[/caption]









[/caption]










[/caption]
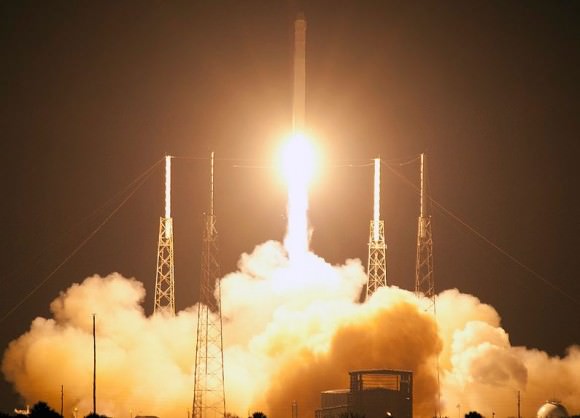
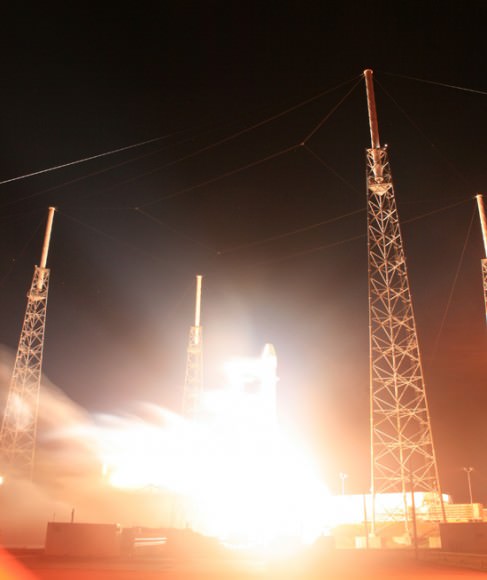
Today’s (May 19) historic launch of the first ever privately developed rocket bound for the International Space Station (ISS) was very surprisingly aborted at the last second when an engine glitch forced a dramatic shutdown of the Falcon 9 rockets 1st stage firing already in progress and as the NASA launch commentator was in the middle of announcing liftoff.
SpaceX and NASA are now targeting liftoff of the mission dubbed COTS 2, for Tuesday, May 22 at 3:44 AM EDT from Space Launch Complex-40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. There is another launch opportunity on May 23.
Later today, SpaceX engineers determined that a faulty valve caused the engine abort failure. They are now in a race against time to complete all the repair work and mandatory assurance testing required in order to be ready to achieve the new May 22 launch date.
The Falcon 9 rocket was designed and developed by SpaceX and the first stage is powered by nine Merlin 1 C engines. As the countdown clock ticked down to T-minus zero, all nine engines ignited. But engine #5 suddenly developed a “high chamber pressure” and computers instantaneously ordered a shutdown of thrust generation by all nine engines just 0.5 seconds from liftoff and the rocket therefore never left the pad, said SpaceX President Gwynne Shotwell at a briefing for reporters.
“We’ve had a cutoff,” announced NASA launch commentator George Diller. “Liftoff did not occur. We’ve had a launch abort. Standing by.”
After draining the explosive propellants, SpaceX engineers began inspecting the engines later today within hours of the aborted liftoff to determine the cause of the rocket engine malfunction.
“This is not a failure,” Shotwell told reporters at a post scrub media briefing. “We aborted with purpose. It would have been a failure if we lifted off with an engine trending in this direction.”
SpaceX may have caught a lucky break by being able to fix the rocket at the pad instead of a time consuming engine changout. Shotwell said that one possibility was to roll the Falcon 9 rocket back into the processing hangar and swap out the engine with a new one.
This evening SpaceX announced they had determined the cause of the engine failure.
“Today’s launch was aborted when the flight computer detected slightly high pressure in the engine 5 combustion chamber, said SpaceX spokeswoman Kirstin Grantham. “We have discovered root cause and repairs are underway.”

“During rigorous inspections of the engine, SpaceX engineers discovered a faulty check valve on the Merlin engine. We are now in the process of replacing the failed valve. Those repairs should be complete tonight. We will continue to review data on Sunday. If things look good, we will be ready to attempt to launch on Tuesday, May 22nd at 3:44 AM Eastern.”
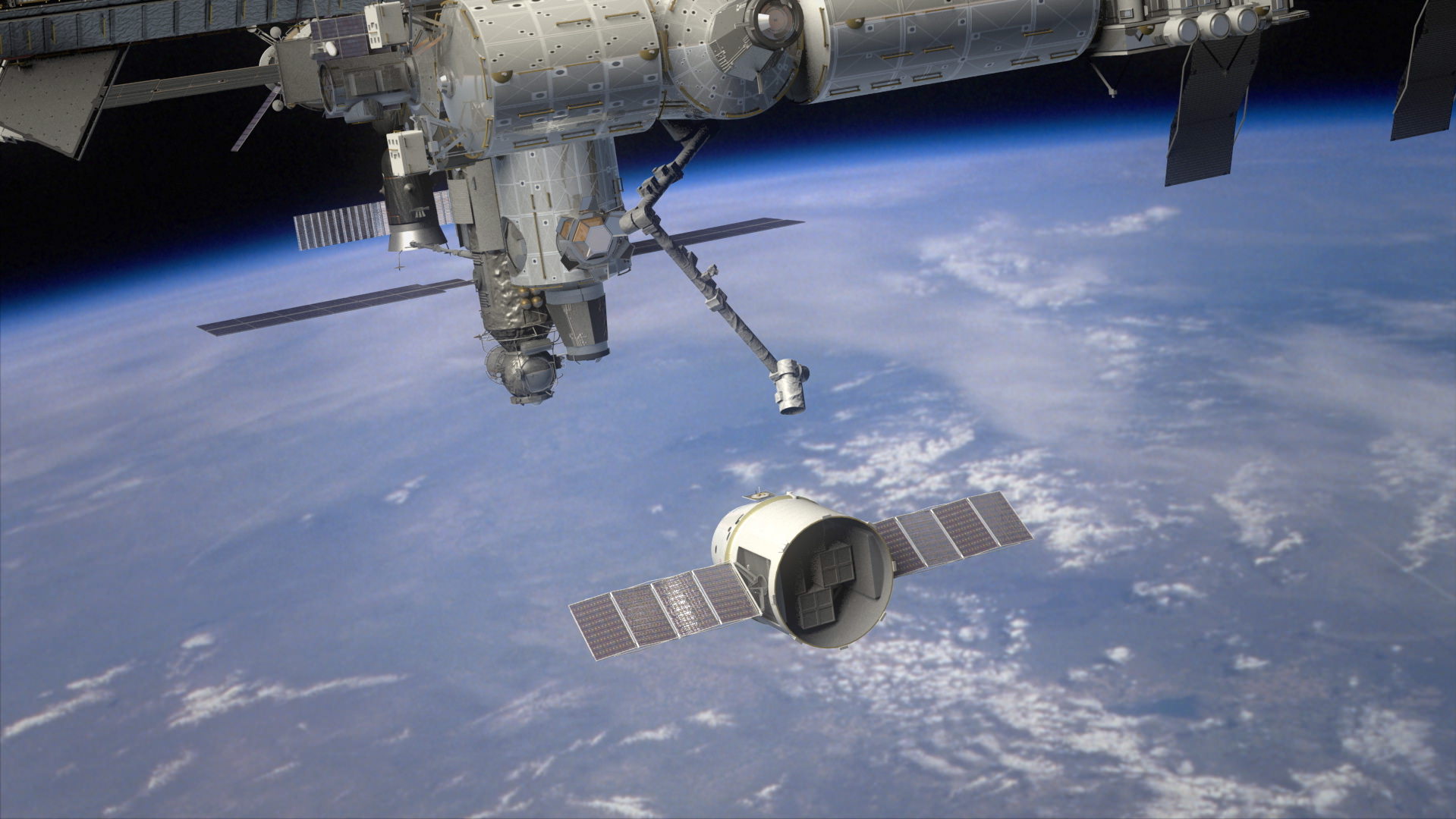
The purpose of Dragon is to carry some 1200 pounds of supplies up to orbit and dock at the ISS and partially replace the capabilities of NASA’s now retired space shuttle.

SpaceX is under contract with NASA to conduct twelve resupply missions to carry about 44,000 pounds of cargo to the ISS for a cost of some $1.6 Billion.

[/caption]
In less than 48 hours, SpaceX is primed to make history and launch the first ever commercial rocket and spacecraft to the International Space Station (ISS) early Saturday morning on May 19.
Following today’s Launch Readiness Review (LRR), SpaceX was just given the official “GO” from NASA to proceed with the blastoff of the Falcon 9 at 4:55 a.m. EDT (0855 GMT) from Space Launch Complex-40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. This also marks the first night time liftoff of the Falcon 9 rocket.
“Just passed final launch review with NASA”, SpaceX CEO Elon Musk tweeted this evening. “All systems go for liftoff on Sat morn”.
The SpaceX developed Dragon cargo resupply spacecraft is bolted on top of the two stage Falcon 9 rocket and stands 157 feet tall for the mission dubbed “COTS 2”. The Falcon 9 booster generates 1 million pounds of thrust
The official Air Force weather forecast gives a 70% chance of acceptable conditions for launch. The primary concern for launch day is a violation of the Cumulus Cloud Rule. On the heels of a significant drought, stormy weather has rolled into the Florida Space Coast and thunder is striking the area at the moment.
In the event of a launch scrub, the next launch opportunity comes in three days on May 22.
The launch will be broadcast live on NASA TV and via SpaceX Webcast at http://spacex.com

Technicians plan to roll the Falcon 9/Dragon duo out to the seaside launch pad tonight. The rocket will be moved on rail tracks about 600 feet from the processing hanger to the pad and vertically erected.
The purpose of Dragon is to carry supplies up to orbit and dock at the ISS and partially replace the capabilities of NASA’s now retired space shuttle. Dragon is a commercial spacecraft designed and developed by SpaceX.
SpaceX is under contract with NASA to conduct twelve resupply missions to the ISS to carry cargo back and forth for a cost of some $1.6 Billion.
The Dragon spacecraft is loaded with nearly 1200 pounds of non-critical cargo such as food and clothing on this flight. A collection of student experiments, commemorative patches, pins and emblems will also be on board Dragon’s upcoming test flight.
On Friday, Ken will be reporting from Space Launch Complex-40 on Cape Canaveral.
[/caption]SpaceX has announced that the upcoming launch of the firms Falcon 9 and Dragon spacecraft on the commercial COTS 2 mission has been postponed to a new target date of no earlier than May 19 with a backup launch date of May 22.
On May 19, the Falcon 9 rocket would lift off on its first night time launch at 4:55 a.m. EDT (0855 GMT) from Space Launch Complex-40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
Two launch opportunities had been available this week on May 7 and May 10, following the most recent slip from April 30.
SpaceX managers made the decision – in consultation with NASA – to delay the COTS 2 launch in order to complete further highly critical testing and verifications of all the flight software requirements for the Dragon spacecraft to safely and successfully carry its mission of rendezvousing and docking with the International Space Station (ISS).
“SpaceX and NASA are nearing completion of the software assurance process, and SpaceX is submitting a request to the Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for a May 19th launch target with a backup on May 22nd,” said SpaceX spokesperson Kirstin Grantham.
“Thus far, no issues have been uncovered during this process, but with a mission of this complexity we want to be extremely diligent.”
May 10 was the last window of opportunity this week because of the pending May 14 blast off of a new Russian Soyuz TMA-04M capsule from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan with three fresh crew members bound for the ISS which will restore the outpost to a full crew complement of 6 human residents.
The Falcon 9 and Dragon can only be launched about every three days.
The purpose of Dragon is to carry supplies up to and back from the ISS. Dragon is a commercial spacecraft developed by SpaceX and designed to replace some of the cargo resupply functions previously conducted by NASA’s fleet of prematurely retired Space Shuttle orbiters. At this moment the US has zero capability to launch cargo or crews to the ISS.

In response to the SpaceX announcement, NASA issued the following statement from from William Gerstenmaier, associate administrator for Human Exploration and Operations at the agency’s Headquarters in Washington:
“After additional reviews and discussions between the SpaceX and NASA teams, we are in a position to proceed toward this important launch. The teamwork provided by these teams is phenomenal. There are a few remaining open items, but we are ready to support SpaceX for its new launch date of May 19.”
SpaceX is under contract with NASA to conduct twelve resupply missions to the ISS to carry cargo back and forth for a cost of some $1.6 Billion.
Dragon is loaded with nearly 1200 pounds of non-critical cargo such as food and clothing on this flight.
The COTS 2 mission has been repeatedly delayed since the originally planned target of mid-2011 when SpaceX requested that the COTS 2 and 3 flights be combined into one mission to save time. The first Dragon docking to the ISS was initially planned for the COTS 3 mission.


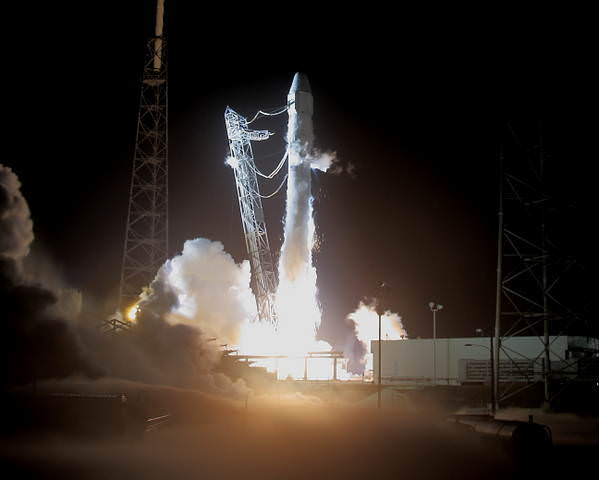
It was short but sweet. SpaceX conducted a 2-second static fire test of their Falcon 9 rocket that will send the first COTS flight to the International Space Station. “Woohoo, rocket hold down firing completed and all looks good!!” Tweeted SpaceX CEO and founder Elon Musk. SpaceX’s Twitter feed said with the successful firing, engineers will now review data as they continue to prepare for the upcoming mission, slated to launch on May 7.
A first attempt was aborted with 30 seconds left in the countdown, due to “overly restrictive redline on second stage engine position.” Engineers recycled all the rocket’s systems and began another countdown.
Fire and smoke erupted just briefly from the base of the rocket, and there seemed to be a bit of confusion on the webcast, as the word “abort” was used, but then there was word of success and the webcast ended abruptly.
[/caption]
For the static fire test, the nine Merlin engines on the first stage of the Falcon 9 rocket were ignited at 20:15 UTC (4:15 p.m. EDT). The test was part of a full dress rehearsal for the SpaceX team. Last week was a final full simulation between NASA and SpaceX for the series of demonstration maneuvers and tests the Dragon capsule will make as it approaches the ISS; then the astronauts on board will capture and berth the cargo capsule to the Harmony module’s Earth-facing docking port.
If the abort problem had occured on the launch day, there would be no second attempt; there is no recycling of the systems for an actual launch. Additionally, the Falcon 9 can only attempt launch every 3 days because of limited propellant on Dragon capsule. SpaceX needs to ensure there is enough propellant on board Dragon for the pre-berthing maneuvers and tests.
If the Falcon 9 launch is delayed by weather or technical problems, another attempt could be made on May 10, but after that they would have to until after the launch of a Russian Soyuz spacecraft that will bring three new crew members to the space station. That mission is scheduled for launch from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan on May 14, and would dock two days later.
The launch of the Falcon 9 and Dragon has been delayed from its initial planned flight in February, but with today’s apparently successful test, SpaceX and NASA are hopeful for going forward with next week’s launch.
SpaceX is one of two companies, along with Orbital Sciences, competing for contracts to deliver cargo to low Earth orbit for NASA under the Commercial Orbital Transportation System program.
The launch is currently set for 13:38 UTC (9:38 a.m. EDT) on Monday.

[/caption]
The first test launch of a commercially built spacecraft to the International Space Station has been delayed by its builder, Space Exploration Technologies or SpaceX, in order to carry out additional testing to ensure that the vehicle is fully ready for the high stakes Earth orbital mission.
SpaceX and NASA had been working towards a Feb. 7 launch date of the company’s Dragon spacecraft and announced the postponement in a statement today (Jan. 16).
A new target launch date has not been set and it is not known whether the delay amounts to a few days, weeks or more. The critical test flight has already been rescheduled several times and was originally planned for 2011.
The unmanned Dragon is a privately developed cargo vessel constructed by SpaceX under a $1.6 Billion contract with NASA to deliver supplies to the ISS and partially replace the transport to orbit capabilities that were fully lost following the retirement of the Space Shuttle in 2011.
“In preparation for the upcoming launch, SpaceX continues to conduct extensive testing and analysis, said SpaceX spokeswoman Kirstin Grantham in the statement.
“We [SpaceX] believe that there are a few areas that will benefit from additional work and will optimize the safety and success of this mission.”
“We are now working with NASA to establish a new target launch date, but note that we will continue to test and review data. We will launch when the vehicle is ready,” said Grantham.
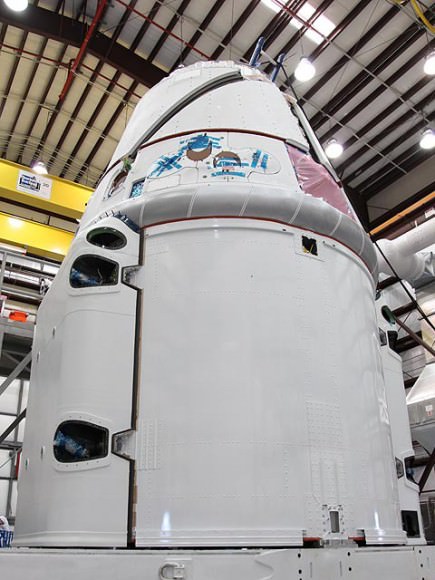

Dragon’s purpose is to ship food, water, provisions, equipment and science experiments to the ISS.
The demonstration flight – dubbed COTS 2/3 – will be the premiere test flight in NASA’s new strategy to resupply the ISS with privately developed rockets and cargo carriers under the Commercial Orbital Transportation Services (COTS) initiative.
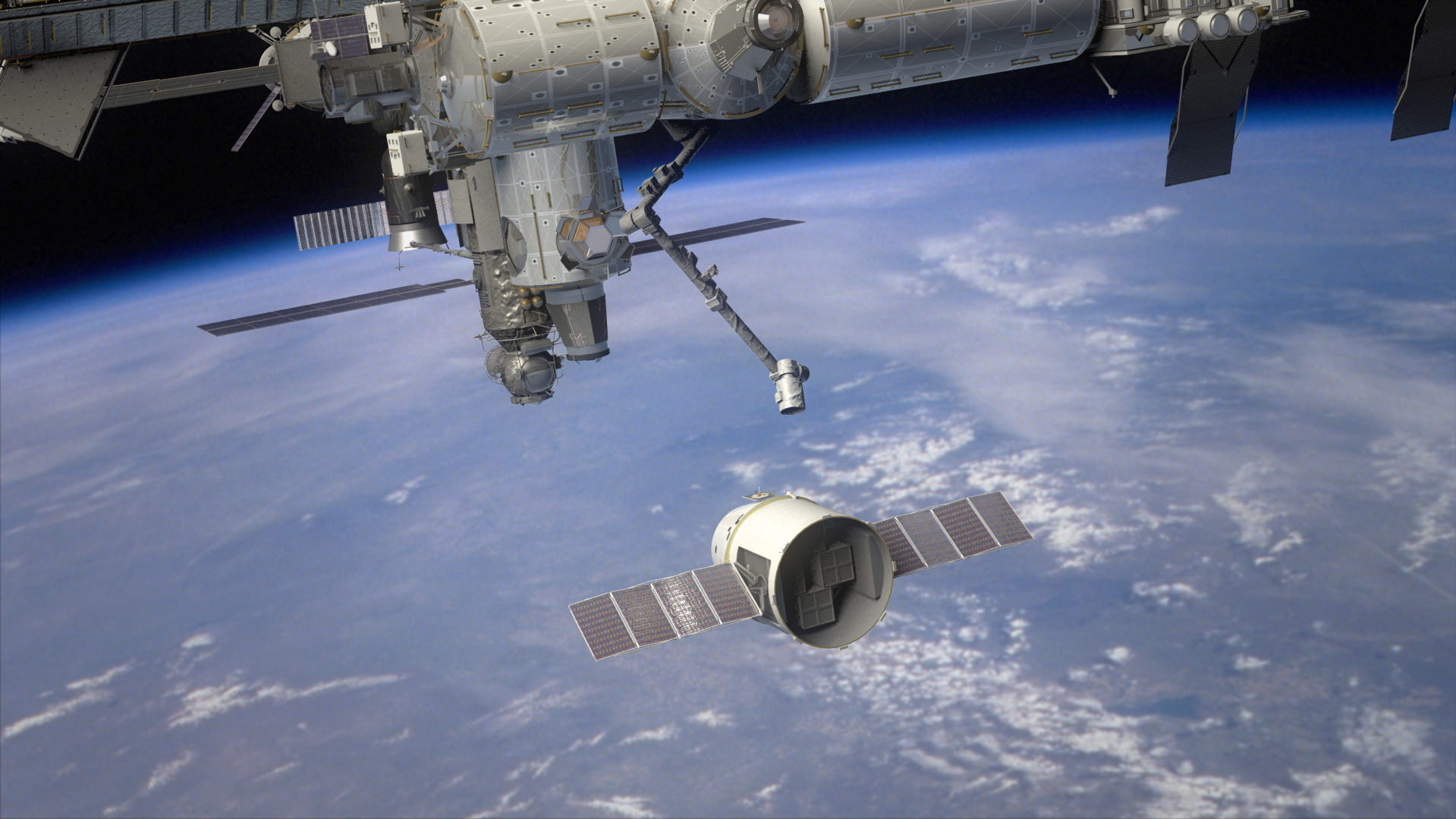
The Dragon will blast off atop a Falcon 9 booster rocket also built by SpaceX and, if all goes well, conduct the first ever rendezvous and docking of a privately built spacecraft with the 1 million pound orbiting outpost.
After closely approaching the ISS, the crew will grapple Dragon with the station’s robotic arm and berth it to the Earth-facing port of the Harmony node.
“We’re very excited about it,” said ISS Commander Dan Burbank in a recent televised interview from space.

Since the demonstration mission also involves many other first time milestones for the Dragon such as the first flight with integrated solar arrays and the first ISS rendezvous, extra special care and extensive preparatory activities are prudent and absolutely mandatory.
NASA’s international partners, including Russia, must be consulted and agree that all engineering and safety requirements, issues and questions related to the docking by new space vehicles such as Dragon have been fully addressed and answered.
William Gerstenmaier, NASA’s associate administrator for the Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate recently stated that the launch date depends on completing all the work necessary to ensure safety and success, “There is still a significant amount of critical work to be completed before launch, but the teams have a sound plan to complete it.”
“As with all launches, we will adjust the launch date as needed to gain sufficient understanding of test and analysis results to ensure safety and mission success.”
“A successful mission will open up a new era in commercial cargo delivery to the international orbiting laboratory,” said Gerstenmaier.
SpaceX is also working on a modified version of the spacecraft, dubbed DragonRider, that could launch astronaut crews to the ISS in perhaps 3 to 5 years depending on the amount of NASA funding available, says SpaceX CEO and founder Elon Musk
Read Ken’s recent features about the ISS and SpaceX/Dragon here:
Dazzling Photos of the International Space Station Crossing the Moon!
Solar Powered Dragon gets Wings for Station Soar
Absolutely Spectacular Photos of Comet Lovejoy from the Space Station
NASA announces Feb. 7 launch for 1st SpaceX Docking to ISS

[/caption]
The Dragon has grown its mighty wings
SpaceX’s Dragon spacecraft has gotten its wings and is set to soar to the International Space Station (ISS) in about a month. NASA and SpaceX are currently targeting a liftoff on Feb. 7 from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
Dragon is a commercially developed unmanned cargo vessel constructed by SpaceX under a $1.6 Billion contract with NASA. The Dragon spacecraft will launch atop a Falcon 9 booster rocket also built by SpaceX, or Space Exploration Technologies.

The Feb. 7 demonstration flight – dubbed COTS 2/3 – represents the first test of NASA’s new strategy to resupply the ISS with privately developed rockets and cargo carriers under the Commercial Orbital Transportation Services (COTS) initiative.
Following the forced retirement of the Space Shuttle after Atlantis final flight in July 2011, NASA has no choice but to rely on private companies to loft virtually all of the US share of supplies and equipment to the ISS.
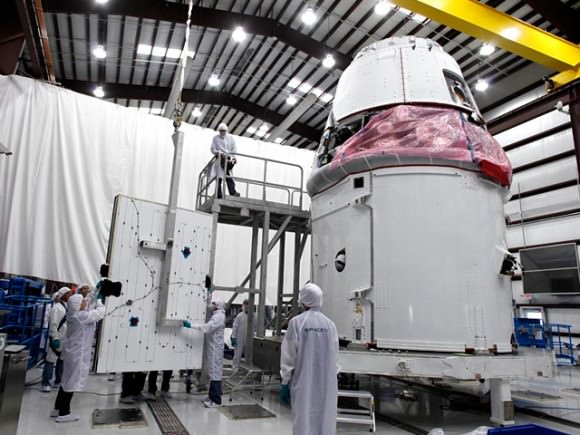
The Feb. 7 flight will be the first Dragon mission actually tasked to dock to the ISS and is also the first time that the Dragon will fly with deployable solar arrays. The twin arrays are the primary power source for the Dragon. They will be deployed a few minutes after launch, following Dragon separation from the Falcon 9 second stage.
The solar arrays can generate up to 5000 watts of power on a long term basis to run the sensors and communications systems, drive the heating and cooling systems and recharge the battery pack.
SpaceX designed, developed and manufactured the solar arrays in house with their own team of engineers. As with all space hardware, the arrays have been rigorously tested for hundreds of hours under the utterly harsh conditions that simulate the unforgiving environment of outer space, including thermal, vacuum, vibration, structural and electrical testing.

The two arrays were then shipped to Florida and have been attached to the side of the Dragon’s bottom trunk at SpaceX’s Cape Canaveral launch processing facilities. They are housed behind protective shielding until commanded to deploy in flight.
Video Caption: SpaceX testing of the Dragon solar arrays. Credit: SpaceX
I’ve toured the SpaceX facilities several times and seen the Falcon 9 and Dragon capsule launching on Feb. 7. The young age and enthusiasm of the employees is impressive and quite evident.
NASA recently granted SpaceX the permission to combine the next two COTS demonstration flights into one mission and dock the Dragon at the ISS if all the rendezvous practice activities in the vicinity of the ISS are completed flawlessly.
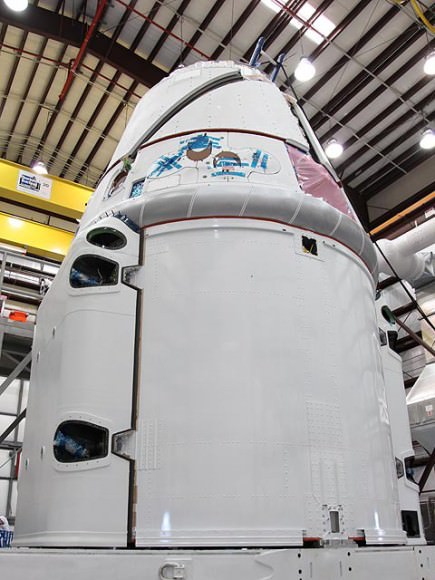

The ISS crew is eagerly anticipating the arrival of Dragon, for whch they have long trained.
“We’re very excited about it,” said ISS Commander Dan Burbank in a televised interview from on board the ISS earlier this week.
The ISS crew will grapple the Dragon with the station’s robotic arm when it comes within reach and berth it to the Earth-facing port of the Harmony node.
“From the standpoint of a pilot it is a fun, interesting, very dynamic activity and we are very much looking forward to it,” Burbank said. “It is the start of a new era, having commercial vehicles that come to Station.”
Burbank is a US astronaut and captured stunning images of Comet Lovejoy from the ISS just before Christmas, collected here.
Read recent features about the ISS and commercial spaceflight by Ken Kremer here:
Dazzling Photos of the International Space Station Crossing the Moon!
Absolutely Spectacular Photos of Comet Lovejoy from the Space Station
NASA announces Feb. 7 launch for 1st SpaceX Docking to ISS
Jan 11: Free Lecture by Ken at the Franklin Institute, Philadelphia, PA at 8 PM for the Rittenhouse Astronomical Society. Topic: Mars & Vesta in 3 D – Plus Search for Life & GRAIL
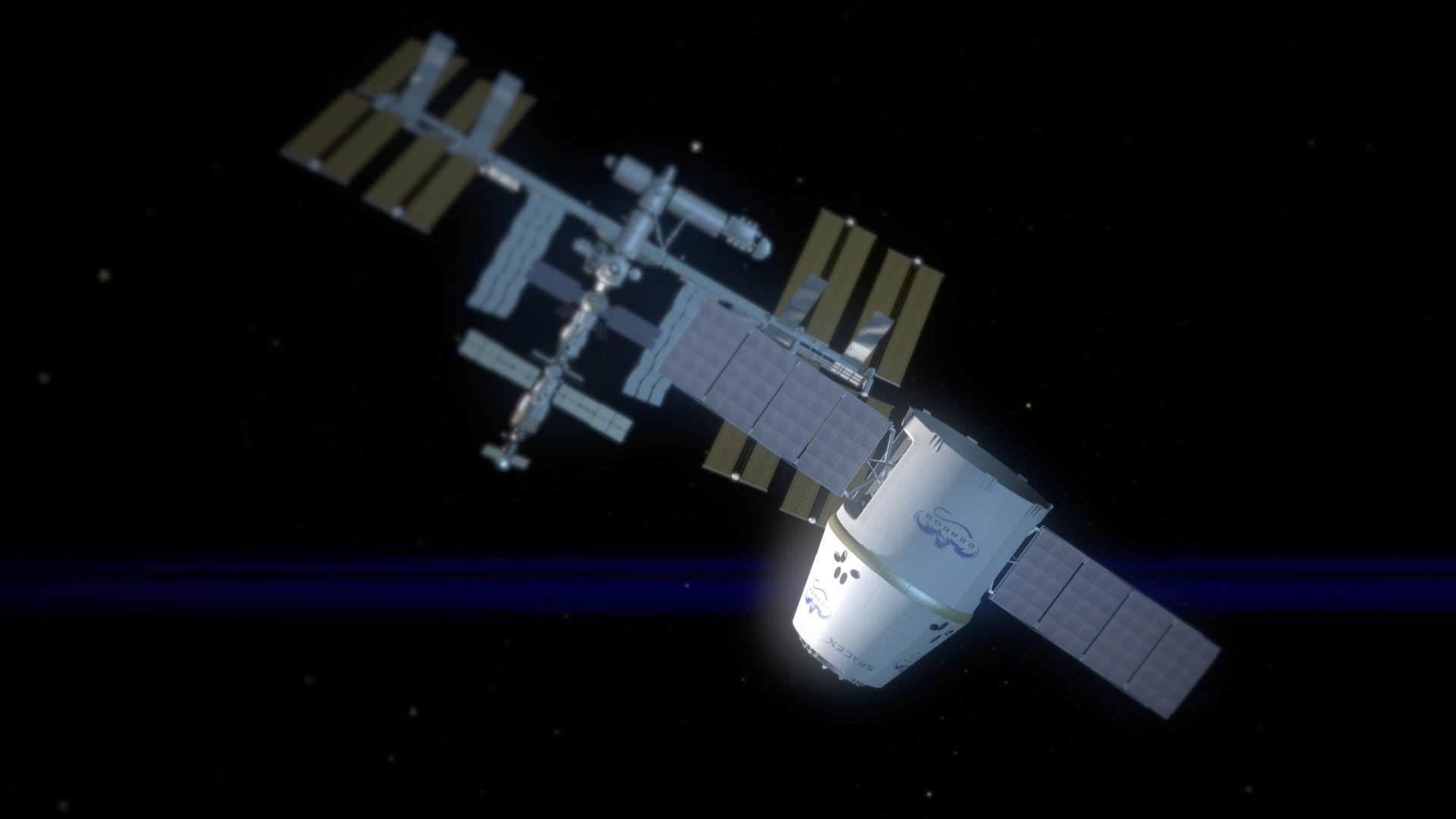

[/caption]
Make or break time for NASA’s big bet on commercial space transportation is at last in view. NASA has announced Feb. 7, 2012 as the launch target date for the first attempt by SpaceX to dock the firms Dragon cargo resupply spacecraft to the International Space Station (ISS), pending final safety reviews.
The Feb. 7 flight will be the second of the so-called Commercial Orbital Transportation Services (COTS) demonstration flights to be conducted by Space Exploration Technologies, or SpaceX, under a contact with NASA.
Several months ago SpaceX had requested that the objectives of the next two COTS flights, known as COTS 2 and COTS 3, be merged into one very ambitious flight and allow the Dragon vehicle to actually dock at the ISS instead of only accomplishing a rendezvous test on the next flight and waiting until the third COTS flight to carry out the final docking attempt.
The Dragon will remain attached to the ISS for about one week and astronauts will unload the cargo. Then the spacecraft will depart, re-enter the Earth atmosphere splashdown in the Pacific Ocean off the coast of California.
“The cargo is hundreds of pounds of astronaut provisions,” SpaceX spokeswoman Kirstin Grantham told Universe Today.

“SpaceX has made incredible progress over the last several months preparing Dragon for its mission to the space station,” said William Gerstenmaier, NASA’s associate administrator for the Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. “We look forward to a successful mission, which will open up a new era in commercial cargo delivery for this international orbiting laboratory.”
Since the forced retirement of NASA’s Space Shuttle following the final fight with orbiter Atlantis in July 2011 on the STS-135 mission, the US has had absolutely zero capability to launch either supplies or human crews to the massive orbiting complex, which is composed primarily of US components.
In a NASA statement, Gerstenmaier added, “There is still a significant amount of critical work to be completed before launch, but the teams have a sound plan to complete it and are prepared for unexpected challenges. As with all launches, we will adjust the launch date as needed to gain sufficient understanding of test and analysis results to ensure safety and mission success.”
SpaceX lofted the COTS 1 flight a year ago on Dec. 8, 2010 and became the first private company to successfully launch and return a spacecraft from Earth orbit. SpaceX assembled both the Falcon 9 booster rocket and the Dragon cargo vessel from US built components.

The new demonstration flight is now dubbed COTS 2/3. The objectives include Dragon safely demonstrating all COTS 2 operations in the vicinity of the ISS by conducting check out procedures and a series of rendezvous operations at a distance of approximately two miles and the ability to abort if necessary.
The European ATV and Japanese HTV cargo vessels carried out a similar series of tests during their respective first flights.
After accomplishing all the rendezvous tasks, Dragon will then receive approval to begin the COTS 3 activities, gradually approaching the ISS from below to within a few meters.
Specially trained astronauts working in the Cupola will then reach out and grapple Dragon with the Station’s robotic arm and then maneuver it carefully into place onto the Earth-facing side of the Harmony node. The operations are expected to take several hours.
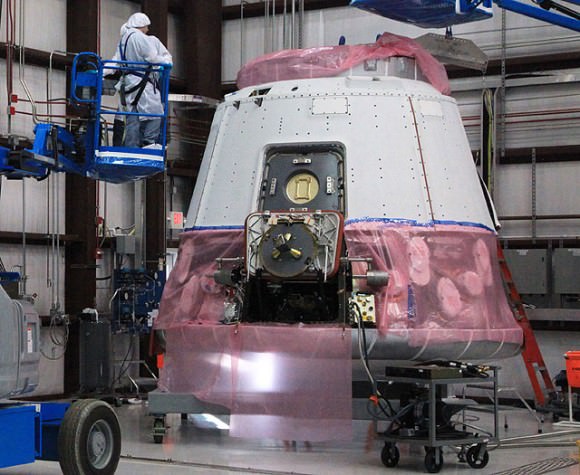

If successful, the Feb. 7 SpaceX demonstration flight will become the first commercial mission to visit the ISS and vindicate the advocates of commercial space transportation who contend that allowing private companies to compete for contracts to provide cargo delivery services to the ISS will result in dramatically reduced costs and risks and increased efficiencies.
The new commercial paradigm would also thereby allow NASA to focus more of its scarce funds on research activities to come up with the next breakthroughs enabling bolder missions to deep space.
If the flight fails, then the future of the ISS could be in serious jeopardy in the medium to long term because there would not be sufficient alternative launch cargo capacity to maintain the research and living requirements for a full crew complement of six residents aboard the orbiting laboratory.
Feb. 7 represents nothing less than ‘High Stakes on the High Frontier’.
NASA is all about bold objectives in space exploration in both the manned and robotic arenas – and that’s perfectly represented by the agencies huge gamble with the commercial cargo and commercial crew initiatives.
[/caption]
Enjoy a few glimpses at history from the Dec. 8 launch of Falcon 9 and Dragon.
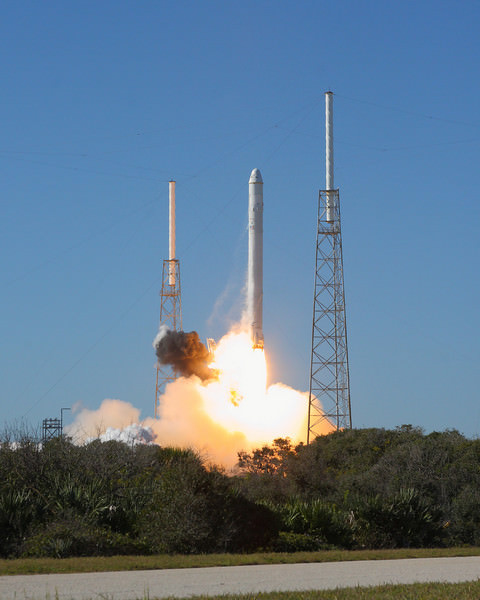



Here is video from a camera on Dragon while in orbit.


And for good measure, here’s the launch video again:
NASA Administrator Charlie Bolden’s statement on the success of the launch:

[/caption]
Hailed as a both a great day for commercial spaceflight as well as for NASA, SpaceX made history on Wednesday with a 100% successful test flight of its Dragon capsule and Falcon 9 rocket. “This is a new way of doing business,” said Alan Lindenmoyer manager of NASA’s Commercial Crew and Cargo Program Office, “and I would say today this is an indication that this public/private partnership is working and has proven to be successful. Thanks to SpaceX for the early Christmas present – this is a great way to start the holidays.”
At the press conference following the flight, SpaceX CEO Elon Musk at first appeared to be speechless: “Really, this has been better than I expected,” he said. “It all went right. I am sort of in semi shock—I wish I could be more articulate in moments like this, bit it’s hard to be articulate with a blown mind!”
But Musk soon found his words – and lots of them (with many great quotes, so keep reading…)

Lindenmoyer said SpaceX’s accomplishments are quite an achievement, since over the last 20 years, for new launch vehicles only about 50% of them are success are successful on their first or second flights, and only 1 out of 3 new vehicles have two successful flights in a row, which SpaceX has achieved.
Musk said the success really shouldn’t be a surprise since the Dragon spacecraft has so many redundancies: 18 thruster engines instead of 9, 3 parachutes when they really could land with one, extra thermal protection, and a very advanced heat shield. But in the end, SpaceX didn’t need to use any of the backup systems.
Preliminary data said the Dragon reentered the atmosphere spot on at a 12% angle of attack, with 2% dispersion. “This is a testament to the incredible work of the people at SpaceX,” he said. “Everyone did their jobs so well.”
Musk also emphasize that his company couldn’t have gotten to where they are without NASA, in not only monetary support ($278 million for the COTS program), but in leading the way in spaceflight.
“The core concepts of Falcon 9 and Dragon were demonstrated decades ago by NASA, and its an old saying, but we are only here because we stand on the shoulders of giants. So thank you,” he said.
Musk noted a few key things about the flight: The restart of Falcon 9’s second stage went perfectly; the second stage as restarted after the release of Dragon, and rose to an altitude of more than 11,000 km (6,800 miles), Musk said. Secondary satellite payloads of nanosatellites were released during the flight. And, Musk added, that altitude was with the trimmed, repaired nozzle. Reaching an altitude that high was not part of SpaceX’s primary objectives, but nice to have, Musk said.
Dragon went to an altitude of 300 km.
Musk also stressed that the difference between this Dragon capsule and one that could carry people isn’t that different.
“People sometimes think the different between cargo and crew required enormous amount of magical pixie dust,” he said “This is not the case. If there would have been people sitting in Dragon today, they would have had a nice ride, feeling about 4-5 G’s, which is about what an amusement park ride is like,” with an 8 meter per second descent speed which is quite comfortable from a landing perspective.

The only differences, Musk said, would be the addition of a launch escape system. And, he revealed, what SpaceX really hopes to do with future spacecraft is not a splashdown in the ocean but a propulsive landing on the ground.
“The architecture you saw today was similar to what was employed in Apollo era, but we are aiming for propulsive landing with gear, kind of like the Eagle landing on the moon, and being able to take off again” he said. “Full reusability of Dragon and Falcon 9 is important as well, and something we want to figure out over time.”
Musk also said this mission didn’t have many significant differences in one that would send the Dragon the ISS. “In our discussions with NASA they said if this flight went well they would strongly consider letting us go to the space station on next mission,” he said. “I hope that is what NASA will allow us to do, we need to still examine the data from this mission first, but I’m highly optimistic. There are additional elements to be added to Dragon such as solar panels and redundancy on flight computers and electronics, but feel highly confident we could make it to the ISS on our next flight by middle of next year.”
Today’s flight tested the fundamentals of a heat shield and precision landing. Musk said the performance of heat shield was spectacular, and projected that is could not only handle Earth reentry, but also lunar and Mars reentry.
SpaceX president Gwynne Shotwell noted some other technical details, of how Dragon was able to maintain attitude and thermal control, as well as maintain communications with ground stations and TEDRIS satellites, which requires specific directional pointing.
The entire launch and two orbit flight took 3 hours 19 min 52 seconds, and initial data said they landed within 10 km of their target, and a communiqué from the Air force said Dragon came within 800 meters.
Asked about the flame flare that came about 2 seconds after launch, Musk said the first look by engineers said it was a check valve on the second stage umbilical that came off and caught fire as the spacecraft engines passed by — not an explosion but a just little fire.
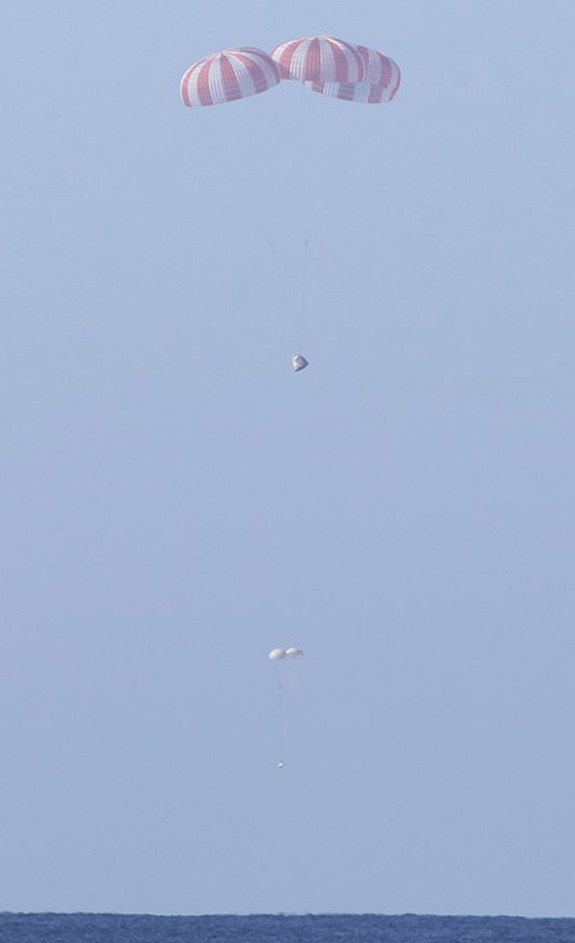
Musk said the point in the flight where he felt the most jubilation and great relief was when the parachutes deployed. “Drogue and main chute deploy were riskiest parts, so when that happened, it was done deal. Just mind-blowingly awesome.”
Asked if the success today would silence any of SpaceX’s critics, Musk said, “I think if there really are people who are going still find a way to cast aversions on what we’ve done today, I pity them. It just wouldn’t make any sense.”
He said politicians who initially wanted to cut commercial crew funds from NASA’s budget soon learned that such a move would not decrease but increase the deficit and also meant increased time with no American access to space. “I think some politicians were initially mislead, but then they realized the value of commercial crew, which is why it the cuts didn’t make it into the final report.”
Asked about the differences in Dragon and NASA’s Orion spacecraft, Musk said that Space X would probably be the most rapid path to an American crew transport system. “If we would have had people on this flight we would have taken them to orbit and returned them safely,” he said. “Going to a crew system is just adding some additional safety systems for highly off nominal activities. Even for cargo missions we will be carrying plants and animals so I think we are in a very strong position to be one of the winners of the commercial crew contract.”
Musk added that competition is good, however, and NASA shouldn’t be too dependent on one company,” so hopefully there will be two or maybe three commercial crew providers and hopefully we are one of them.”
Musk agreed with Lindenmoyer on how this appears to vindicate the public/private model of space flight and shows that the commercial model works just as well in space flight as in air flight, or other arenas.
“The air mail program was a huge boost when the Post Office went commercial,” he said “and that resulted in explosion of innovation and improvement in technology. It really was the dawn of aviation in American where it went from joy rides that rich people could do, to today where aviation is accessible to almost everyone. I think historically COTS program will be seen in that light.”
On board Dragon was a few small satellites, and look for Musk to reveal tomorrow the nature of a humorous item that was on board. “I’m not going to reveal it today, as I don’t want some of the editors to use it in the first headlines,” he said. “It is kind of funny and if you like Monty Python you’ll like this one.”
Spam in a can?
Universe Today extends their congratulations to SpaceX. The future appears to be now.