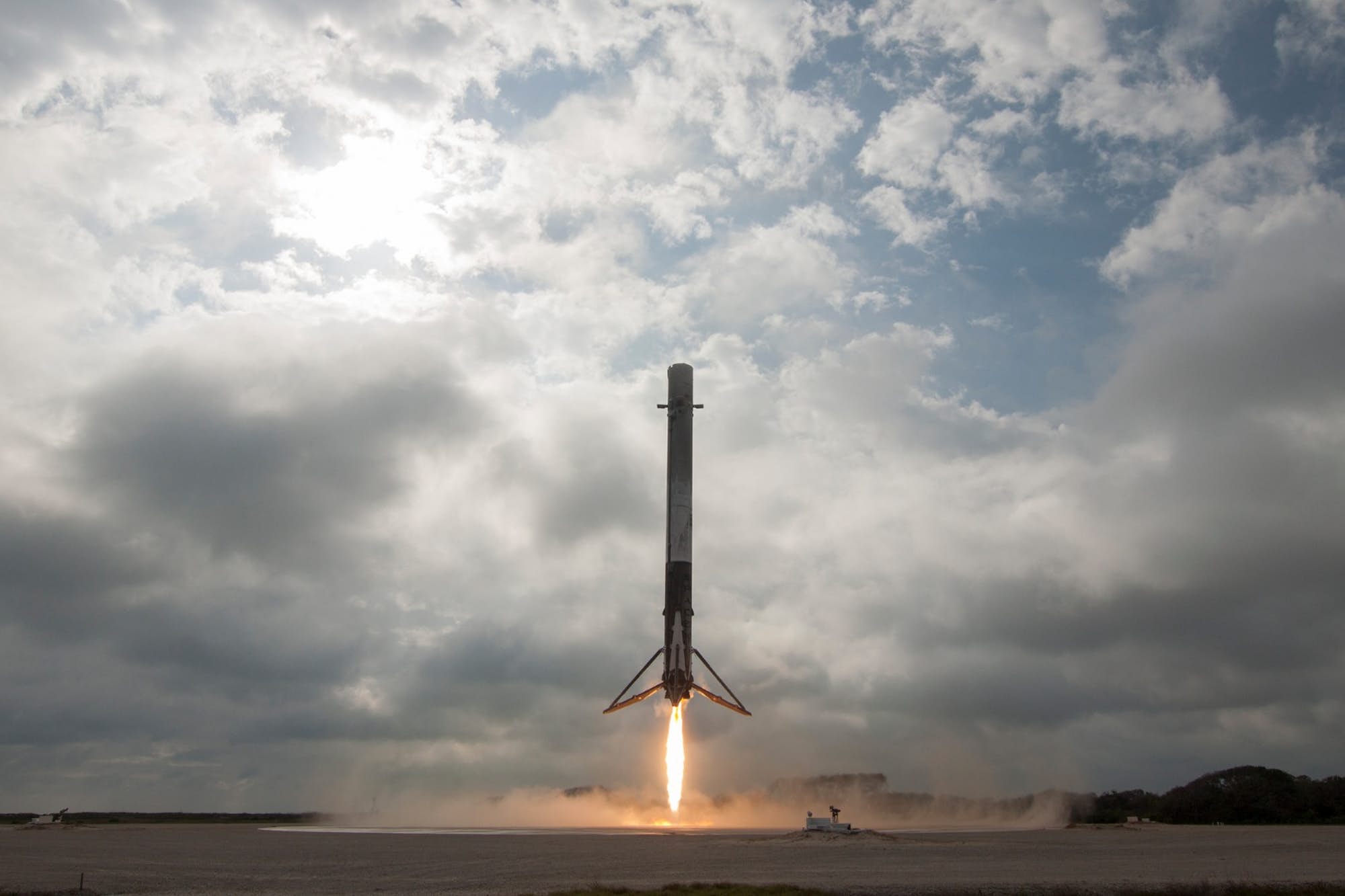
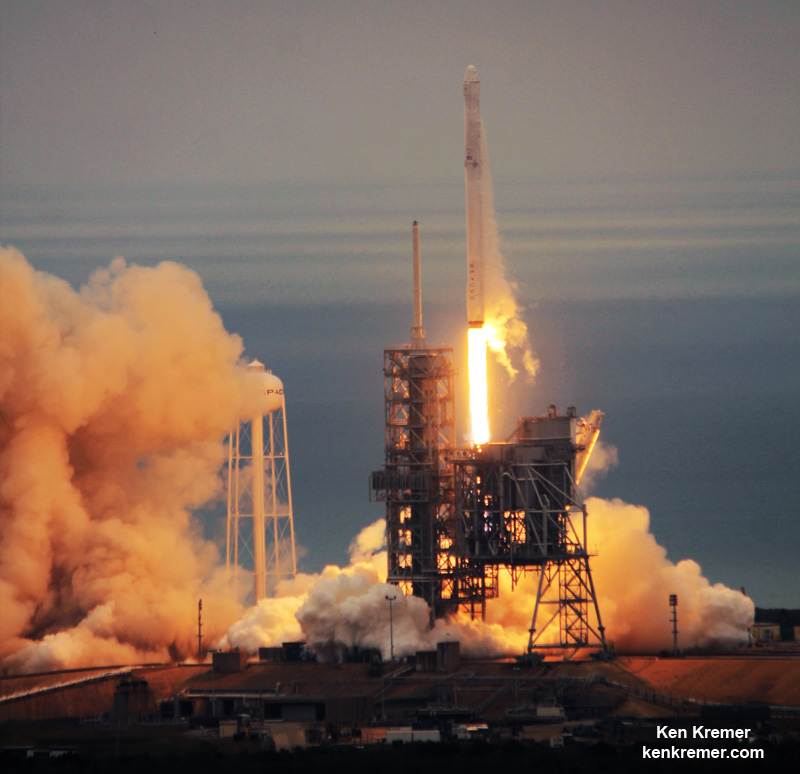
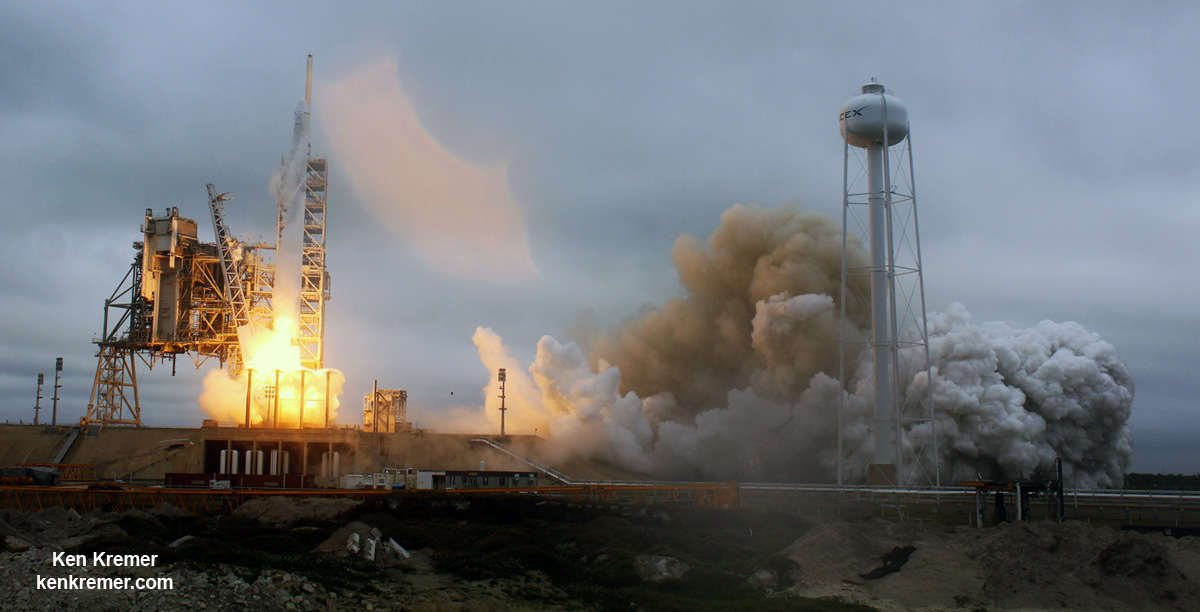
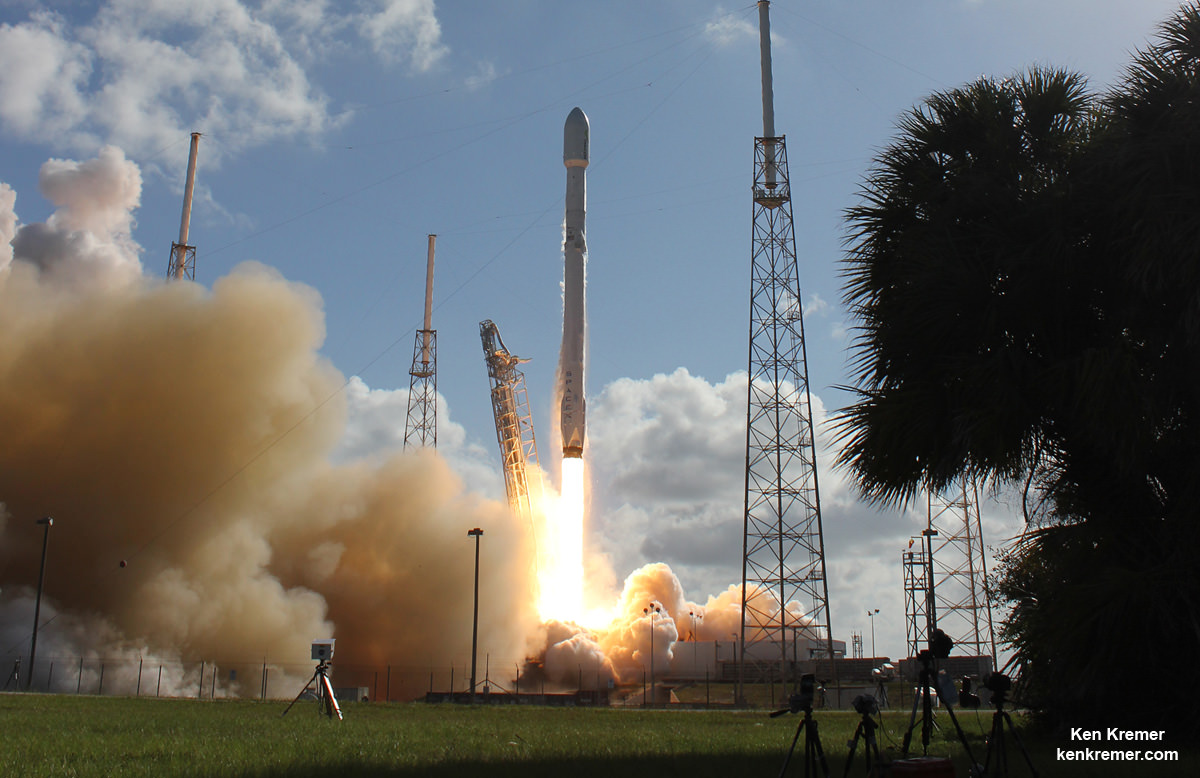
When Elon Musk launched SpaceX in 2002, he did so with the intention of making reusability a central feature of his company. Designed to lower the costs associated with launches, being able to reuse boosters was also a means of making space more accessible. “If one can figure out how to effectively reuse rockets just like airplanes,” he said, “the cost of access to space will be reduced by as much as a factor of a hundred.”
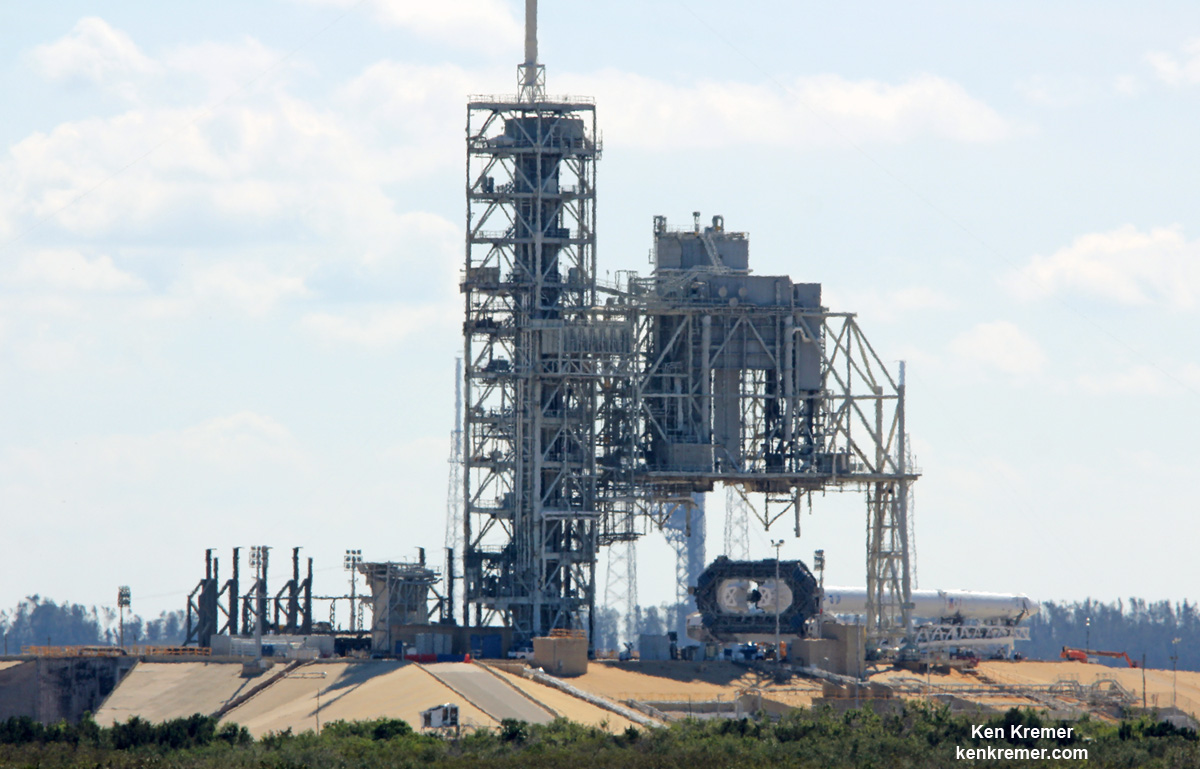
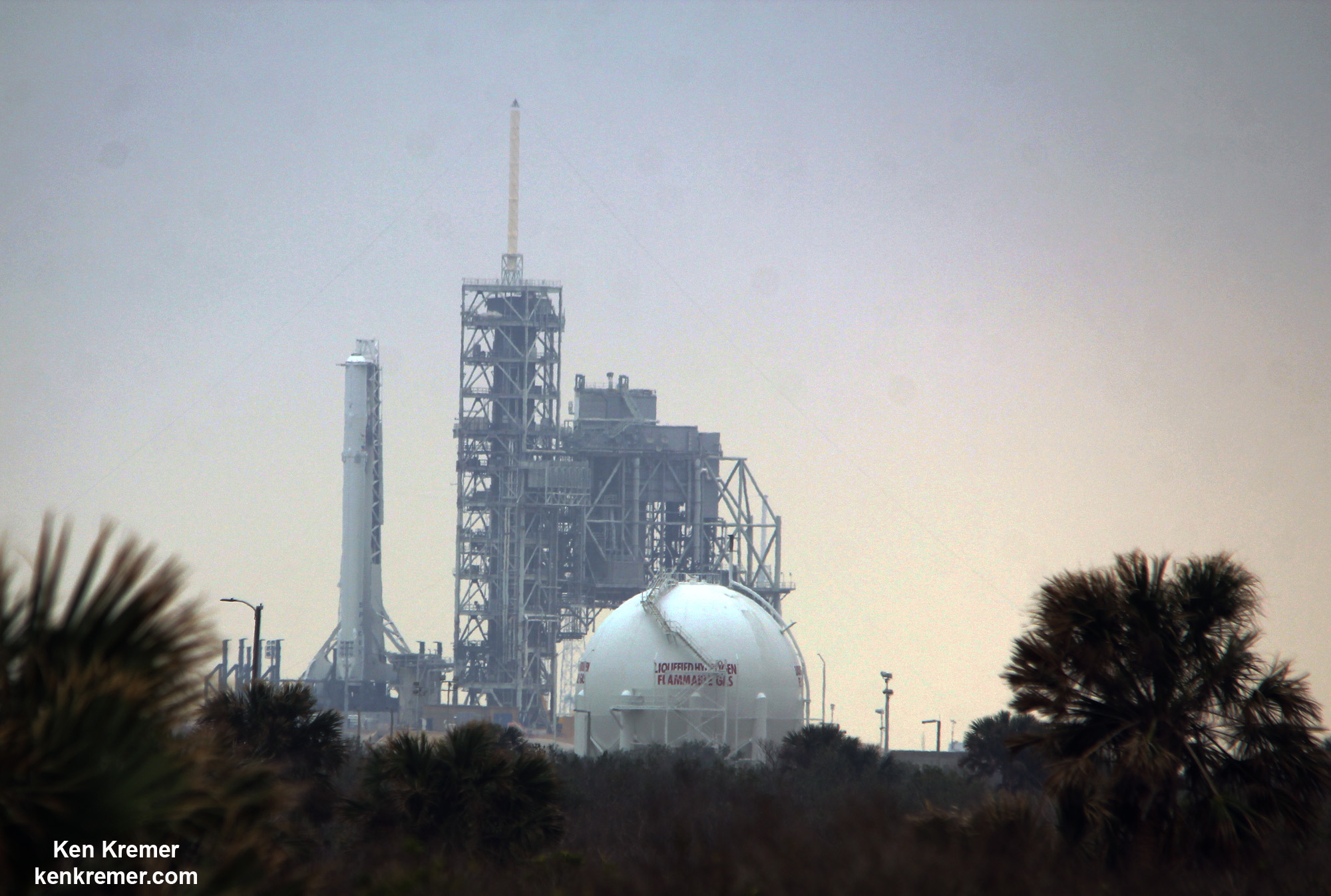
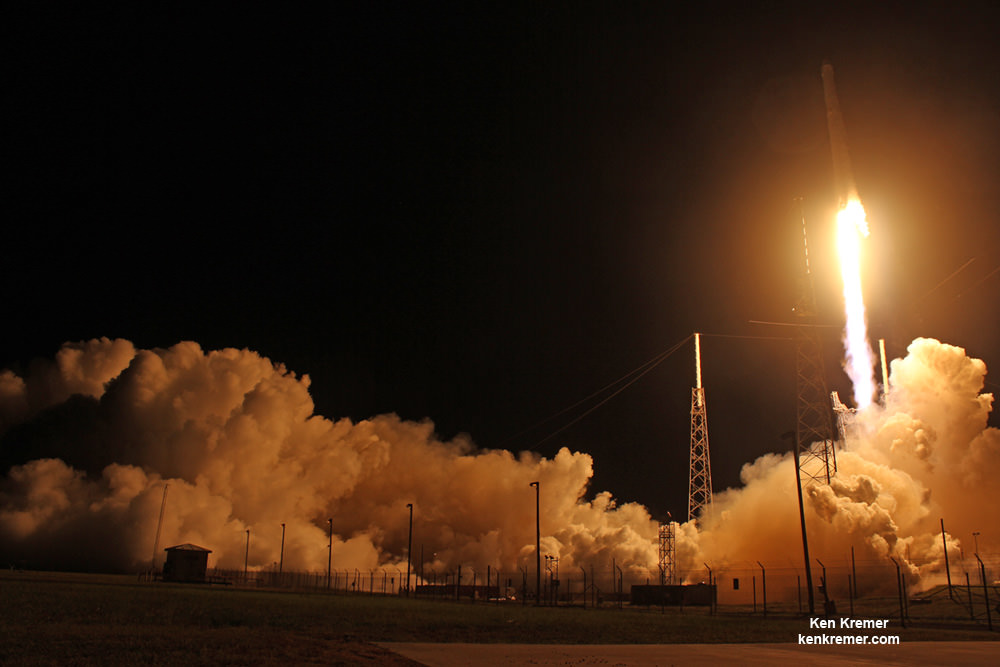
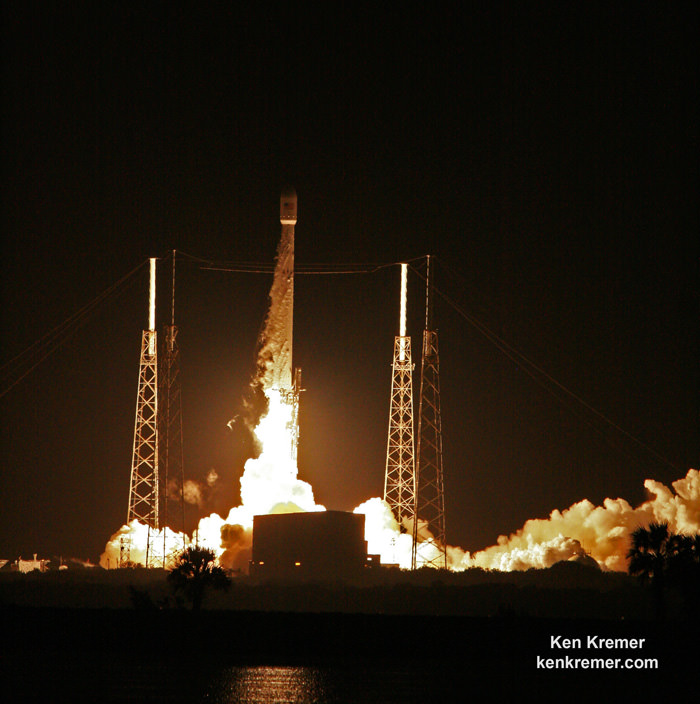
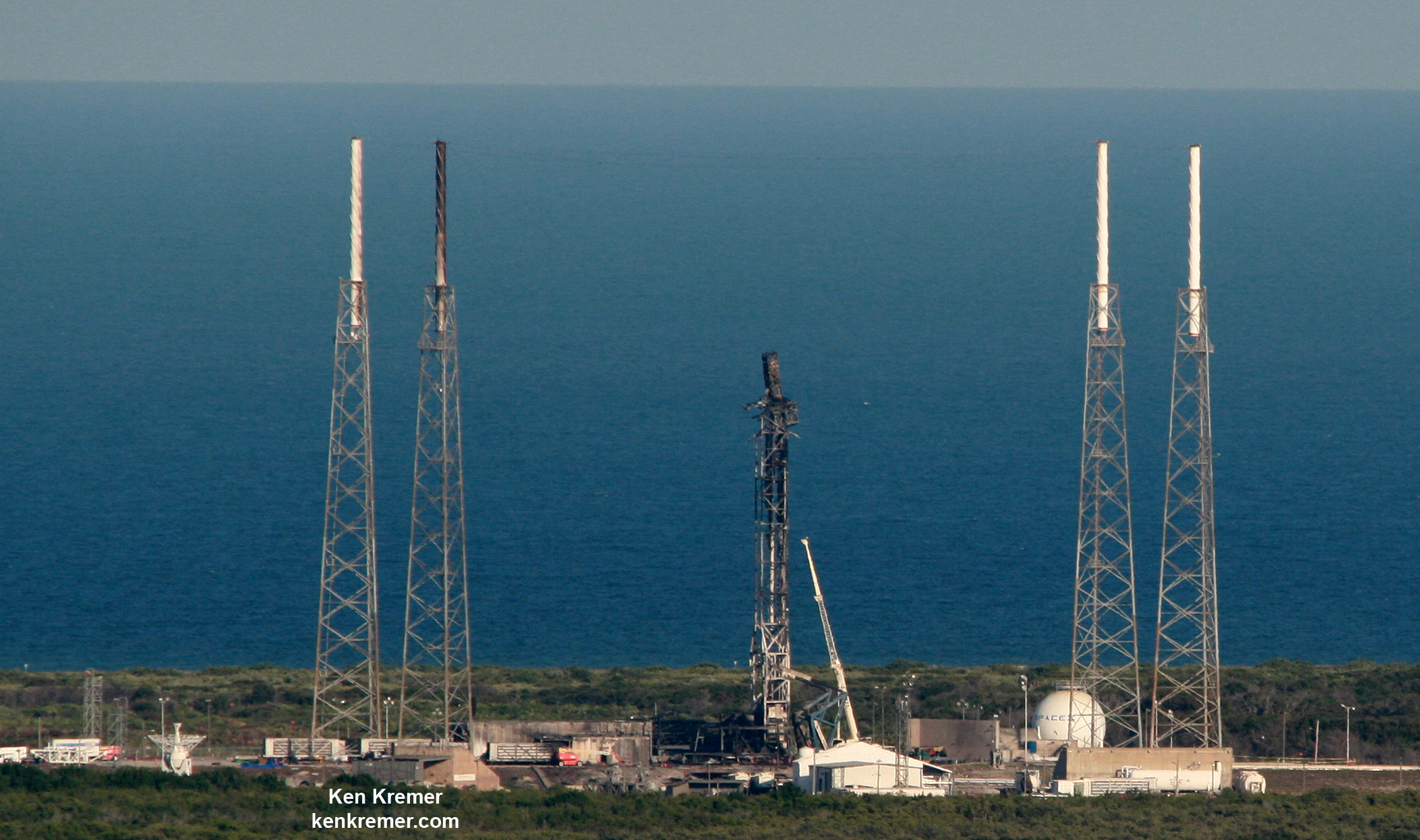
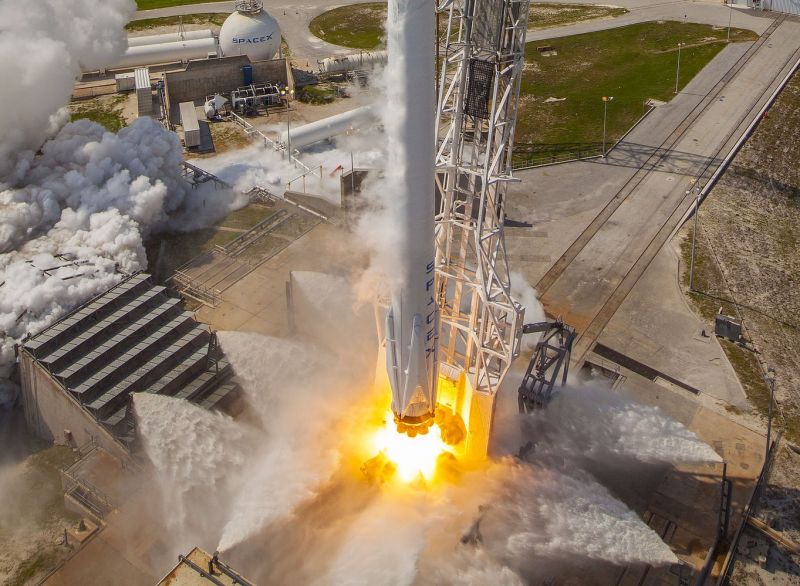
And with last week’s successful launch of the first reusable Falcon 9 (the SES-10 Mission) Musk chose to unveil more details about his company’s next major milestone. According to Musk, the demonstration flight of the Falcon Heavy – which is scheduled to take place this summer – will involve two recovered Falcon 9 cores and the attempted recovery of the rocket’s upper-stage.
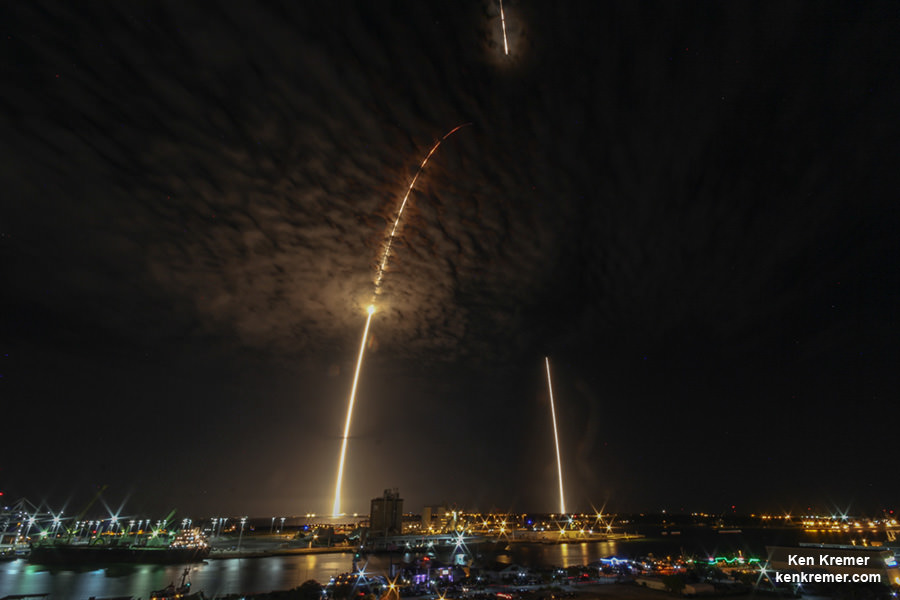
In other words, on its maiden flight, two of the three boosters sending the Falcon Heavy into orbit will be reused, and SpaceX may even try to attempt to make the first-ever recovery of a second stage. Such a feat, if successful, will signal that Musk’s dream of total reusability – where the first stage, payload fairings, and second stage of their launch vehicles are all recoverable – has come to fruition.

According to details shared at the news conference that accompanied the launch of SES-10, Musk indicated that the test flight would make use of boosters that were recovered from two successful Falcon 9 launches, and that all three would be recovered after launch. As he was quoted as saying by Stephen Clark at SpaceFlightNow:
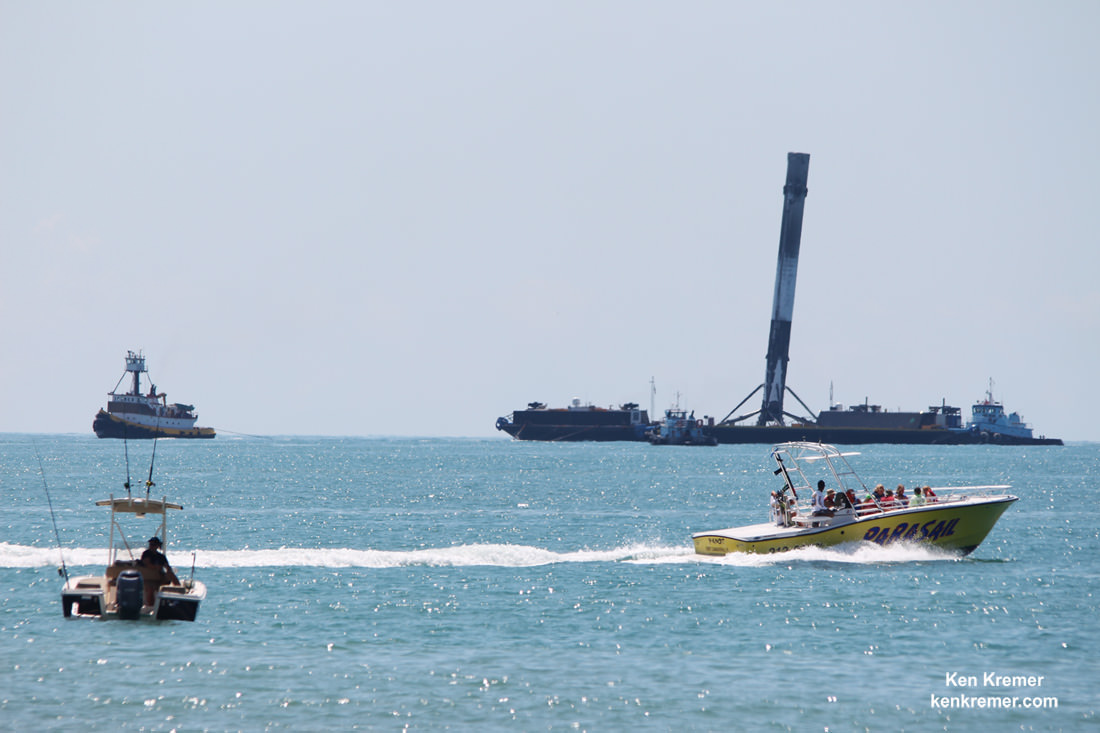
“That will be exciting mission, one way or another. Hopefully in a good direction. The two side boosters will come back and do sort of a synchronized aerial ballet and land. Two of the side boosters will land back at the Cape. That’ll be pretty exciting to see two come in simultaneously, and the center core will land downrange on the drone ship.”
On the following day – Friday, March. 31st, 11:44 am – Musk followed this up with a tweet that indicated that the test flight could also involve something that has never before been attempted. “”Considering trying to bring upper stage back on Falcon Heavy demo flight for full reusability,” he wrote. “Odds of success low, but maybe worth a shot.”
Such a plan is in keeping with what Musk had initially hoped for his company, which was to make all of its rockets entirely reusable. While reusable boosters were not a part of the initial designs for the Falcon Heavy, the numerous successful recoveries (on land and at sea) of the first stage of the Falcon 9 indicated that the Heavy‘s outer cores could be recovered and reused in the same way.
Musk also reiterated that the demo flight would be taking place this summer, and that it would be carrying something comically-inspired. “Silliest thing we can imagine!” he tweeted, in response to a question of what the cargo would be. “Secret payload of 1st Dragon flight was a giant wheel of cheese. Inspired by a friend & Monty Python.”
For those unfamiliar with what Musk was referring to “The Cheese Shop”, a classic Monty Python sketch. From this, we can safely assume that Musk has something similar in mind for the inaugural Falcon Heavy launch. Perhaps some wine and bread to go with that cheese?
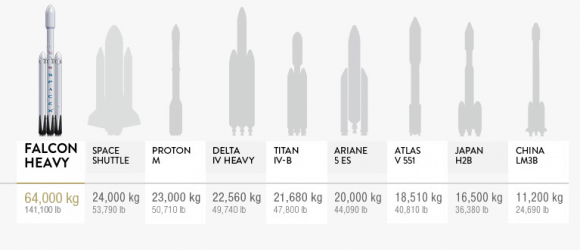
The demonstration flight – which will take place on launch pad 39A at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida – is already expected to be a momentous event. With the ability to lift payloads of over 64 metric tons (64,000 kg or 141,096 lbs) to Low Earth Orbit (LEO), the Falcon Heavy will be the most powerful rocket currently in operation.
In fact, its capacity will be about twice that of the Arianespace Ariane 5 and United Launch Alliance’s Delta IV Heavy rockets – which are capable of lifting 21,000 kg (46,000 lb) and 28,790 kg (63,470 lb) to LEO, respectively. However, SpaceX has indicated that the payload performance to geosynchronous transfer orbit (GTO) would be reduced with the addition of reusable technology.

Whereas its original capacity to GTO was said to be 22,200kg (48,940 lb), full reusability on all three booster cores will reduce this to 7,000 kg (15,000 lb), while having two reusable outside cores will reduce it to approximately 14,000 kg (31,000 lb). But of course, these reductions in payloads have to be considered against significantly reduced launch costs.
For the time being, the plan is to recover all three boosters of the Falcon Heavy. This may change, depending on the success of the maiden flight, to the point where just the outer boosters are deemed reusable and the central core expendable. And depending on the success of the second stage recovery, SpaceX may begin pursuing reusability with the second stages of their Falcon 9 as well.
Musk has also indicated that at present, SpaceX will be primarily focused on the many commercial missions it has planned using the Falcon 9 launch vehicle. But if all goes according to plan, this summer will be the second time in the space of a single year that Musk’s and the aerospace company he started knocked it out of the park and silenced all those who said he was attempting the impossible.
Further Reading: SpaceFlightNow, SpaceX