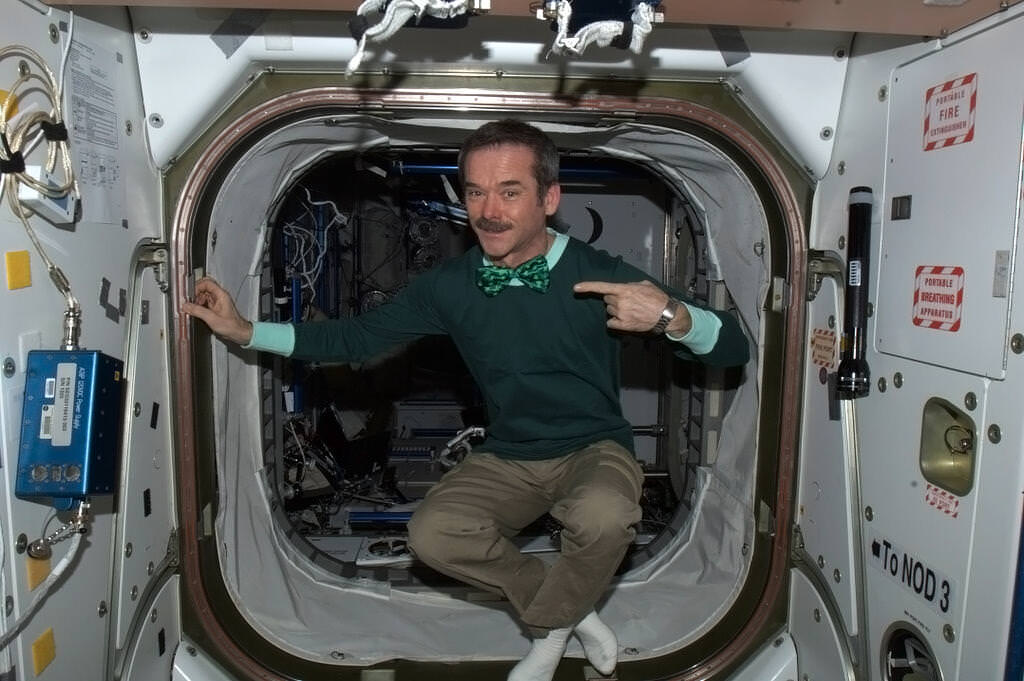
No tears in heaven? Expedition 35 Commander Chris Hadfield shows that while you really can cry in space, tears don’t fall like they do here on Earth, and instead just end up as a big ball of water on your face. It’s physics, baby!
Happy Easter Sunday from the ISS ! Crew Hunts Easter Eggs & Goodies

ISS Commander Chris Hadfield plans surprise Easter egg hunt for station crew today – Easter Sunday, March 31, 2013. Credit: NASA/Chris Hadfield
Updated with more astounding ‘Easter from Space’ photos by Chris Hadfield !
Dont miss the scrumptious ‘Easter Finale’ – below
Thank you Chris ![/caption]
Hush, hush !
Don’t’ tell his crew, but Canadian astronaut Chris Hadfield has secretly planned a delightful space station surprise sure to also warm the hearts of Earth’s children celebrating the joyous occasion of this Easter Sunday – and there’s delicious photos below too.
They’re going on an Easter egg hunt !
“Don’t tell my crew, but I brought them Easter Eggs :)”, tweeted Hadfield from the ISS – where he currently serves as Commander of the Expedition 35 crew.
And Hadfield sends his greetings and ‘Easter from Space’ photos to all of us down here on the good Earth on this Holy Day.
“Good Morning, Earth! A fine Easter Sunday morning to you, from the crew of the International Space Station.”
You can follow along with Hadfield’s adventures from space as – @Cmdr_Hadfield

Occasionally, Mission Control relents and lets the astronauts have fun, taking a break from their out of this world chores.
But given the weightless of space, it’s not obvious how they’ll accomplish the traditional Easter egg roll. Perhaps we’ll hear about that later.
And there’s no word back yet on Easter Bunny sightings.
Well, to get ready Hadfield has been busy stashing assorted Easter goodies & gifts in the gazillion nooks and crannies aboard the ISS – and snapping fun photos for all the kids to play along.
“Sometimes the best place to hide an item is floating right above your nose. Or in this case, your sleep pod.”
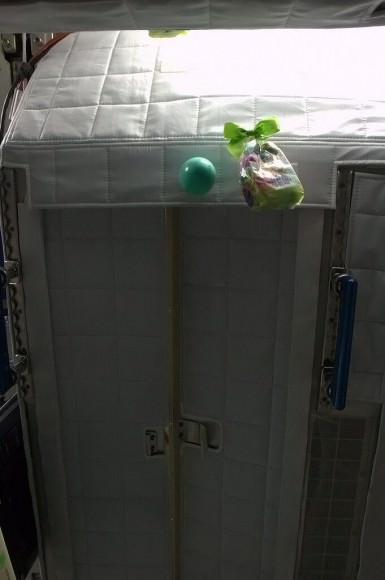
Hadfield just couldn’t resist the temptation of some weightless juggling – and he’s not telling if they went .. splat !!
“It appears that I’m as bad at juggling in weightlessness as I am on Earth. Hopefully I’m better at hiding them… ”

Time will tell whether the crew of six guys are indeed clever enough to figure out all the secret hiding spots.
The Easter egg hunt could be especially trying for the three ‘new guys’ who just arrived on Thursday, March 28, on the Russian Soyuz express capsule – comprising of Russian cosmonauts Pavel Vinogradov and Alexander Misurkin and NASA astronaut Chris Cassidy. They join Hadfield, astronaut Tom Marshburn and cosmonaut Roman Romanenko who will stay aboard the station until May.
In the meantime, Hadfield is playfully diverting everyone’s concentration with gorgeous shots of Earth, like the Easter sunrise glinting across North America’s heartland – below.

And the Canadian Space Agency has now passed along an Easter greeting card.
Astronaut and cosmonaut crews have a decade’s long tradition of celebrating religious holidays in space. Probably the most famous occasion was when the three man American crew of Apollo 8 read scriptures from Genesis marking the first time in history that humans were orbiting the Moon – back in 1968.
All in all it’s been a busy week aboard the massive orbiting lab complex.
On Tuesday, March 26, the SpaceX Dragon capsule departed the station, loaded with a long awaited trove of science goodies and successfully splashed down in the ocean. Two days later the trio of new space men arriving aboard the Soyuz restored the ISS to its full crew complement of six.
Since arriving at the station just before Christmas 2012, Hadfield has been doing a stellar job enlightening folks about what it’s like to live and work in space in fun and understandable ways.
Happy Easter !

…………….
Learn more about the ISS, Curiosity, SpaceX, Antares, and NASA missions at Ken’s upcoming lecture presentations:
April 20/21 : “Curiosity and the Search for Life on Mars – (in 3-D)”. Plus Orion, SpaceX, Antares, ISS, the Space Shuttle and more! NEAF Astronomy Forum, Suffern, NY
April 28: “Curiosity and the Search for Life on Mars – (in 3-D)”. Plus the Space Shuttle, SpaceX, Antares, Orion and more. Washington Crossing State Park, Titusville, NJ, 130 PM
Chris Hadfield’s Top 5 Videos from Space
Chris Hadfield — the ever-tweeting, always charming Canadian running the space station these days — has had an eventful few months in space. If he’s not chatting with Captain Kirk, he’s playing guitar or, as it turns out, making very watchable videos.
Being on television requires a certain flair. You need to talk in sound bites, cultivate a charismatic presence, and keep the action moving enough so people don’t flip the channel. For an astronaut, who usually works methodically, carefully and slowly, working on television must be fully alien (pun intended) to how one does the technical parts of the job.
But Hadfield — who knows how to study a situation and make the most of it — has created videos with hundreds of thousands of views on YouTube. Whatever he’s doing is working.
Universe Today checked up on Hadfield’s secrets to success by watching the most popular videos in a playlist curated by the Canadian Space Agency. Here are the top five. Strangely, the last one doesn’t even include Hadfield’s face or voice.
5) Chris Hadfield Talks with the Queen’s Representative in Canada
If you’re all about cute questions from kids, or enjoy a brush with royalty, this lengthy press conference with Hadfield is very interesting. This is a bit of a marathon charm session on Hadfield’s part, but he pulls it off with his charismatic aplomb. One of the best answers demonstrates what he’s learned about weightless life: “I can fly. I can go in different directions,” Hadfield says enthusiastically, spinning before the camera.
4) Chris Hadfield Demonstrates How Astronauts Wash Their Hands in Zero G
For a question that came out of a routine Q&A with kids, Hadfield’s performance is pretty good. He demonstrates that soapy water looks like some sort of Teenage Mutant Ninja Turtles-like ooze in space, and compares life on the space station to life on a sailboat, all while simply washing his hands. It’s almost existential.
3) Nail Clipping in Space
It turns out that Hadfield chooses to cut his nails because long ones interfere with his guitar playing. We wouldn’t want that to happen (and neither would the Barenaked Ladies), so fortunately Hadfield gets right on the problem, positions himself over an air vent and trims them with an ordinary nail clipper. Charmingly, this was not fully scripted, as he makes a mistake with the first clipping.
2) Chris Hadfield’s Space Kitchen (aka how to make a peanut butter sandwich in space)
With words you’d never hear on Martha Stewart — “We’ve got one tortilla. Oh, got away!” — Hadfield slathers condiments on to a tortilla and eats it. His sense of humor helps break up a very routine act; we’d be scared to be one of his kids after seeing the stern way in which he says, “Disinfectant wipe!”
1) Mixed Nuts in Space
This video is oddly mesmerizing, and that’s not just because of the UFO-type music near the beginning. It’s quite a simple setup: Hadfield shoots a bunch of nuts floating around inside of a can. But face it, it looks awfully weird for those of us used to grabbing similar packages off the kitchen shelf. Maybe that’s why this video has more than 4 million views.
Former Navy SEAL Survived ‘Hell Week’ En Route to Space

If a meteor hit the station, or a fire suddenly broke out, you’d want some pretty quick-thinking people on board to solve the problem. Thankfully, Chris Cassidy — a former Navy SEAL — is on his way to station in just a couple of weeks as a part of Expedition 35/36.
SEAL training is perhaps the most vigorous military program in the world. Even a quick look at the tests candidates must pass makes us feel exhausted. You need to master a suite of skills that range from demolition to navigation to, of course, fast swimming. There’s something called “combat diving”, which is supposed to test how well these Navy people “perform in stressful and often uncomfortable environments.”
And don’t forget “hell week.” Candidates only get to sleep four hours in 5.5 days. They rack up 200 miles of running through physically training for 20 hours a day. (No, those numbers are not typos. It’s real.)
Cassidy — who by the way, passed that gruelling SEAL training on the first try without getting hurt or going crazy — told Universe Today last week about what he would do should he be faced with an emergency in space.
I think just the training that I got in the field, training in the early part of my Navy career, and during my time being an astronaut will all combine together. What I know from combat in the Navy, there’s a sort of calmness that comes over people who are well-trained and know what to do. Muscle memory kicks in, and it’s not until after the thing is over that you realize what you went through.
I kind of think that’s how me as an individual, and we as a crew, will respond to any dicey dynamic event like that. Just work through the procedures that we’ve been trained, make the place safe if we can, and if we can’t, we are trained to evacuate. And the procedures all get us to that point.
Cassidy further joked that some of the humor SEALs use might not be appropriate in his most recent job title; former SEAL and International Space Station Expedition 1 commander William Shepherd once told Cassidy he might be “kicked out of a NASA meeting” if he used some of the language.
More seriously, though, Cassidy said he is particularly looking forward to doing experiments measuring bone mass on the International Space Station. Since that research has applications for people on Earth (particularly those facing osteoporosis he said it’s a demonstration of how spaceflight can help further health work on the ground.
His ultimate goal? “To be called back [to station] a second time.” Let’s hope he makes it.
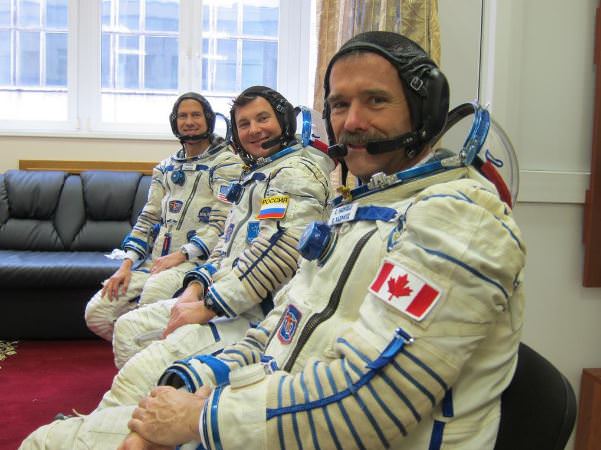
Cassidy and his crewmates Pavel Vinogradov and Alexander Misurkin are scheduled to launch from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan on March 29. Here a look at some of the final training the crew received at the Gagarin Cosmonaut Training Center in Star City, Russia:
Video: Dragon Grappled and Berthed at Space Station
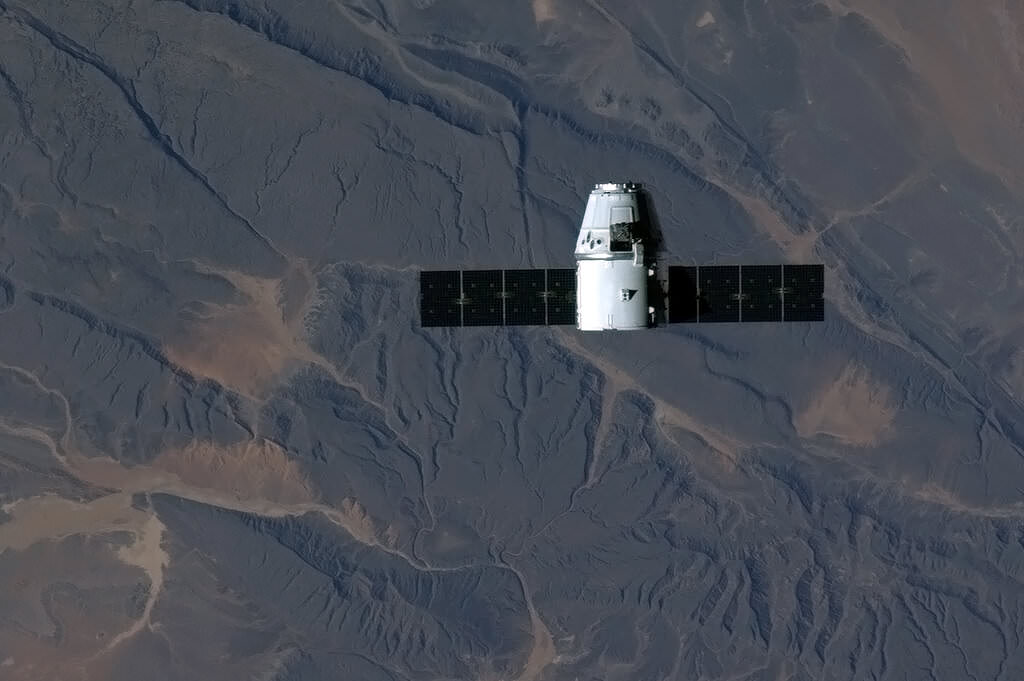
SpaceX’s Dragon spacecraft has arrived at the International Space Station! After overcoming a problem with its thrusters after reaching orbit on on Friday, today, Dragon successfully approached the Station, where it was captured by Expedition 34 Commander Kevin Ford and crewmate Tom Marshburn using the station’s Canadarm2 robotic arm. Dragon was grappled at 5:31 a.m. EST, and was berthed to the Earth-facing port of the Harmony module at approximately 8:56 a.m. EST on March 3.
Below, Canadian astronaut Chris Hadfield snapped a photo of Dragon as it approached the station over sub-Saharan Africa. “A surreal juxtaposition,” Hadfied said via Twitter.
SpaceX Dragon Recovers from Frightening Propulsion System Failure – Sunday Docking Set
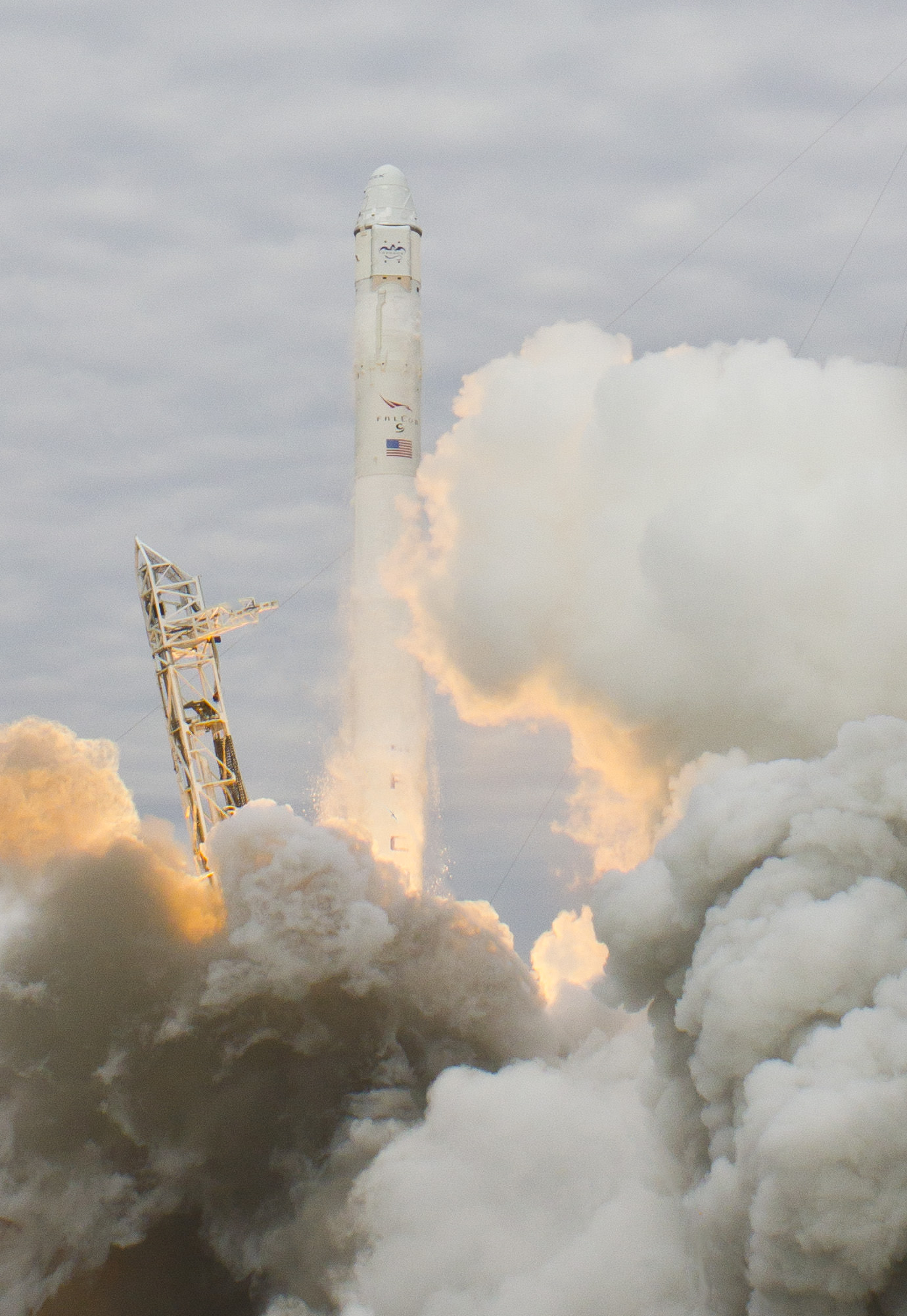

Kennedy Space Center – Barely 11 minutes after the spectacular Friday morning, March 1 launch of the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket and unmanned Dragon capsule bound for the International Space Station (ISS), absolute glee suddenly threatened to turn to total gloom when the mission suffered an unexpected failure in the critical propulsion system required to propel the Dragon to the Earth orbiting outpost.
An alarming issue with the Dragons thrust pods prevented three out of four from initializing and firing.
For several hours the outlook for the $133 million mission appeared dire, but gradually began to improve a few hours after launch.
“It was a little frightening,” said SpaceX CEO Elon Musk at a Friday afternoon media briefing for reporters gathered at the Kennedy Space Center, commenting on the moments after the glitch appeared out of nowhere.
“We noticed after separation that only one of the four thruster pods engaged or was ready to engage,” Musk explained. “And then we saw that the oxidizer pressure in three of the four tanks was low.”

The situation progressed onto the road to recovery after SpaceX engineers immediately sprang into action and frantically worked to troubleshoot the thruster problems in an urgent bid to try and bring the crucial propulsion systems back on line and revive the mission.
By late Saturday afternoon sufficient recovery work had been accomplished to warrant NASA, ISS and SpaceX managers to give the go-ahead for the Dragon to rendezvous with the station early Sunday morning, March 3.
“The station’s Mission Management Team unanimously agreed that Dragon’s propulsion system is operating normally along with its other systems and ready to support the rendezvous two days after Friday’s launch on a Falcon 9 rocket from the Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida,” NASA announced in a statement on Saturday, March 2.
A failure to ignite the thrusters within 1 or 2 days would have resulted in unacceptable orbital decay and a quick and unplanned fiery reentry into the earth’s atmosphere, said Musk.
Reentry would cause a total loss of the mission – carrying more than a ton of vital supplies, science gear, research experiments, spare parts, food, water and provisions to orbit for the stations six man crew.
Shortly after the Dragon achieved orbit and separated from the second stage, the solar arrays failed to deploy and the live webcast stopped prematurely.
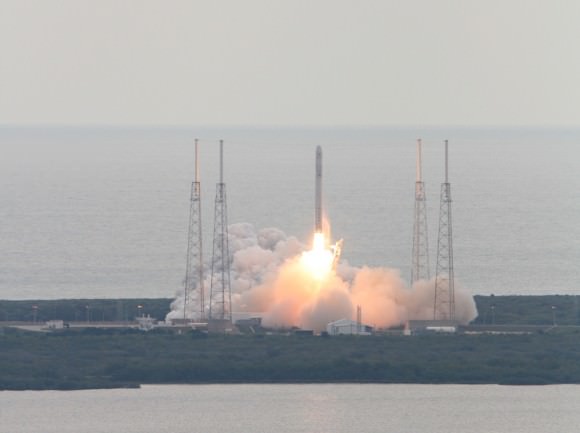

During the course of the Friday afternoon briefing, Musk and NASA officials received continuous updates indicating the situating was changing and slowly improving.
Musk confirmed that SpaceX was able to bring all four of Dragon’s thruster pods back up and running. Engineers were able to identify and correct the issue, normalizing the pressure in the oxidation tanks.
The problem may have been caused by stuck valves or frozen oxidizer in the lines. Dragon has four oxidizer tanks and four fuel tanks.
“We think there may have been a blockage of some kind or stuck check valves going from the helium pressure tank to the oxidizer tank,” Musk hypothesized. “Whatever that blockage is seems to have alleviated.”
Three of the four thruster pods must be active before the Dragon would be permitted to dock, said Mike Suffredini, NASA program manager for the ISS. There are a total of 18 Draco thrusters.
SpaceX and the ISS partners conducted a thorough review process to assure that the thrusters will work as advertised and allow the Dragon to safely enter the stations keep out zone and physically dock at the berthing port onto the Earth-facing port of the Harmony module.
“SpaceX said it has high confidence there will be no repeat of the thruster problem during rendezvous, including its capability to perform an abort, should that be required,” NASA said in a statement.
Dragon is now slated to be grappled early Sunday morning at 6:31 a.m. by NASA Expedition 34 Commander Kevin Ford and NASA Flight Engineer Tom Marshburn – that’s one day past the originally planned Saturday morning docking.
Video: Falcon 9 SpaceX CRS-2 launch on March 1, 2013 bound for the ISS – shot from the roof of the Vehicle Assembly Building. Credit: Matthew Travis/Spacearium
NASA says that despite the one-day docking delay, the Dragon unberthing and parachute assisted return to Earth will still be the same day as originally planned on March 25.
There are numerous docking opportunities available in the coming days if SpaceX and NASA determined that more time was needed to gain confidence that Dragon could safely carry out an attempt.
Musk said the Dragon could stay on orbit for several additional months if needed.
We have to review the data with NASA before docking to make sure it’s safe, Musk emphasized on Friday.

The mission dubbed CRS-2 will be only the 2nd commercial resupply mission ever to berth at the ISS. SpaceX is under contract to NASA to conduct a dozen Dragon resupply flight to the ISS over the next few years at a cost of about $1.6 Billion.
NASA TV coverage of rendezvous and grapple on Sunday, March 3 will begin at 3:30 a.m. EST. Coverage of berthing operations on NASA TV will begin at 8 a.m.
SpaceX’s live coverage at http://www.spacex.com/webcast begins at 6:00 a.m. Eastern.

NASA to BEAM Up Inflatable Space Station Module
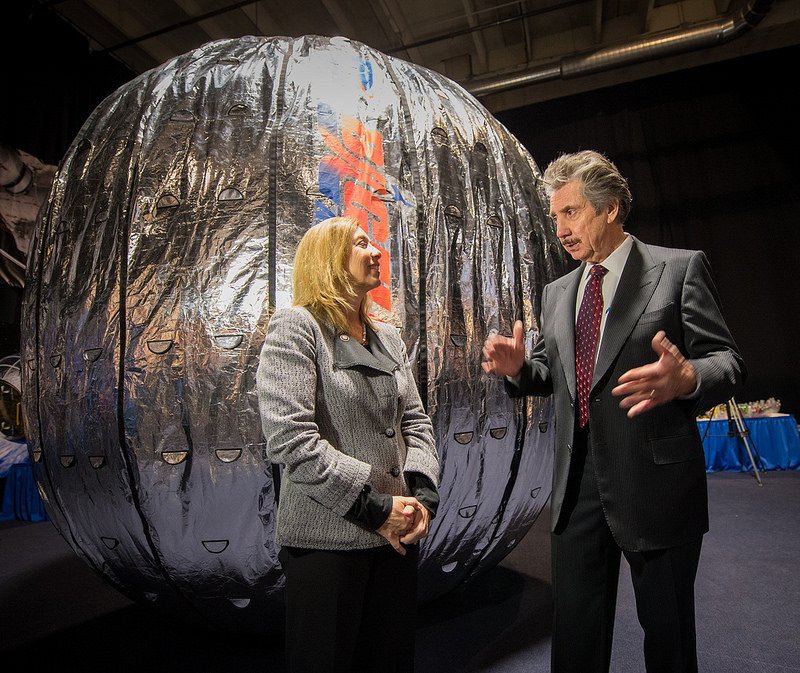

More details have emerged on NASA’s plan to add the first commercial module to the International Space Station, an inflatable room built by Bigelow Aerospace. The Bigelow Expandable Activity Module (BEAM), which is scheduled to arrive at the space station in 2015 for a two-year technology demonstration. It will be delivered by another commercial company, SpaceX, on what is planned to be the eighth cargo resupply mission too the ISS for Dragon and the Falcon 9 rocket. Astronauts will use the station’s robotic arm to install the module on the aft port of the Tranquility node. NASA Deputy Administrator Lori Garver announced Wednesday NASA has awarded a $17.8 million contract to Bigelow Aerospace for BEAM.
“Today we’re demonstrating progress on a technology that will advance important long-duration human spaceflight goals,” Garver said. “NASA’s partnership with Bigelow opens a new chapter in our continuing work to bring the innovation of industry to space, heralding cutting-edge technology that can allow humans to thrive in space safely and affordably.”
BEAM is a cylindrical module, like all other ISS modules, and is about somewhat similar in size to the US Harmony module, as BEAM is about 4 meters (13 feet) long and 3.2 meters (10.5 feet) wide; Harmony 7.2 meters (24 ft) in length, and it has a diameter of 4.4 meters (14 ft). But weight is where the two vastly differ: Harmony weighs in 14,288 kilograms (31,500 lb), while BEAM weighs roughly 1,360 kg (3,000 pounds). And that is the big advantage of inflatable structures for use in space: their mass and volume are relatively small when launched, reducing launch costs.
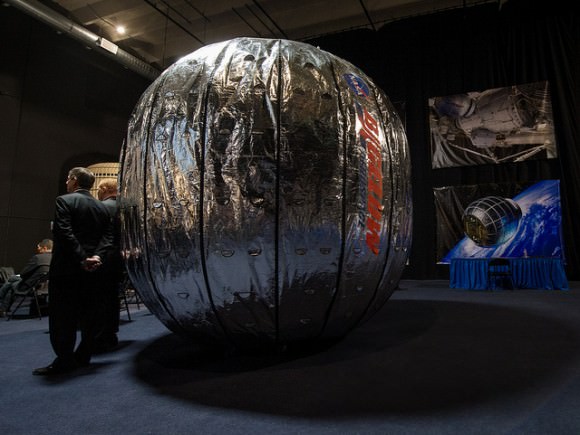

Leonard David reports on Space.com that the BEAM module should be much quieter than the other modules due to the non-metallic nature of the structure.
Read: Sounds of the Space Station
After the module is berthed to the Tranquility node, the station crew will activate a pressurization system to expand the structure to its full size using air stored within the packed module.
During the two-year test period, station crew members and ground-based engineers will gather performance data on the module, including its structural integrity and leak rate. An assortment of instruments embedded within module also will provide important insights on its response to the space environment. This includes radiation and temperature changes compared with traditional aluminum modules.
BEAM will also be assessed for future habitats for long-duration space missions, said Bill Gerstenmaier, associate administrator for human exploration and operations at NASA.
Watch how the BEAM module will be attached and inflated:
Astronauts periodically will enter the module to gather performance data and perform inspections. Following the test period, the module will be jettisoned from the station, and will burn up on re-entry.
Bigelow Aerospace says the BEAM 330 module can function as an independent space station, or several of the inflatable habitats can be connected together in a modular fashion to create an even larger and more capable orbital space complex.
Bigelow also lists their radiation shielding as equivalent to or better than the other modules on the International Space Station and substantially reduces the dangerous impact of secondary radiation, while their innovative Micrometeorite and Orbital Debris Shield “provides protection superior to that of the traditional ‘aluminum can’ designs, according to the Bigelow Aerospace website.

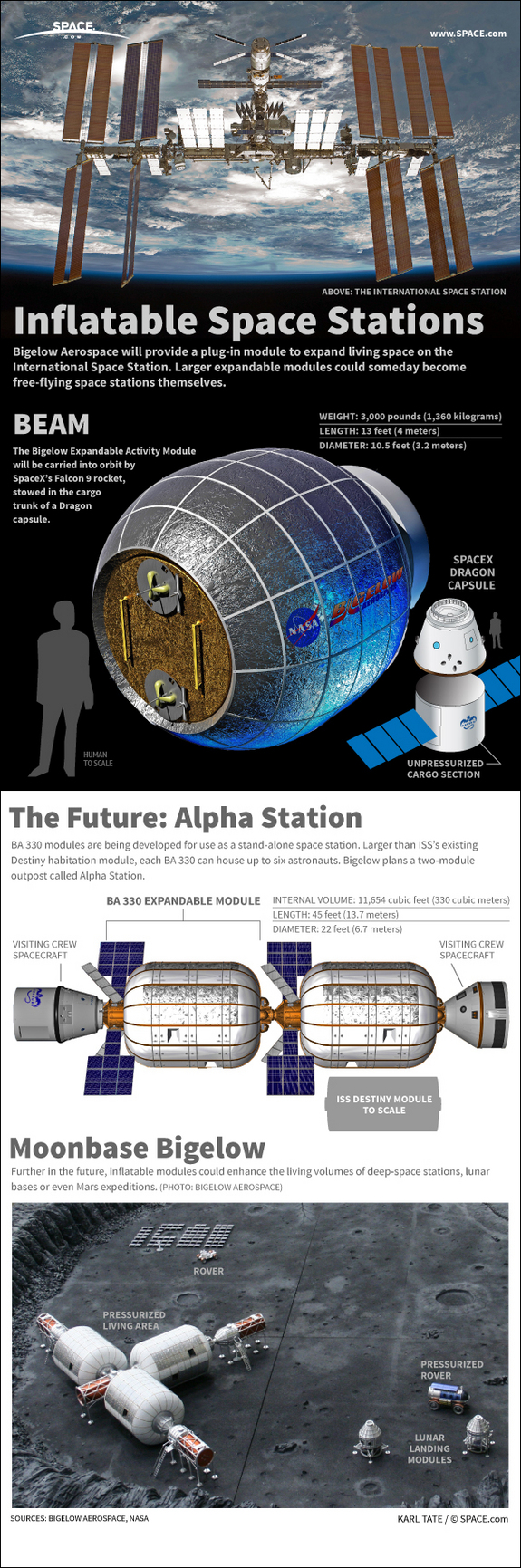
Source SPACE.com.
Space Station Gets a New Telescope
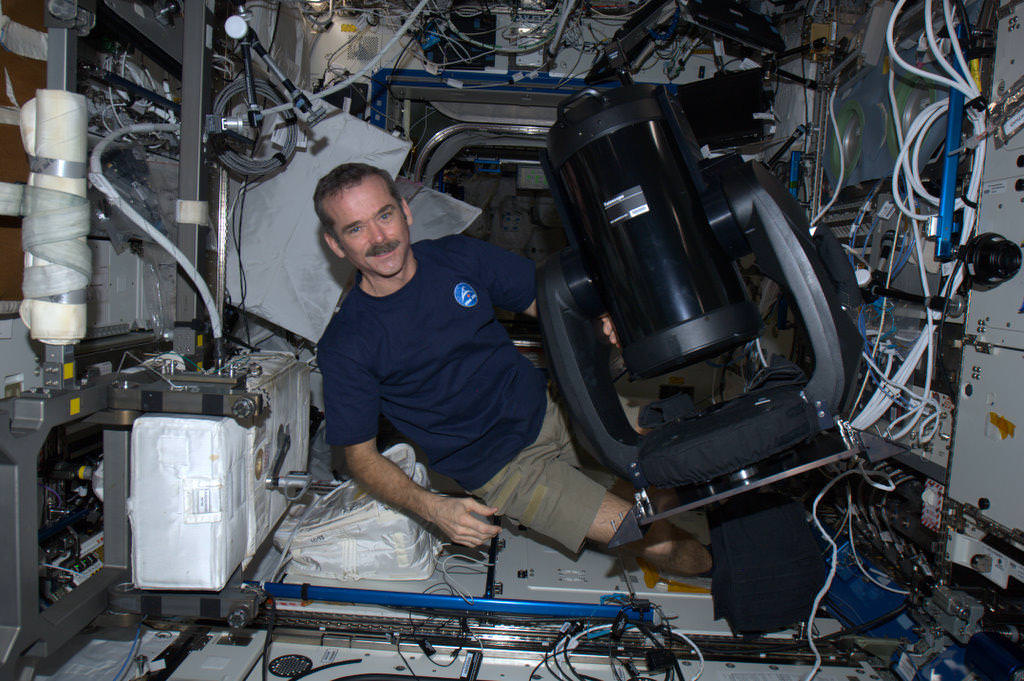

Astronauts on the International Space Station today are installing a new modified Celestron telescope. This won’t be used to observe the stars, but instead look back to Earth to acquire imagery of specific areas of the world for disaster analysis and environmental studies. Called ISERV (International Space Station SERVIR Environmental Research and Visualization System), it is a new remote-controlled imaging system.
“Essentially, it will be pointed out of one of the windows of the Space Station, and used for Earth imaging,” Andrea Tabor, social media coordinator for Celestron told Universe Today, “especially for natural disasters and to help countries that may not have their own Earth-observing satellites to help assess damage and assist with evacuations.”
ISERV will be installed in the Window Observational Research Facility (WORF) in the station’s Destiny laboratory.
The Celestron CPC 925, is a 9.25″ diffraction limited Schmidt-Cassegrain telescope and off-the-shelf sells for $2,500 including the mount, (just the 9.25 inch optical tube sells for $1,479). It was modified at the Marshall Space Flight Center.
“They used the fork mount that comes with it,” Tabor said, “but they just removed the tripod and replaced it with a specialized mount to anchor and stabilize it on the ISS.”
Because it is pointed out of a window and because the ISS is moving so fast, it would be difficult to align it with the sky and do any celestial imaging, Tabor said.
ISERV is the first of what is hoped to be a series of space station Earth-observing instruments, each to feature progressively more capable sensors to help scientists gain operational experience and expertise, as well as help design better systems in the future. Scientists envision that future sensors could be mounted on the exterior of the station for a clearer, wider view of Earth.
It arrived on the ISS in July of 2012 on board the Japanese HTV-3.
“It’s been up there sitting in a box, so today was unboxing and assembly day,” Tabor said. She added that they hope to post some of the first images from the telescope on their Twitter and Facebook pages.
The telescope will normally be operated by remote-controlled from Earth and so the astronauts won’t likely be working with it directly except for assessing its operation or troubleshooting any problems.
“Images captured from ISERV on the ISS could provide valuable information back here on Earth,” said Dan Irwin, SERVIR program director at Marshall. “We hope it will provide new data and information from space related to natural disasters, environmental crises and the increased effects of climate variability on human populations.”
New Crew Arrives at Space Station
The latest crew has arrived to the International Space Station! Cosmonaut and Expedition 34/35 Soyuz Commander Roman Romanenko, Flight Engineer Tom Marshburn of NASA and Flight Engineer Chris Hadfield of the Canadian Space Agency docked their Soyuz TMA-07M at 14:09 UTC (9:09 a.m. EST) to the Rassvet module on the Russian segment of the ISS. We extend special congratulations to Hadfield, as we have been featuring him in our series about his training for the mission. He told us how much he is looking forward to his 5-month mission in space. “After a lot of lucky coincidences and a lot of hard work I get to be one of those who stays for an extended period off the planet. I’m really looking forward to it,” he said.
Hatches are expected to open at 16:15 UTC (11:15 am EST) after checking for leaks, etc. The new crew will be welcomed by Expedition 34 commander Kevin Ford and Russian cosmonauts Evgeny Tarelkin and Oleg Novitskiy, who have been on board since Oct. 23.
NASA says the crew will begin with a relatively light schedule and a break for the holidays of Christmas, New Years and the Russian Christmas holiday on January 6. But they’ll be busy during their mission with the arrival of Russian and European Space Agency resupply and two commercial companies, SpaceX and Orbital are scheduled to send their cargo ships to the ISS in March and April.
Ford, Novitskiy and Tarelkin are scheduled to leave the ISS in the middle of March, and at that point, Hadfield will become commander of Expedition 35, the first Canadian to to command the ISS.
Hadfield, Marshburn and Romanenko during their final Soyuz sim on Earth. Credit: NASA
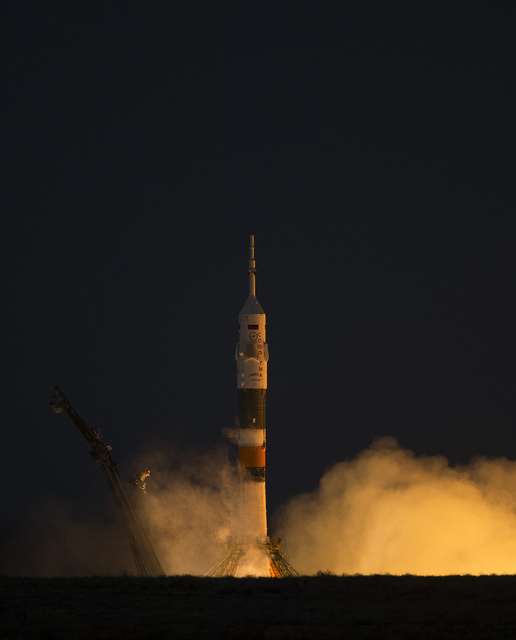
International Crew Launches to Space Station
The Soyuz TMA-07M rocket launches from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan on Wednesday, Dec. 19, 2012 carrying the Expedition 34 crew to the International Space Station. Credit: NASA/Carla Cioffi
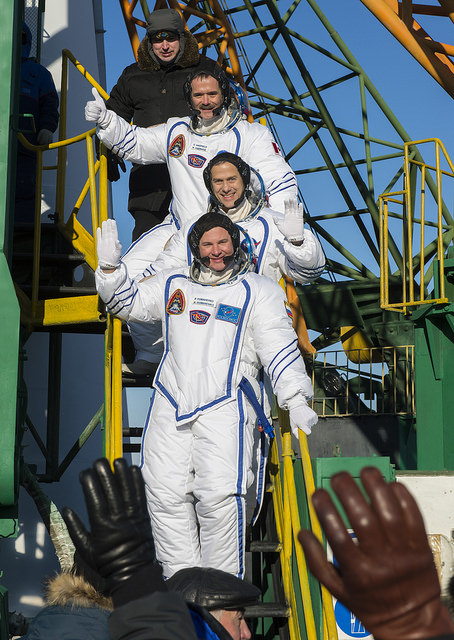
Heading off just as the Sun was setting amid frigid conditions at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan, a trio of international explorers launched to space, on their way to the International Space Station. Chris Hadfield of the Canadian Space Agency, Tom Marshburn of NASA, Roman Romanenko of the Russian Federal Space Agency (Roscosmos) launched Wednesday at 12:12 UTC (7:12 a.m. EST, 6:12 p.m. Baikonur time). Their Soyuz TMA-07M performed flawlessly, and the crew is expected to dock with the Rassvet module on the Russian segment of the space station at 14:12 UTC (9:12 a.m. EST) on Friday, Dec. 21.
See the launch video below:
Temperatures were below freezing, with a windchill reported of -34 C at launch time. But as Hadfield told Universe Today, the Soyuz rocket is just as robust and one of the most reliable rockets ever. “The Soyuz launches all-weather, -40 degrees to +40 degrees,” Hadfield said. “It is rugged, built on experience, and it is not delicate. I trust it with my life.”
Hadfield, Marshburn and Romanenko will join their Expedition 34 crewmates already on board the ISS — Commander Kevin Ford and Flight Engineers Oleg Novitskiy and Evgeny Tarelkin — to bring the crew back to the standard size of six.
Two minutes into flight, the Soyuz rocket’s four liquid-fueled first stage boosters were jettisoned. Via NASA TV.
Hadfield will make history on March 15, 2013 as he will become the first Canadian astronaut to take command of the ISS.
The focus of Expedition 34/35 is scientific research, with the astronauts serving as subjects for human physiology tests, including examinations of astronaut bone loss.
While not officially decided yet, Hadfield indicated a spacewalk may be in order for him and one of his ISS crewmates to perform some needed maintenance outside the space station.
Expedition 34 NASA Flight Engineer Chris Hadfield of the Canadian Space Agency (CSA), top, NASA Flight Engineer Tom Marshburn and Soyuz Commander Roman Romanenko wave farewell from the bottom of the Soyuz rocket. Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)
During their stay, the crew will be busy welcoming both a Russian Progress and ESA’s ATV cargo ships, as well as two commercial resupply missions from SpaceX and the first flight of Orbital Science’s Cygnus spacecraft.
The crew also will also be conducting a wide range of physical science, Earth observation, human research and technology demonstration investigations. Experiments will investigate how fire behaves in space, which could help improve engine fuel efficiency and fire suppression methods in space and on Earth. Other research will look at fluids that change physical properties in the presence of a magnet, which could improve bridge and building designs to better withstand earthquakes. With the help of cameras set up by the crew, students on Earth are capturing photos of our planet.
For a look at the training done by Chris Hadfield in preparation for his flight, see our series “How to Train for Long Duration Space Flight.”
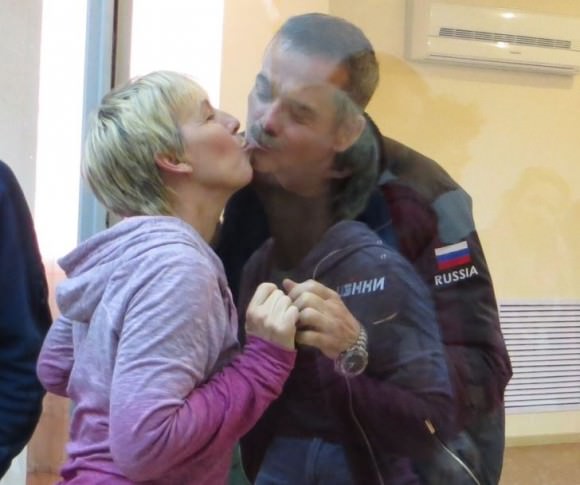
“One last kiss before I go – love under glass with my wife. It’s launch morning, I slept well, feel great,” Hadfield Tweeted this morning before launch.








