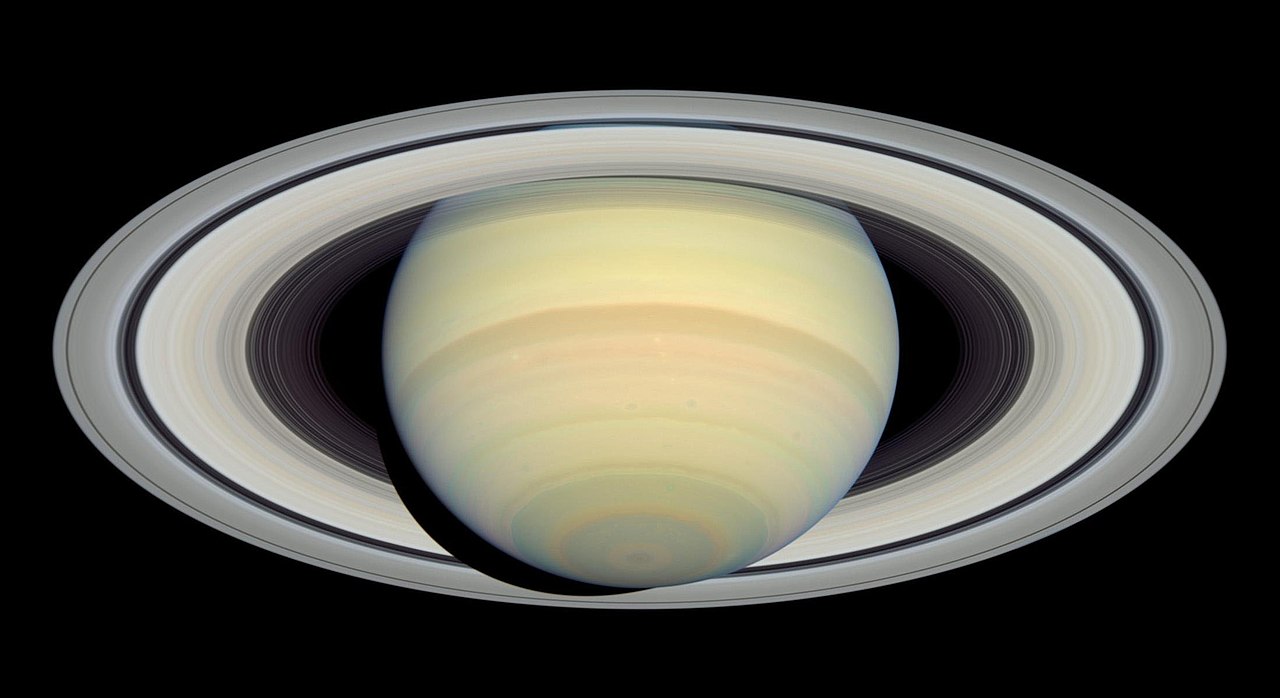
When the name Saturn is uttered, what comes to mind? For most people, the answer would probably be, “its fabulous system of rings.” There’s no doubt they are iconic, but what is perhaps lesser-known is that Jupiter, Uranus, and Neptune all have ring systems of their own. However, whereas Saturn’s rings are composed mainly of ice particles (making them highly reflective), Jupiter’s rings are composed mainly of dust grains. Meanwhile, Uranus and Neptune have rings of extremely dark particles known as tholins that are very hard to see. For this reason, none of the other gas giants get much recognition for their rings.
However, the question of why Jupiter doesn’t have larger, more spectacular rings than Saturn has been bothering astronomers for quite some time. As the larger and more massive of the two bodies, Jupiter should have rings that would dwarf Saturn’s by comparison. This mystery may have finally been resolved thanks to new research by a team from UC Riverside. According to their study, Jupiter’s massive moons (aka. Jupiter’s Galilean Moons) prevented it from developing a big, bright, beautiful ring system that would put Saturn’s to shame.
Continue reading “Jupiter's Giant Moons Prevent it From Having Rings Like Saturn”