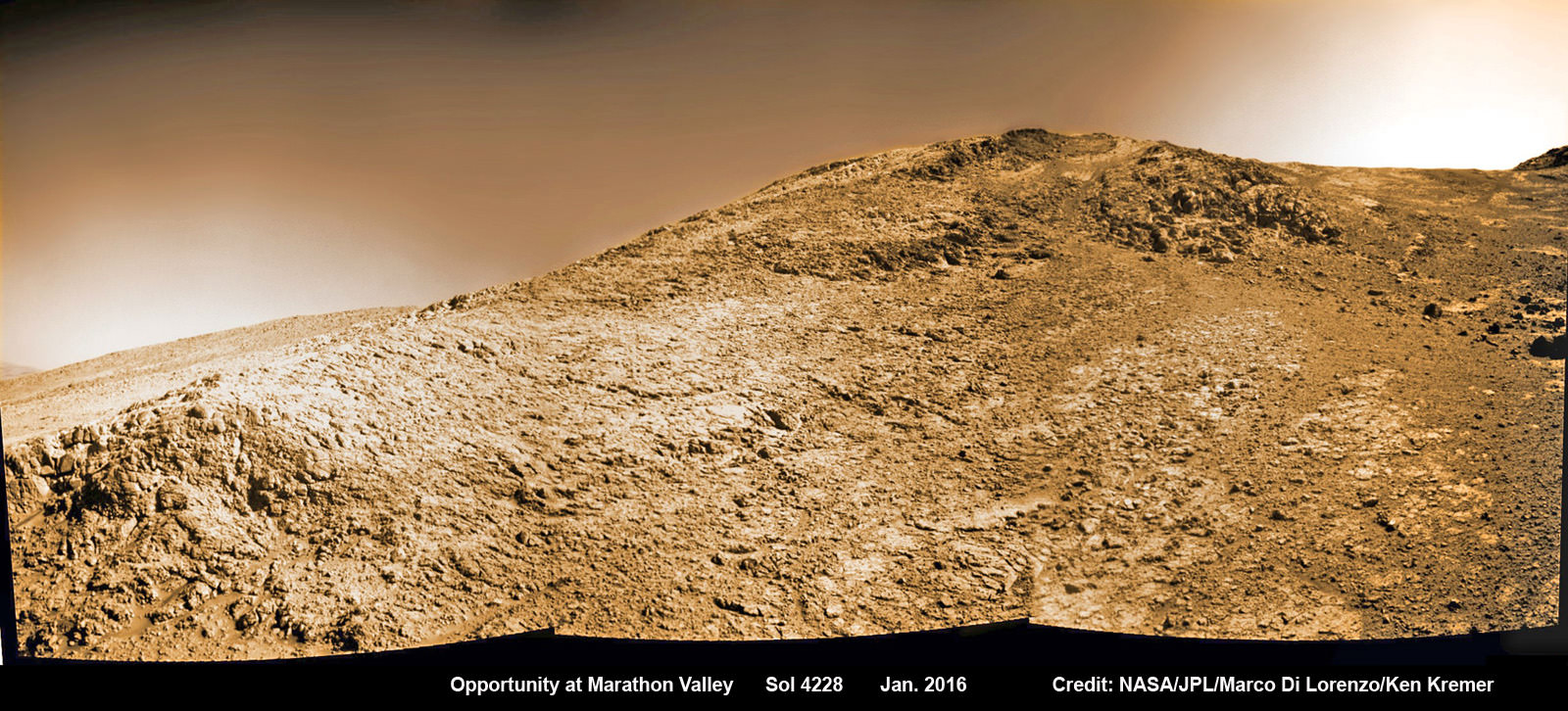
Starting in late January, scientists commanded the golf cart sized Opportunity to drive up the steepest slopes ever attempted by any Mars rover in order to reach rock outcrops where she can conduct breakthrough science investigations on smectite (phyllosilicate) clay mineral bearing rocks yielding clues to Mars watery past.
“We are beginning an imaging and contact science campaign in an area where CRISM spectra show evidence for deep absorptions associated with Fe [Iron], Mg [Magnesium] smectites,” Arvidson explained.

This is especially exciting to researchers because the phyllosilicate clay mineral rocks formed under water wet, non-acidic conditions that are more conducive to the formation of Martian life forms – billions of years ago when the planet was far warmer and wetter.
“We have been in the smectite [phyllosilicate clay mineral] zone for months, ever since we entered Marathon Valley.”
The smectites were discovered via extensive, specially targeted Mars orbital measurements gathered by the CRISM (Compact Reconnaissance Imaging Spectrometer for Mars) spectrometer on NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) – accomplished earlier at the direction of Arvidson.
So the ancient, weathered slopes around Marathon Valley became a top priority science destination after they were found to hold a motherlode of ‘smectite’ clay minerals based on the CRISM data.
“Marathon Valley is unlike anything we have ever seen. Looks like a mining zone!”
At this moment, the rover is driving to an alternative rock outcrop located on the southwest area of the Knudsen Ridge hilltops after trying three times to get within reach of the clay minerals by extending her instrument laden robotic arm.

Unfortunately, but not unexpectedly, the rover kept slipping on the steep walled slopes – tilted as much as 32 degrees – while repeatedly attempting close approaches to the intended target. Ultimately she came within 3 inches of the surface science target ‘Pvt. Joseph Whitehouse’ – named after a member of the Corps of Discovery.
In fact despite rotating her wheels enough to push uphill about 66 feet (20 meters) if there had been no slippage, engineers discerned from telemetry that slippage was so great that “the vehicle progressed only about 3.5 inches (9 centimeters). This was the third attempt to reach the target and came up a few inches short,” said NASA.
“The rover team reached a tough decision to skip that target and move on.”
So they backed Opportunity downhill about 27 feet (8.2 meters), then drove about 200 feet (about 60 meters) generally southwestward and uphill, toward the next target area.
NASA officials noted that “the previous record for the steepest slope ever driven by any Mars rover was accomplished while Opportunity was approaching “Burns Cliff” about nine months after the mission’s January 2004 landing on Mars.”
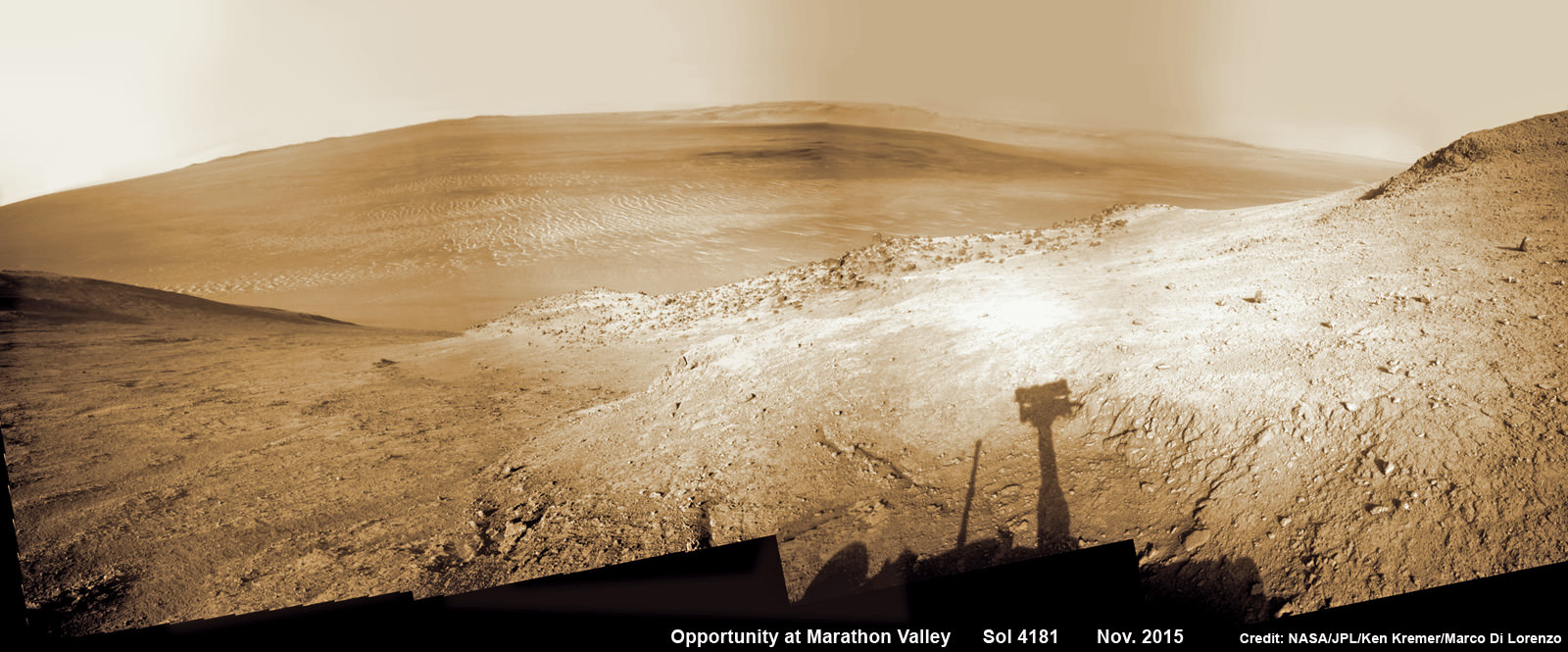
Marathon Valley measures about 300 yards or meters long. It cuts downhill through the west rim of Endeavour crater from west to east – the same direction in which Opportunity is currently driving downhill from a mountain summit area atop the crater rim. See our route map below showing the context of the rovers over dozen year long traverse spanning more than the 26 mile distance of a Marathon runners race.
Endeavour crater spans some 22 kilometers (14 miles) in diameter. Opportunity has been exploring Endeavour since arriving at the humongous crater in 2011.

Why are the dust devils a big deal?
Offering more than just a pretty view, the dust devils actually have been associated with springtime Martian winds that clear away the dust obscuring the robots life giving solar panels.
“Opportunity is largely in winter mode sitting on a hill side getting maximum power. But it is in a better power status than in many past winters,” Jim Green, Director of NASA Planetary Sciences at NASA HQ, told Universe Today exclusively.
“I think I know the reason. As one looks across the vistas of Mars in this mosaic Oppys best friend is on its way.”
“The dust devils have been kind to this rover. Even I have a smile on my face when I see what’s coming.”
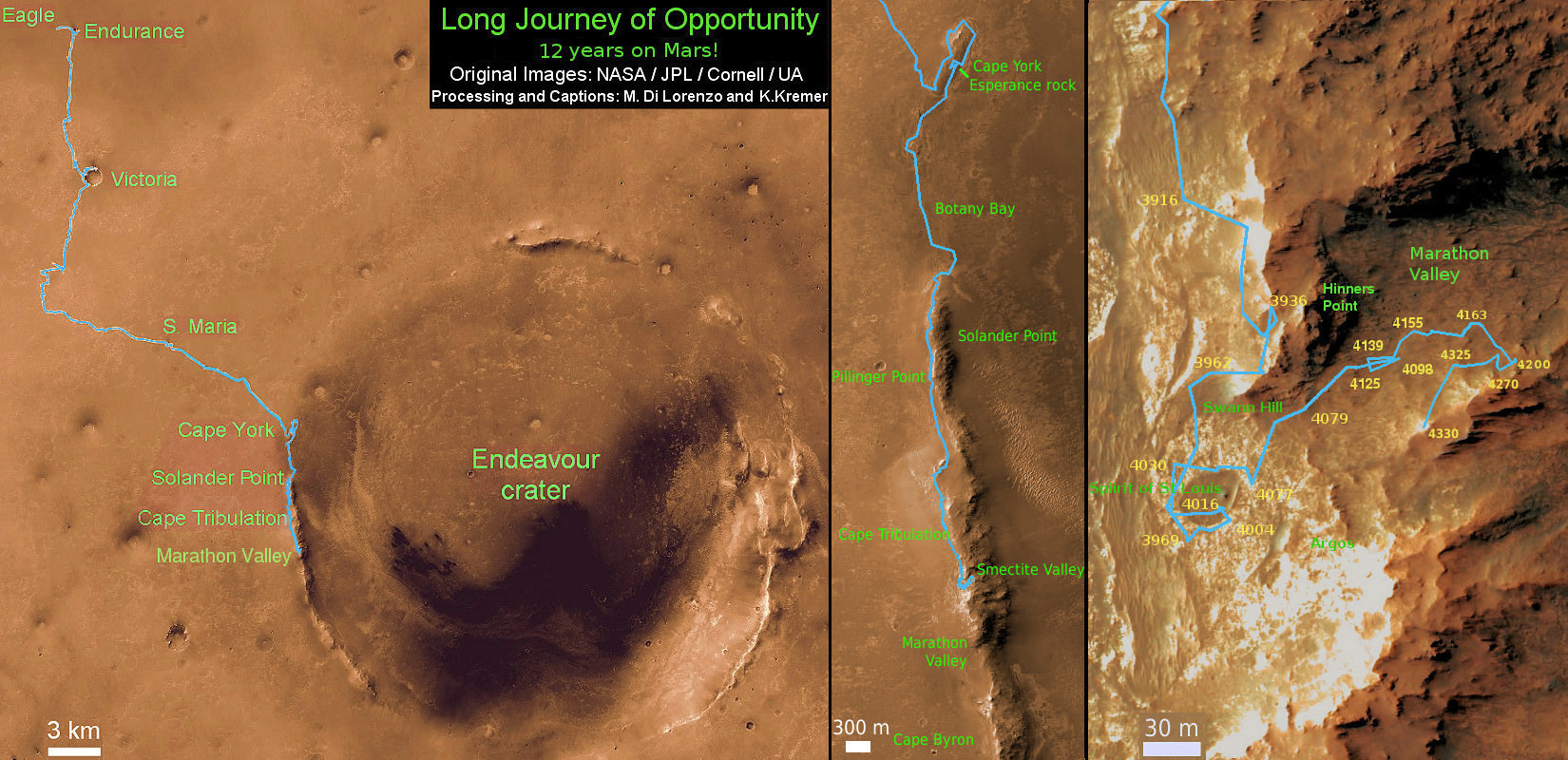
As of today, Sol 4332, Apr. 1, 2016, Opportunity has taken over 209,200 images and traversed over 26.53 miles (42.69 kilometers) – more than a marathon.
The power output from solar array energy production has climbed to 576 watt-hours, now just past the depths of southern hemisphere Martian winter.
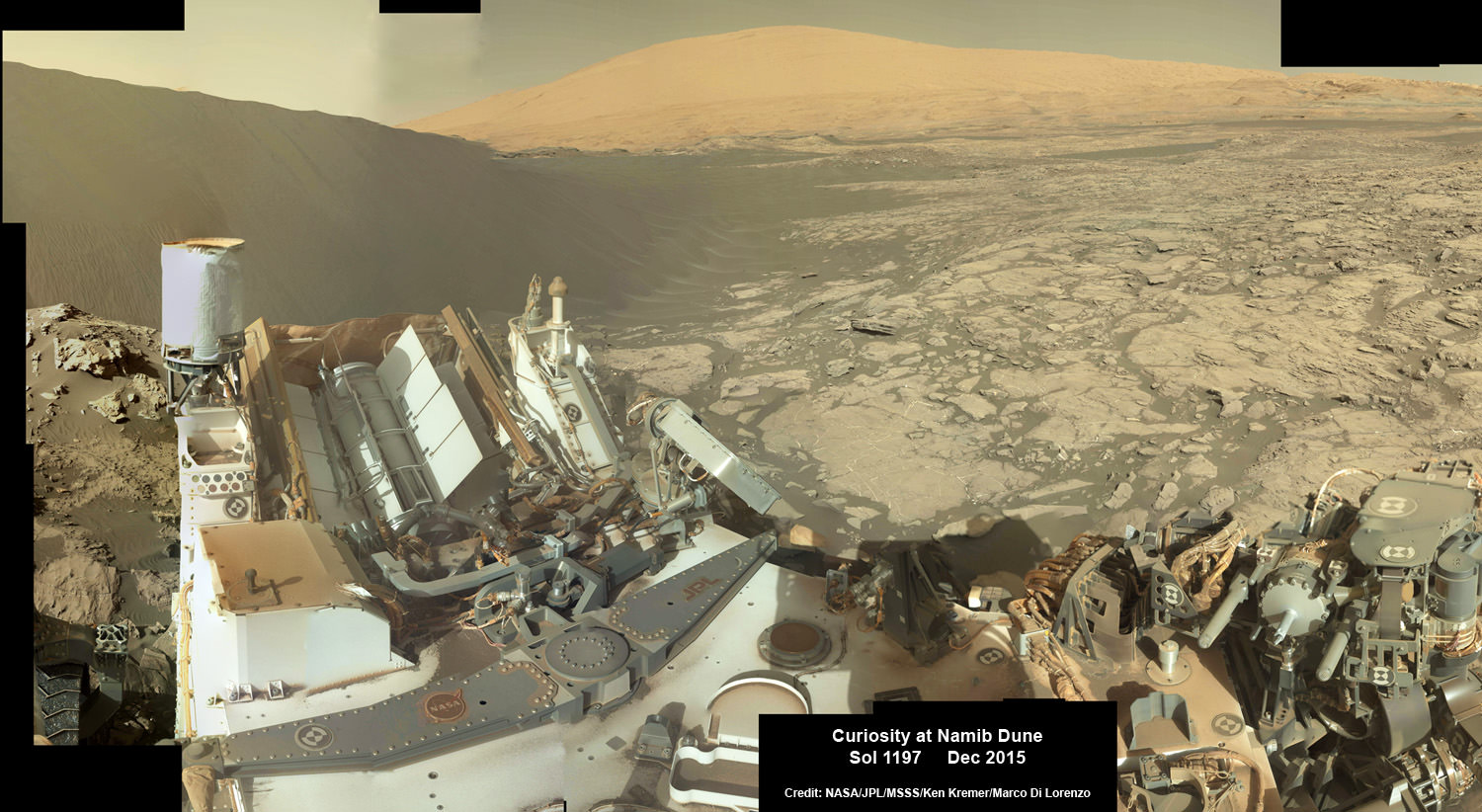
Meanwhile Opportunity’s younger sister rover Curiosity traverses and drills into the basal layers at the base of Mount Sharp.

Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and planetary science and human spaceflight news.
………….
Learn more about NASA Mars rovers, Orion, SLS, ISS, Orbital ATK, ULA, SpaceX, Boeing, Space Taxis, NASA missions and more at Ken’s upcoming outreach events:
Apr 9/10: “NASA and the Road to Mars Human Spaceflight programs” and “Curiosity explores Mars” at NEAF (NorthEast Astronomy and Space Forum), 9 AM to 5 PM, Suffern, NY, Rockland Community College and Rockland Astronomy Club – http://rocklandastronomy.com/neaf.html
Apr 12: Hosting Dr. Jim Green, NASA, Director Planetary Science, for a Planetary sciences talk about “Ceres, Pluto and Planet X” at Princeton University; 7:30 PM, Amateur Astronomers Assoc of Princeton, Peyton Hall, Princeton, NJ – http://www.princetonastronomy.org/
Apr 17: “NASA and the Road to Mars Human Spaceflight programs”- 1:30 PM at Washington Crossing State Park, Nature Center, Titusville, NJ – http://www.state.nj.us/dep/parksandforests/parks/washcros.html