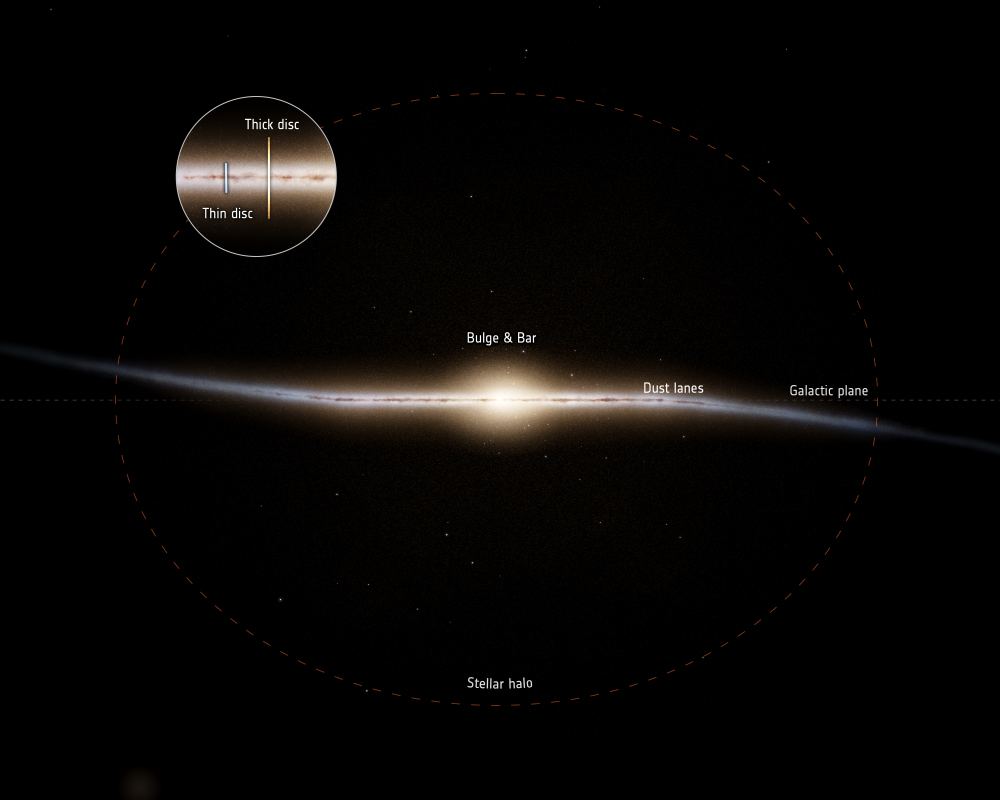
The Milky Way is only as massive as it is because of collisions and mergers with other galaxies. This is a messy process, and we see the same thing happening with other galaxies throughout the Universe. Currently, we see the Milky Way nibbling at its two satellite galaxies, the Large and Small Magellanic Clouds. Their fate is likely sealed, and they’ll be absorbed into our galaxy.
Researchers thought the last major merger occurred in the Milky Way’s distant past, between 8 and 11 billion years ago. But new research amplifies the idea that it was much more recent: less than 3 billion years ago.
Continue reading “The Milky Way’s Last Merger Event Was More Recent Than Thought”