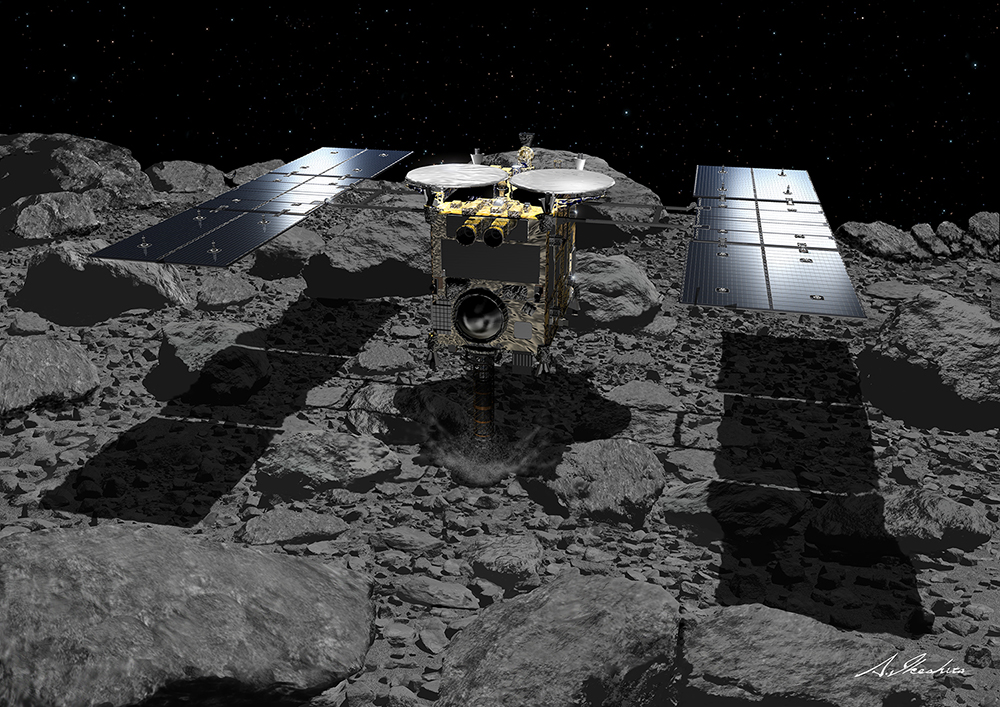
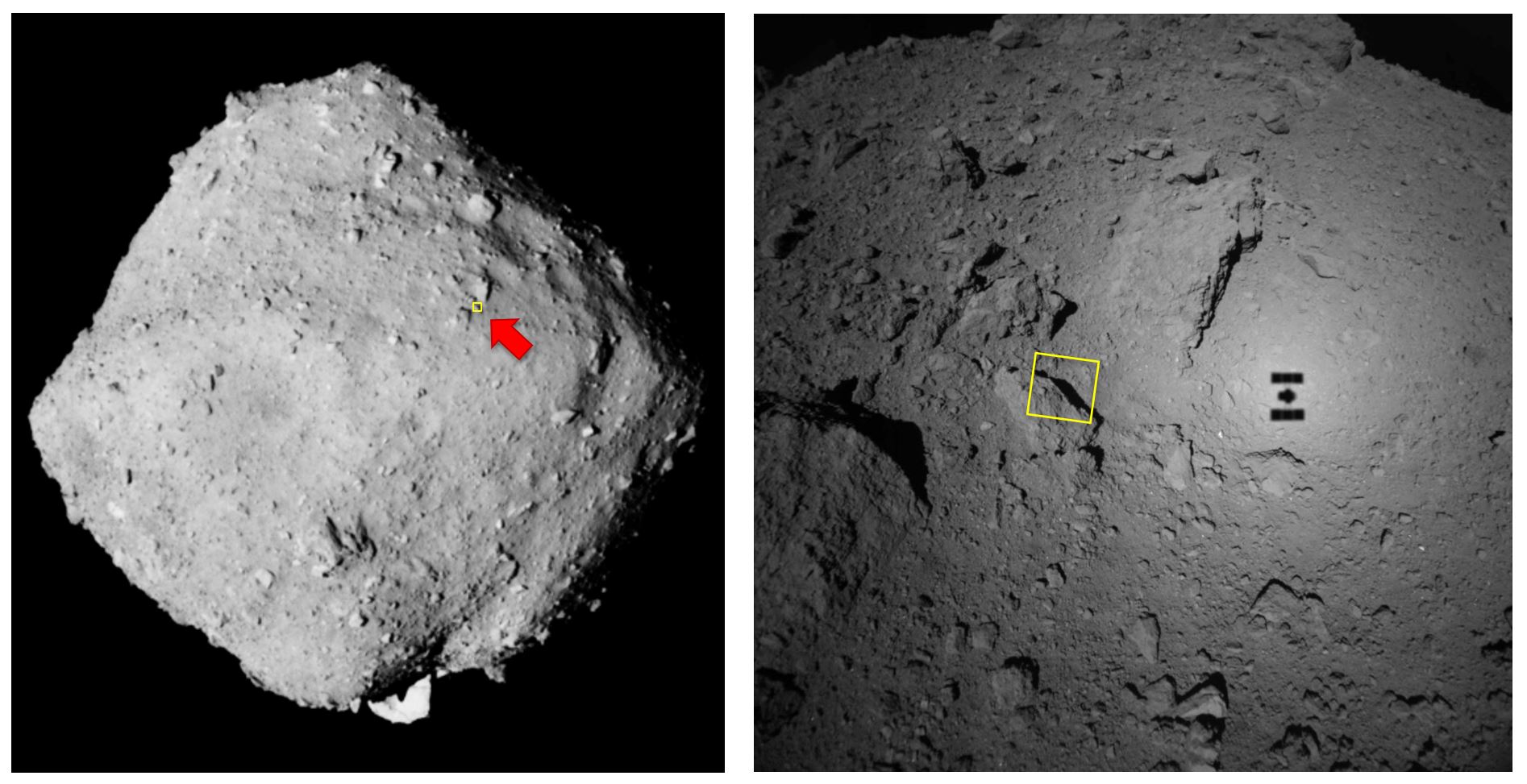
In 2014, the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) dispatched its Hayabusa2 spacecraft to rendezvous with 162173 Ryugu, a Near-Earth Asteroid (NEA) that periodically passes close to Earth. In 2018, this sample-return mission reached Ryugu and spent the next year and a half studying its surface and obtaining samples from its surface and subsurface. By 2020, these samples made it back to Earth, where scientists began analyzing them in the hopes of learning more about the early history of the Solar System and answering key questions about the origins of life.
Earlier this year, the first results of the analysis showed that Ryugu is (as expected) rich in carbon, organic molecules, and volatiles (like water) and hinted at the possibility that it was once a comet. Based on a more recent analysis, eight teams of Japanese researchers (including one from JAXA) recently announced that Ryugu carries strains of no less than 20 different amino acids -the building blocks of DNA and life itself! These findings could provide new insight into how life is distributed throughout the cosmos and could mean that it is more common than previously thought.
Continue reading “Samples of Asteroid Ryugu Contain More Than 20 Amino Acids”