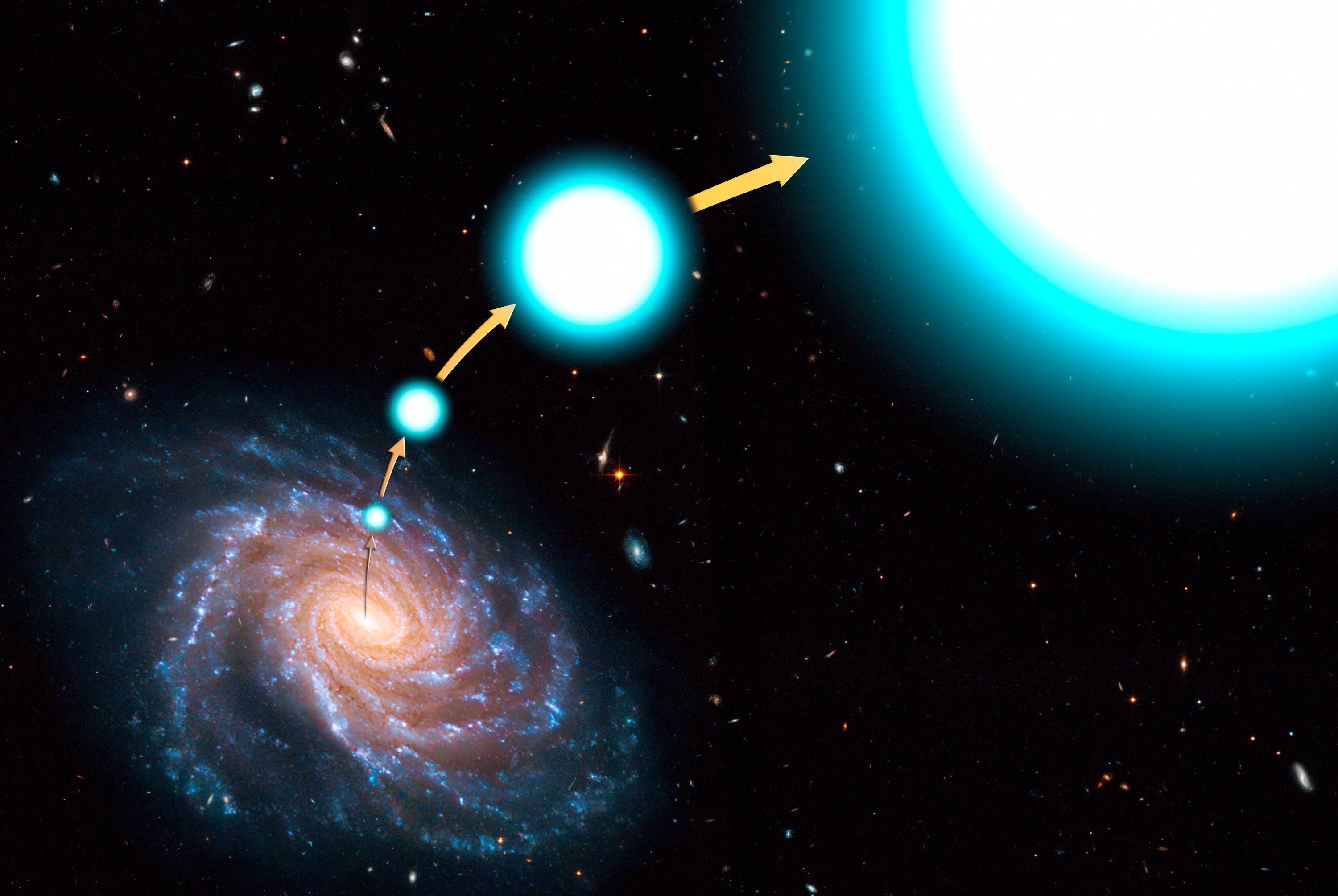
Astronomers have solid evidence for the existence of stellar-mass black holes and supermassive black holes. However, evidence for Intermediate Black Holes (IMBHs) is more elusive. Their existence remains hypothetical.
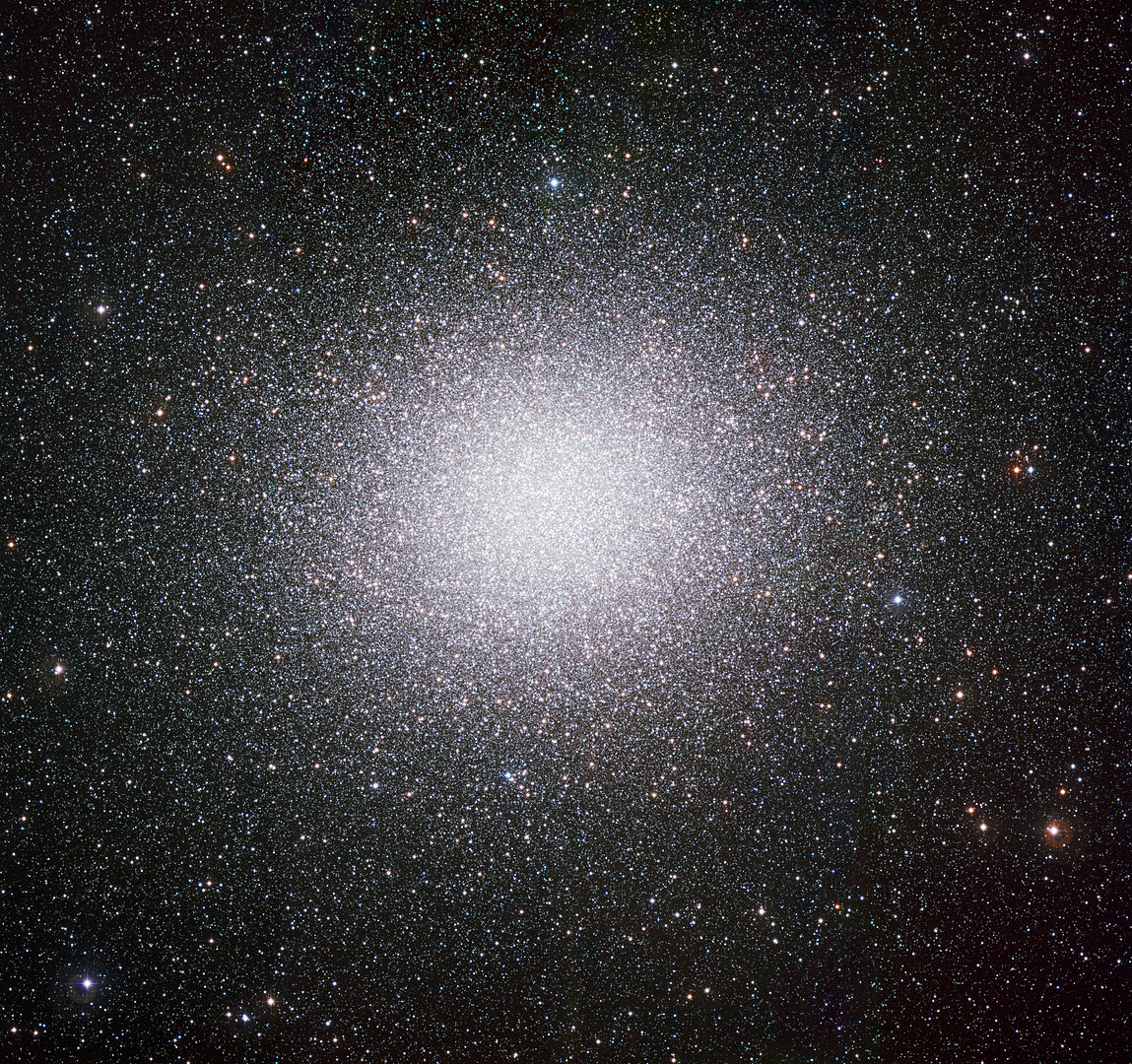
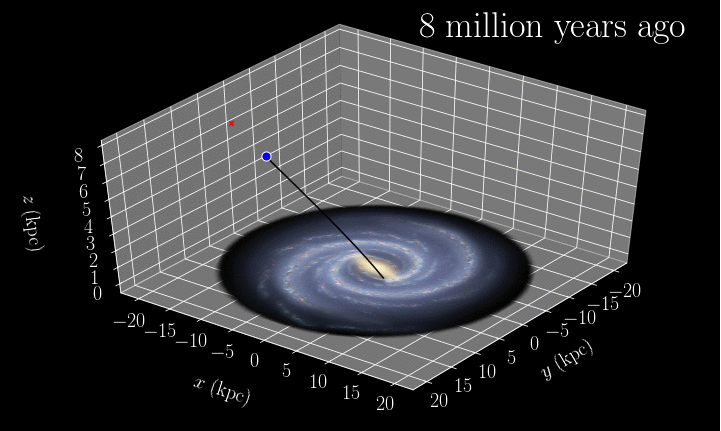
However, study by study, evidence is accumulating for IMBHs. The latest comes from the globular cluster M15, where a fast-moving star suggests the presence of something massive. Could it be an elusive IMBH?
Continue reading “A Star Was Kicked Out of a Globular Cluster by an Intermediate-Mass Black Hole”