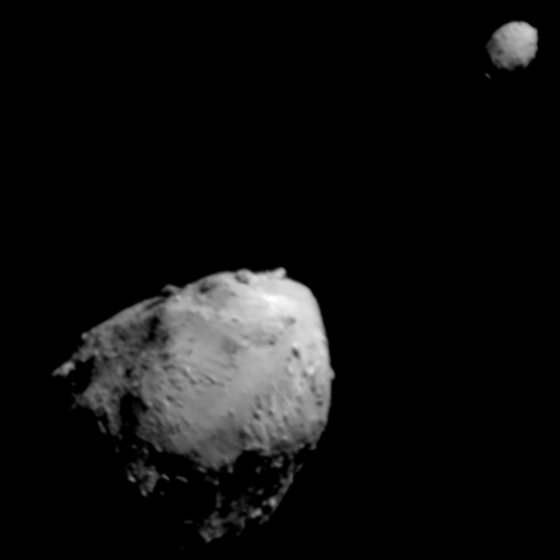
The European Space Agency’s Hera spacecraft is on its way to do follow-up observations of Dimorphos, two years after an earlier probe knocked the mini-asteroid into a different orbital path around a bigger space rock.
Scientists say the close-up observations that Hera is due to make millions of miles from Earth, starting in 2026, will help them defend our planet from future threats posed by killer asteroids.
Continue reading “Hera Probe Heads Off to See Aftermath of DART’s Asteroid Impact”