Subsurface oceans of liquid water are a common feature of the moon’s of Jupiter and Saturn. Researchers are exploring whether the icy moons of Uranus and Neptune might have them as well. Their new paper suggests future missions to the outer Solar System could measure the rotation of the moons and detect any wobbles pointing to liquid oceans. Less wobble means the moons is mostly solid but large wobbles can indicate ice floating on an ocean of liquid.
Continue reading “Uranus’s Wobbling Moons Could Point to Oceans Under the Ice”A Single Grain of Ice Could Hold Evidence of Life on Europa and Enceladus

The Solar System’s icy ocean moons are primary targets in our search for life. Missions to Europa and Enceladus will explore these moons from orbit, improving our understanding of them and their potential to support life. Both worlds emit plumes of water from their internal oceans, and the spacecraft sent to both worlds will examine those plumes and even sample them.
New research suggests that evidence of life in the moons’ oceans could be present in just a single grain of ice, and our spacecraft can detect it.
Continue reading “A Single Grain of Ice Could Hold Evidence of Life on Europa and Enceladus”What Can We Learn Flying Through the Plumes at Enceladus?

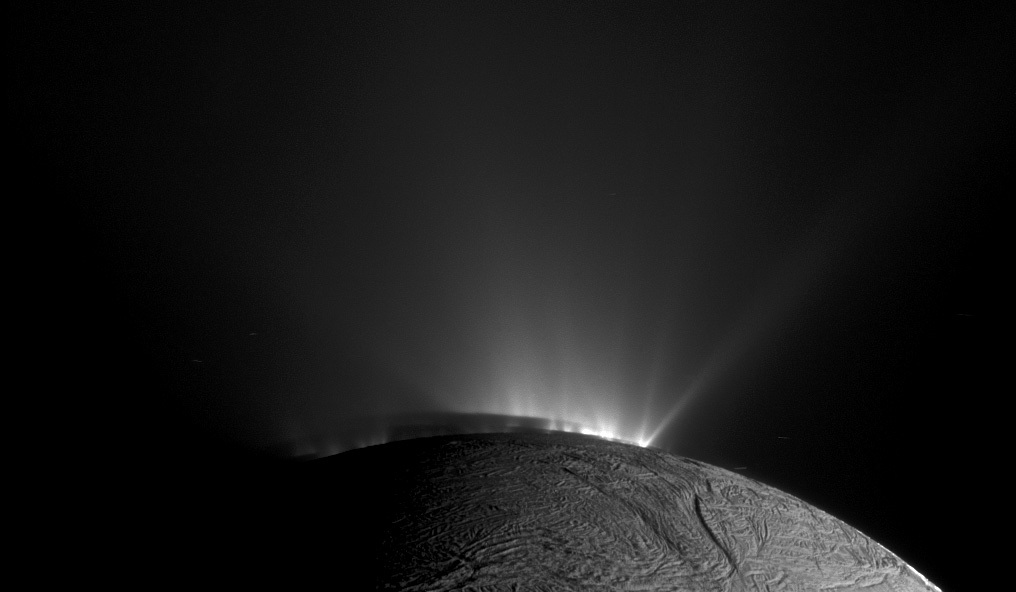
In the next decade, space agencies will expand the search for extraterrestrial life beyond Mars, where all of our astrobiology efforts are currently focused. This includes the ESA’s JUpiter ICy moon’s Explorer (JUICE) and NASA’s Europa Clipper, which will fly past Europa and Ganymede repeatedly to study their surfaces and interiors. There’s also NASA’s proposed Dragonfly mission that will fly to Titan and study its atmosphere, methane lakes, and the rich organic chemistry happening on its surface. But perhaps the most compelling destination is Enceladus and the lovely plumes emanating from its southern polar region.
Since the Cassini mission got a close-up look at these plumes, scientists have been aching to send a robotic mission there to sample them – which appear to have all the ingredients for life in them. This is not as easy as it sounds, and there’s no indication flying through plumes will yield intact samples. In a recent paper, researchers from the University of Kent examined how the velocity of a passing spacecraft (and the resulting shock of impact) could significantly affect its ability to sample water and ice within the plumes.
Continue reading “What Can We Learn Flying Through the Plumes at Enceladus?”How Warm Are the Oceans on the Icy Moons? The Ice Thickness Provides a Clue.

Scientists are discovering that more and more Solar System objects have warm oceans under icy shells. The moons Enceladus and Europa are the two most well-known, and others like Ganymede and Callisto probably have them too. Even the dwarf planet Ceres might have an ocean. But can any of them support life? That partly depends on the water temperature, which strongly influences the chemistry.
We’re likely to visit Europa in the coming years and find out for ourselves how warm its ocean is. Others on the list we may never visit. But we may not have to.
Continue reading “How Warm Are the Oceans on the Icy Moons? The Ice Thickness Provides a Clue.”NASA Tests a Robotic Snake That Could Explore Other Worlds
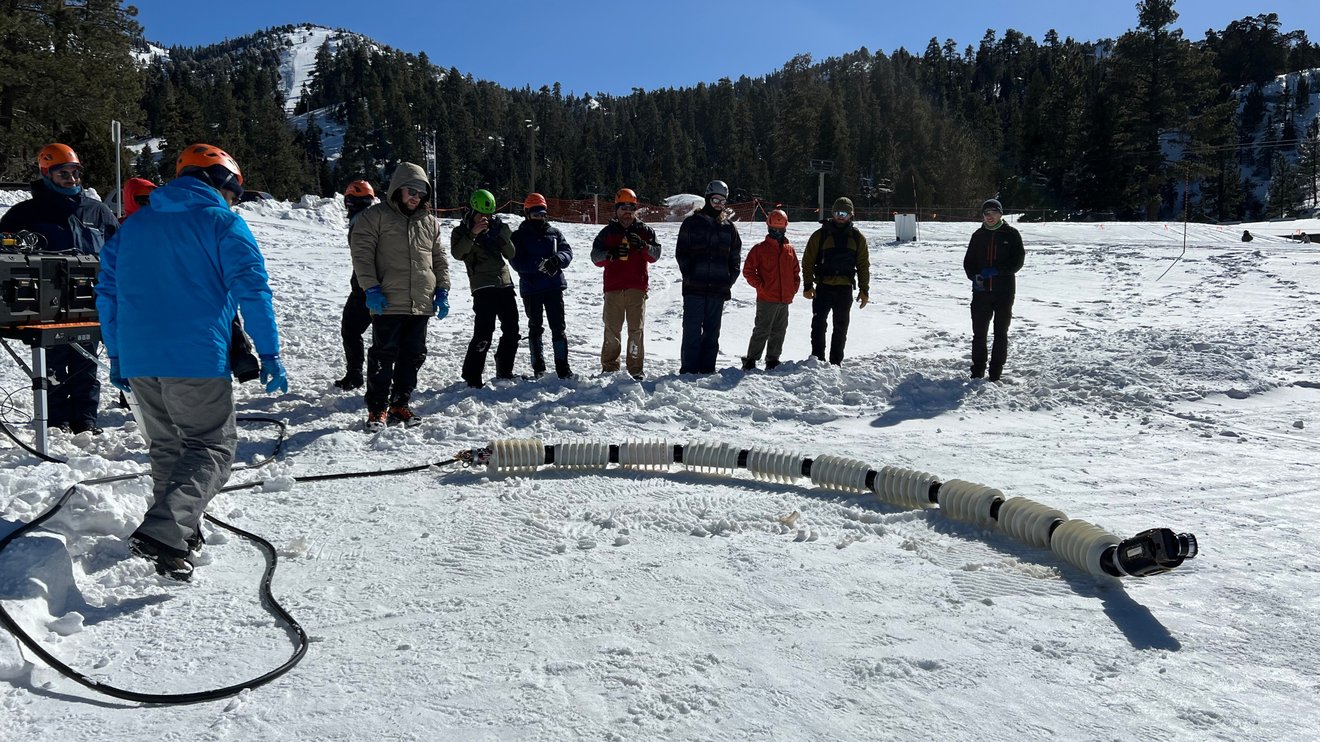

Rovers have enabled some amazing explorations of other worlds like the Moon and Mars. However, rovers are limited by the terrain they can reach. To explore inaccessible terrain, NASA is testing a versatile snake-like robot that could crawl up steep slopes, slither across ice, and even slide into lava tubes. Called Exobiology Extant Life Surveyor (or EELS), this robot could cross different terrains and create a 3D map of its surrounding to autonomously pick its course, avoiding hazards to reach its destination.
Continue reading “NASA Tests a Robotic Snake That Could Explore Other Worlds”Hurray! Juice Deploys its Stuck Antenna
ESA’s Juice mission launched last month on April 14, beginning its long journey to explore Jupiter’s icy moons, Ganymede, Europa, and Callisto. But soon after launch, mission controllers realized a 16-meter (52.5 ft)-long antenna for a radar instrument was jammed and couldn’t deploy. The Radar for Icy Moons Exploration (RIME) antenna is mission critical, as it gathers data for the instrument that will be able to map beneath the ice at these moons.
But, whew, the story has a happy ending. After nearly a month of efforts to free the stuck antenna, engineers figured out a fix for the RIME antenna. They fired a mechanical device in the jammed bracket, which created enough jiggling and rattling to allow the antenna to fully deploy.
Continue reading “Hurray! Juice Deploys its Stuck Antenna”We Could Soon See Landslides on Europa and Ganymede
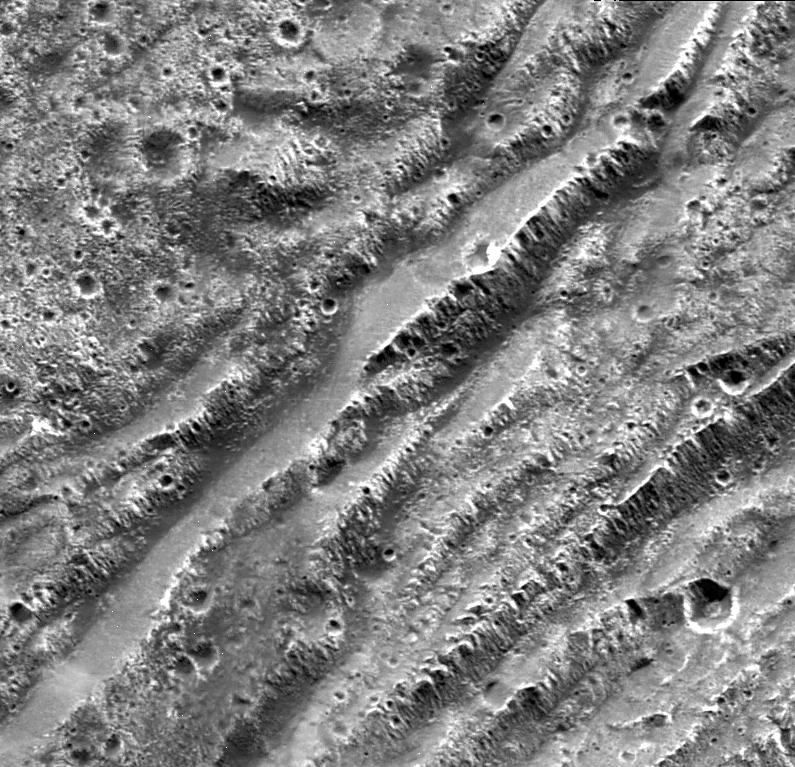
The European Space Agency’s (ESA) recently launched Jupiter Icy Moons Explorer (JUICE) mission and NASA’s upcoming Europa Clipper mission could allow scientists to image landslides on the icy moons of Europa and Ganymede due to potential moonquakes on these small worlds. This comes after a recent study examined fault scarps on Europa and Ganymede orbiting Jupiter and Enceladus and Dione orbiting Saturn with the goal of drawing a connection between tectonic activity (quakes) and observed mass wasting (landslides) on these surfaces. The researchers “consider whether such smooth material can be generated by mass wasting triggered from local seismic shaking”, according to the study.
Continue reading “We Could Soon See Landslides on Europa and Ganymede”Comet Impacts Could Have Brought the Raw Ingredients for Life to Europa’s Ocean
Jupiter is the most-visited planet in the Solar System, thanks largely to NASA. It all started with Pioneer 10 and 11, followed by Voyager 1 and 2. Those were all flyby missions, and it wasn’t until 1996 that the Galileo spacecraft became the first to orbit the gas giant and even send a probe into its atmosphere. Then in 2016, the Juno spacecraft entered orbit around Jupiter and is still there today.
All of these missions were focused on Jupiter, but along the way, they gave us tantalizing hints of the icy moon Europa. The most impactful thing we’ve learned is that Europa, though frozen on the surface, holds an ocean under all that ice. And that warm, salty ocean might contain more water than all of Earth’s oceans combined.
Might it hold life?
Continue reading “Comet Impacts Could Have Brought the Raw Ingredients for Life to Europa’s Ocean”There Could be as Many Water Worlds as Earths in the Milky Way
On July 12th, 2022, NASA released the first images acquired by the James Webb Space Telescope, which were taken during its first six months of operation. Among its many scientific objectives, Webb will search for smaller, rocky planets that orbit closer to their suns – especially dimmer M-type (red dwarf) stars, the most common in the Universe. This will help astronomers complete the census of exoplanets and gain a better understanding of the types of worlds that exist out there. In particular, astronomers are curious about how many terrestrial planets in our galaxy are actually “water worlds.”
These are rocky planets that are larger than Earth but have a lower density, which suggests that volatiles like water make up a significant amount (up to half) of their mass-fraction. According to a recent study by researchers from the University of Chicago and the Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias (IAC), water worlds may be just as common as “Earth-like” rocky planets. These findings bolster the case for exoplanets that are similar to icy moons in the Solar System (like Europa) and could have significant implications for future exoplanet studies and the search for life in our Universe.
Continue reading “There Could be as Many Water Worlds as Earths in the Milky Way”Europa’s Nightside Glows in the Dark
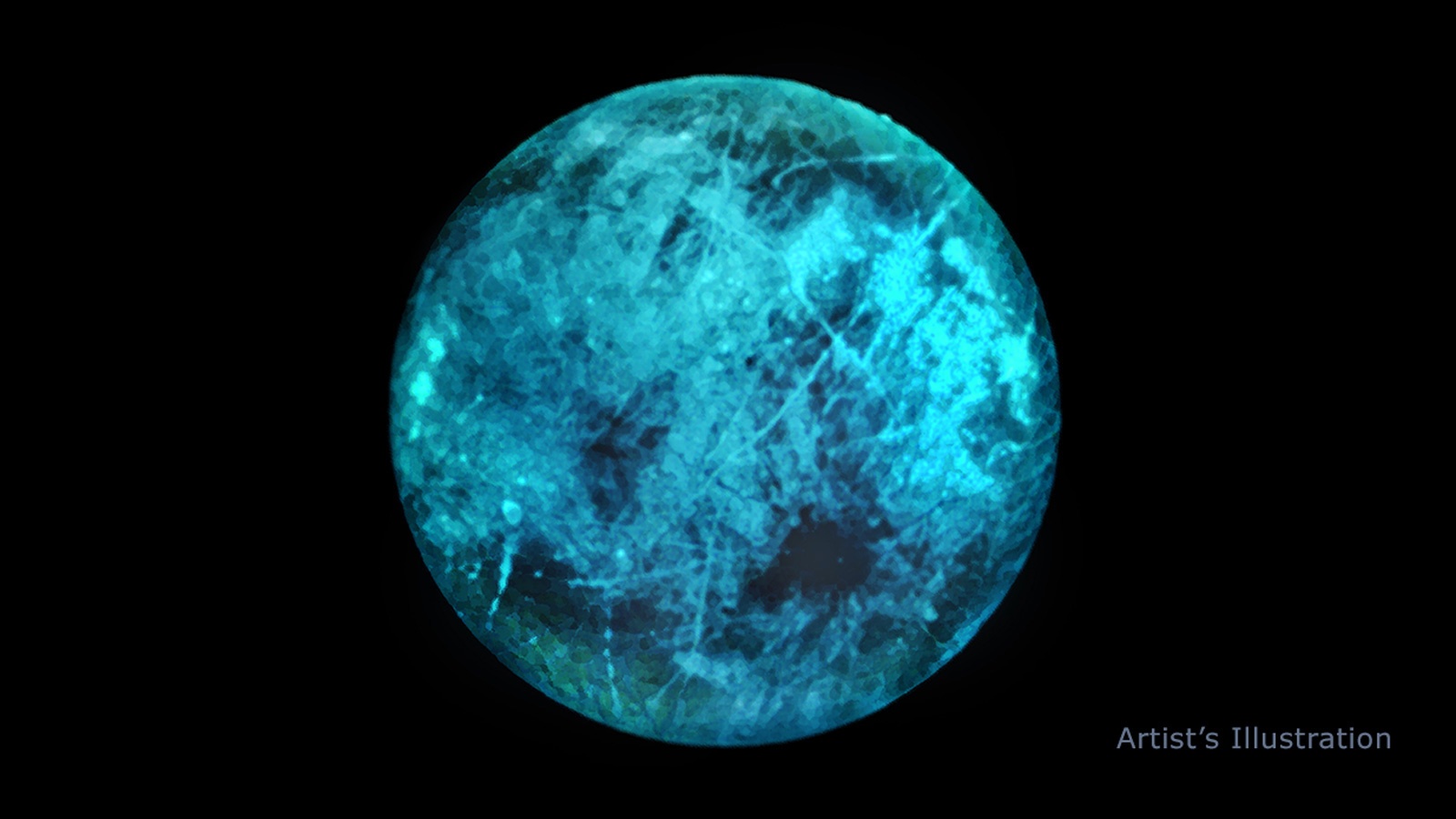

In a few years, NASA will be sending a spacecraft to explore Jupiter’s icy moon Europa. Known as the Europa Clipper mission, this orbiter will examine the surface more closely to search for plume activity and evidence of biosignatures. Such a find could answer the burning question of whether or not there is life within this moon, which is something scientists have speculated about since the 1970s.
In anticipation of this mission, scientists continue to anticipate what it will find once it gets there. For instance, scientists from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory recently conducted a study that showed how Europa might glow in the dark. This could be the result of Europa constantly being pummeled with high-energy radiation from Jupiter’s magnetic field, the study of which could tell scientists more about the composition of Europa’s ice.
Continue reading “Europa’s Nightside Glows in the Dark”


