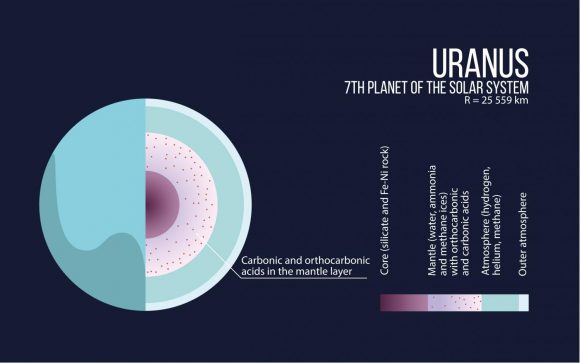
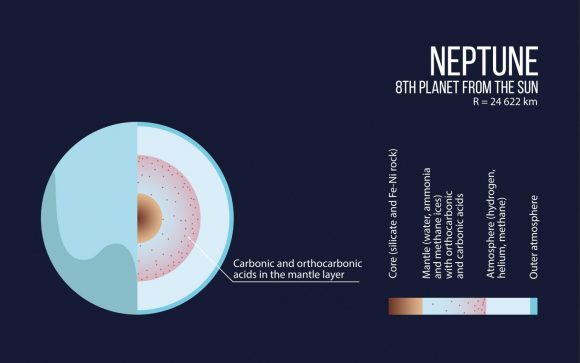
Earlier this week, NASA hosted the “Planetary Science Vision 2050 Workshop” at their headquarters in Washington, DC. Running from Monday to Wednesday – February 27th to March 1st – the purpose of this workshop was to present NASA’s plans for the future of space exploration to the international community. In the course of the many presentations, speeches and panel discussions, many interesting proposals were shared.
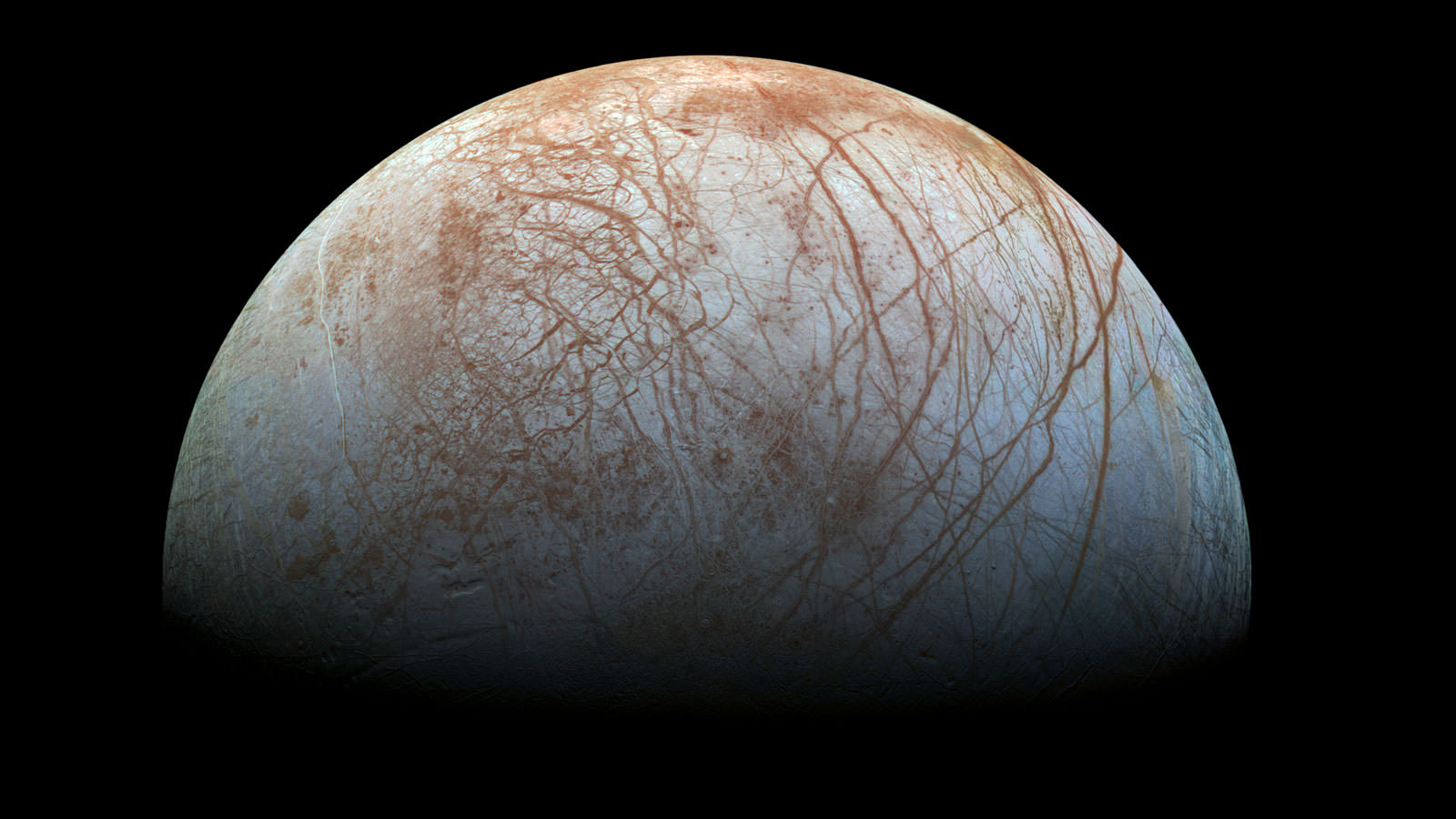
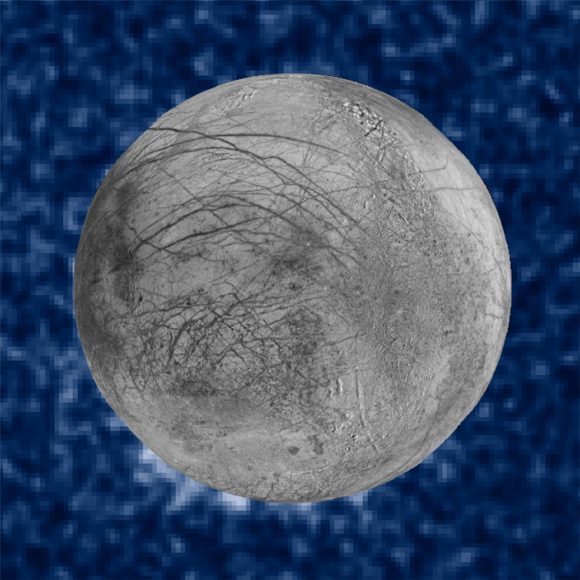
Among them were two presentations that outlined NASA’s plan for the exploration of Jupiter’s moon Europa and other icy moons. In the coming decades, NASA hopes to send probes to these moons to investigate the oceans that lie beneath theirs surfaces, which many believe could be home to extra-terrestrial life. With missions to the “ocean worlds” of the Solar System, we may finally come to discover life beyond Earth.
The first of the two meetings took place on the morning of Monday, Feb. 27th, and was titled “Exploration Pathways for Europa after initial In-Situ Analyses for Biosignatures“. In the course of the presentation, Kevin Peter Hand – the Deputy Chief Scientist for Solar System Exploration at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory – shared findings from a report prepared by the 2016 Europa Lander Science Definition Team.
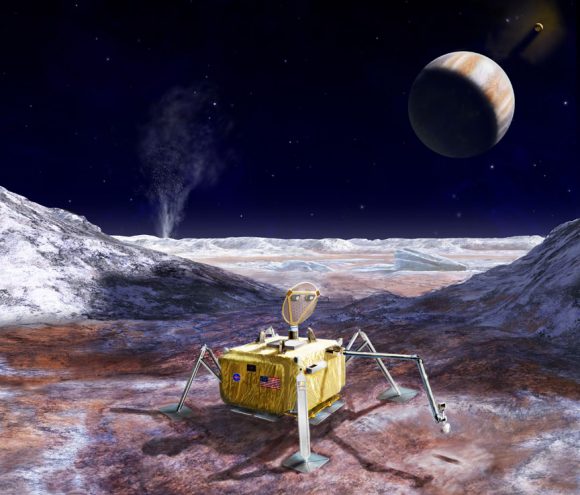

This report was drafted by NASA’s Planetary Science Division (PSD) in response to a congressional directive to begin a pre-Phase A study to assess the scientific value and engineering design of a Europa lander mission. These studies, which are known as Science Definition Team (SDT) reports, are routinely conducted long before missions are mounted in order to gain an understanding of the types of challenges it will face, and what the payoffs will be.
In addition to being the co-chair of the Science Definition Team, Hand also served as head of the project science team, which included members from the JPL and the California Institute of Technology (Caltech). The report he and his colleagues prepared was finalized and issued to NASA on February 7th, 2017, and outlined several objectives for scientific study.
As was indicated during the course of the presentation, these objectives were threefold. The first would involve searching for biosignatures and signs of life through analyses of Europa’s surface and near-subsurface material. The second would be to conduct in-situ analyses to characterize the composition of non-ice near-subsurface material, and determine the proximity of liquid water and recently-erupted material near the lander’s location.
The third and final goal would be to characterize the surface and subsurface properties and what dynamic processes are responsible for shaping them, in support for future exploration missions. As Hand explained, these objectives are closely intertwined:
“Were biosignatures to be found in the surface material, direct access to, and exploration of, Europa’s ocean and liquid water environments would be a high priority goal for the astrobiological investigation of our Solar System. Europa’s ocean would harbor the potential for the study of an extant ecosystem, likely representing a second, independent origin of life in our own solar system. Subsequent exploration would require robotic vehicles and instrumentation capable of accessing the habitable liquid water regions in Europa to enable the study of the ecosystem and organisms.”

In other words, if the lander mission detected signs of life within Europa’s ice sheet, and from material churned up from beneath by resurfacing events, then future missions – most likely involving robotic submarines – would definitely be mounted. The report also states that any finds that are indicative of life would mean that planetary protections would be a major requirement for any future mission, to avoid the possibility of contamination.
But of course, Hand also admitted that there is a chance the lander will find no signs of life. If so, Hand indicated that future missions would be tasked with gaining “a better understanding of the fundamental geological and geophysical process on Europa, and how they modulate exchange of material with Europa’s ocean.” On the other hand, he claimed that even a null-result (i.e. no signs of life anywhere) would still be a major scientific find.
Ever since the Voyager probes first detected possible signs of an interior ocean on Europa, scientists have dreamed of the day when a mission might be possible to explore the interior of this mysterious moon. To be able to determine that life does not exist there could no less significant that finding life, in that both would help us learn more about life in our Solar System.
The Science Definition Team’s report will also be the subject of a townhall meeting at the 2017 Lunar and Planetary Science Conference (LPSC) – which will be taking place from March 20th to 24th in The Woodlands, Texas. The second event will be on April 23rd at the Astrobiology Science Conference (AbSciCon) held in Mesa, Arizona. Click here to read the full report.

The second presentation, titled “Roadmaps to Ocean Worlds” took place later on Monday, Feb. 27th. This presentation was put on by members of the the Roadmaps to Ocean Worlds (ROW) team, which is chaired by Dr. Amandra Hendrix – a senior scientist at the Planetary Science Institute in Tuscon, Arizona – and Dr. Terry Hurford, a research assistant from NASA’s Science and Exploration Directorate (SED).
As a specialist in UV spectroscopy of planetary surfaces, Dr. Hendrix has collaborated with many NASA missions to explore icy bodies in the Solar System – including the Galileo and Cassini probes and the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO). Dr. Hurford, meanwhile, specializes in the geology and geophysics of icy satellites, as well as the effects orbital dynamics and tidal stresses have on their interior structures.
Founded in 2016 by NASA’s Outer Planets Assessment Group (OPAG), ROW was tasked with laying the groundwork for a mission that will explore “ocean worlds” in the search for life elsewhere in the Solar System. During the course of the presentation, Hendrix and Hurford laid out the findings from the ROW report, which was completed in January of 2017.
As they state in this report, “we define an ‘ocean world’ as a body with a current liquid ocean (not necessarily global). All bodies in our solar system that plausibly can have or are known to have an ocean will be considered as part of this document. The Earth is a well-studied ocean world that can be used as a reference (“ground truth”) and point of comparison.”

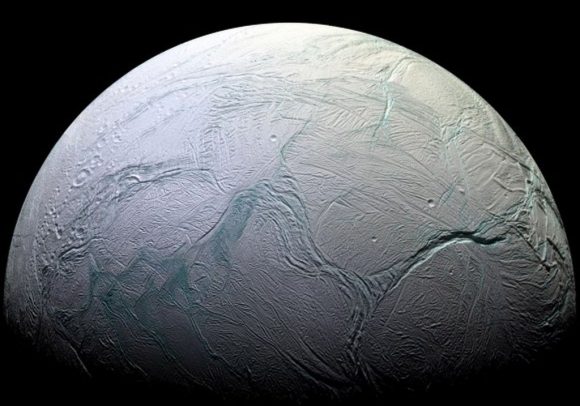
By this definition, bodies like Europa, Ganymede, Callisto, and Enceladus would all be viable targets for exploration. These worlds are all known to have subsurface oceans, and there has been compelling evidence in the past few decades that point towards the presence of organic molecules and prebiotic chemistry there as well. Triton, Pluto, Ceres and Dione are all mentioned as candidate ocean worlds based on what we know of them.
Titan also received special mention in the course of the presentation. In addition to having an interior ocean, it has even been ventured that extremophile methanogenic lifeforms could exist on its surface:
“Although Titan possesses a large subsurface ocean, it also has an abundant supply of a wide range of organic species and surface liquids, which are readily accessible and could harbor more exotic forms of life. Furthermore, Titan may have transient surface liquid water such as impact melt pools and fresh cryovolcanic flows in contact with both solid and liquid surface organics. These environments present unique and important locations for investigating prebiotic chemistry, and potentially, the first steps towards life.”
Ultimately, the ROW’s pursuit of life on “ocean worlds” consists of four main goals. These include identifying ocean worlds in the solar system, which would mean determining which of the worlds and candidate worlds would be well-suited to study. The second is to characterize the nature of these oceans, which would include determining the properties of the ice shell and liquid ocean, and what drives fluid motion in them.

The third sub-goal involves determining if these oceans have the necessary energy and prebiotic chemistry to support life. And the fourth and final goal would be to determine how life might exist in them – i.e. whether it takes the form of extremophile bacteria and tiny organisms, or more complex creatures. Hendrix and Hurford also covered the kind of technological advances that will be needed for such missions to happen.
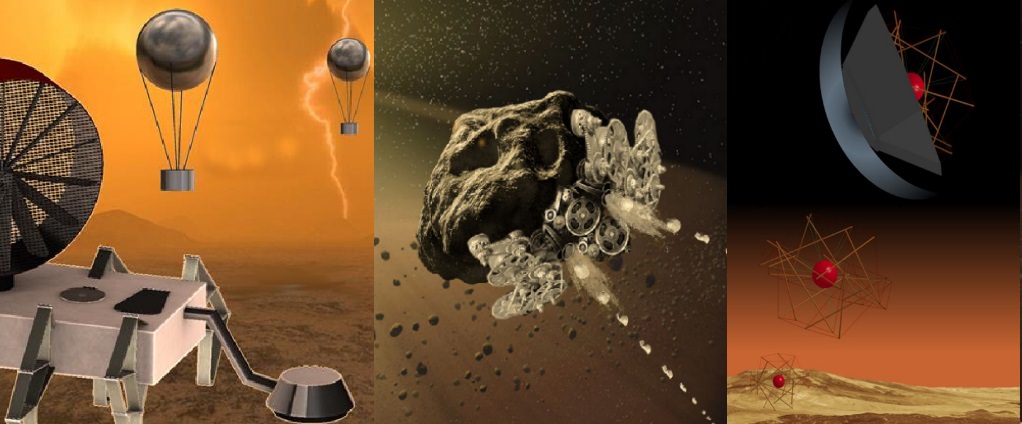
Naturally, any such mission would require the development of power sources and energy storage systems that would be suitable for cryogenic environments. Autonomous systems for pinpoint landing and technologies for aerial or landed mobility would also be needed. Planetary protection technologies would be necessary to prevent contamination, and electronic/mechanical systems that can survive in an ocean world environment too,
While these presentations are merely proposals of what could happen in the coming decades, they are still exciting to hear about. If nothing else, they show how NASA and other space agencies are actively collaborating with scientific institutions around the world to push the boundaries of knowledge and exploration. And in the coming decades, they hope to make some substantial leaps.
If all goes well, and exploration missions to Europa and other icy moons are allowed to go forward, the benefits could be immeasurable. In addition to the possibility of finding life beyond Earth, we will come to learn a great deal about our Solar System, and no doubt learn something more about humanity’s place in the cosmos.