According to our predominant cosmological models, Dark Matter accounts for roughly 85% of the mass in the Universe. While ongoing efforts to study this mysterious, invisible mass have yielded no direct evidence, astrophysicists have been able to measure its influence by observing Dark Matter Haloes, gravitational lenses, and the effect of General Relativity on large-scale cosmic structures. And with the help of next-generation missions like the ESA’s Euclid and NASA’s Nancy Grace Roman space telescopes, Dark Matter may not be a mystery for much longer!
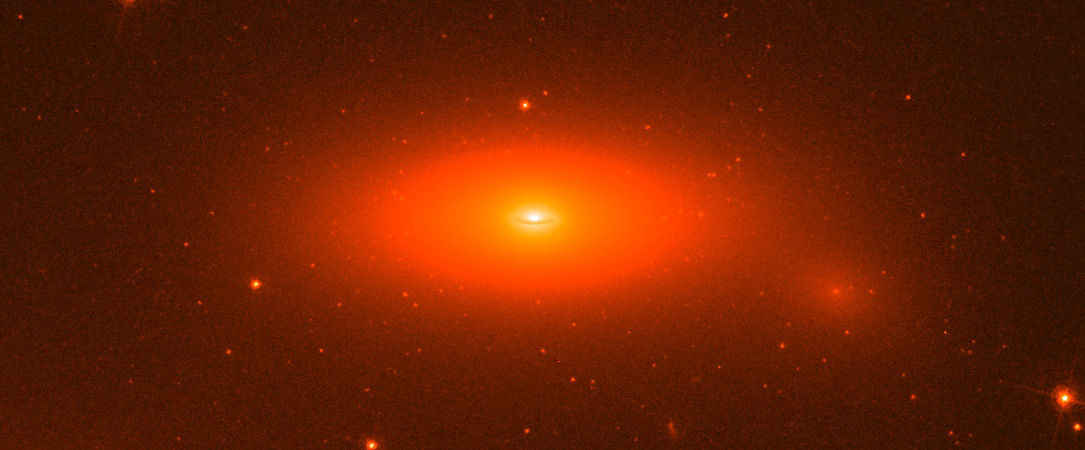
And then something like this comes along: a massive galaxy that appears to have little or no Dark Matter! This is precisely what a team of astronomers led by members of the Instituto Astrofisica de Canarias (IAC) noticed when observing NGC 1277. This lenticular galaxy, located 240 million light-years away in the constellation Perseus, is several times more massive than the Milky Way. This is the first time a massive galaxy has been found that doesn’t show signs of Dark Matter, which is a serious challenge to our current cosmological models.
Continue reading “A Massive Galaxy With Almost No Dark Matter”