Orbital ATK is on the rebound with return to flight of their Antares rocket slated in early 2016 following the catastrophic launch failure that doomed the last Antares in October 2014 on a resupply mission for NASA to the International Space Station (ISS).
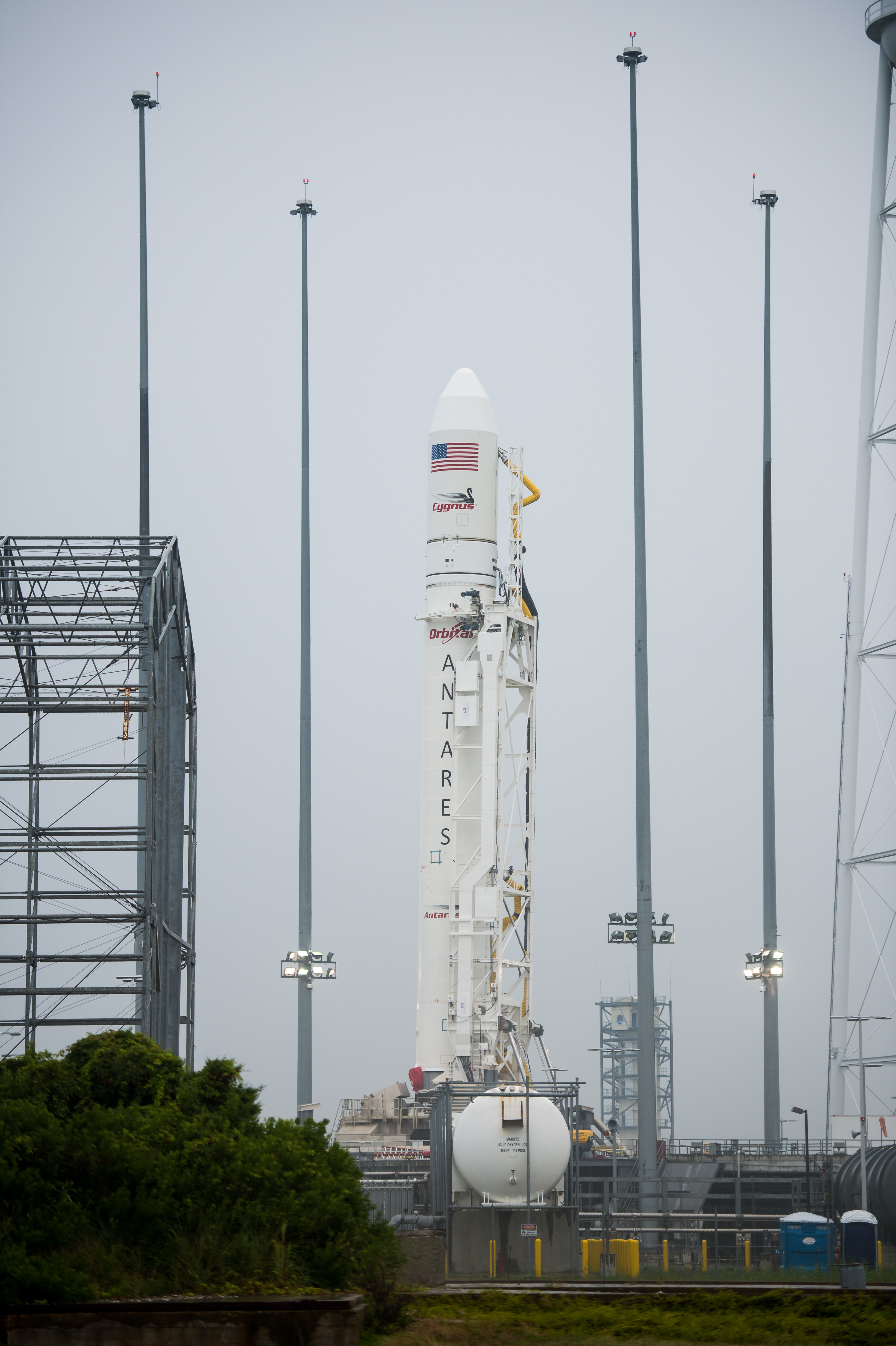
Engineers are making “excellent progress” assembling a modified version of Antares that is currently on track to blast off as soon as March 2016 with the company’s Cygnus resupply ship and resume critical deliveries of research experiments and life sustaining provisions to the multinational crews serving aboard the orbiting outpost.
“We are on track for the next Antares launch in early 2016,” said David Thompson, President and Chief Executive Officer of Orbital ATK in a progress update.
Resuming Antares launches is a key part of the company’s multipronged effort to fulfil their delivery commitments to NASA under the Commercial Resupply Services (CRS) contract.
“The focus all along has been to do everything we can to fulfill our commitments to delivering cargo to the space station for NASA,” Thompson stated.
“After the Antares launch failure last October … our team has been sharply focused on fulfilling that commitment.”
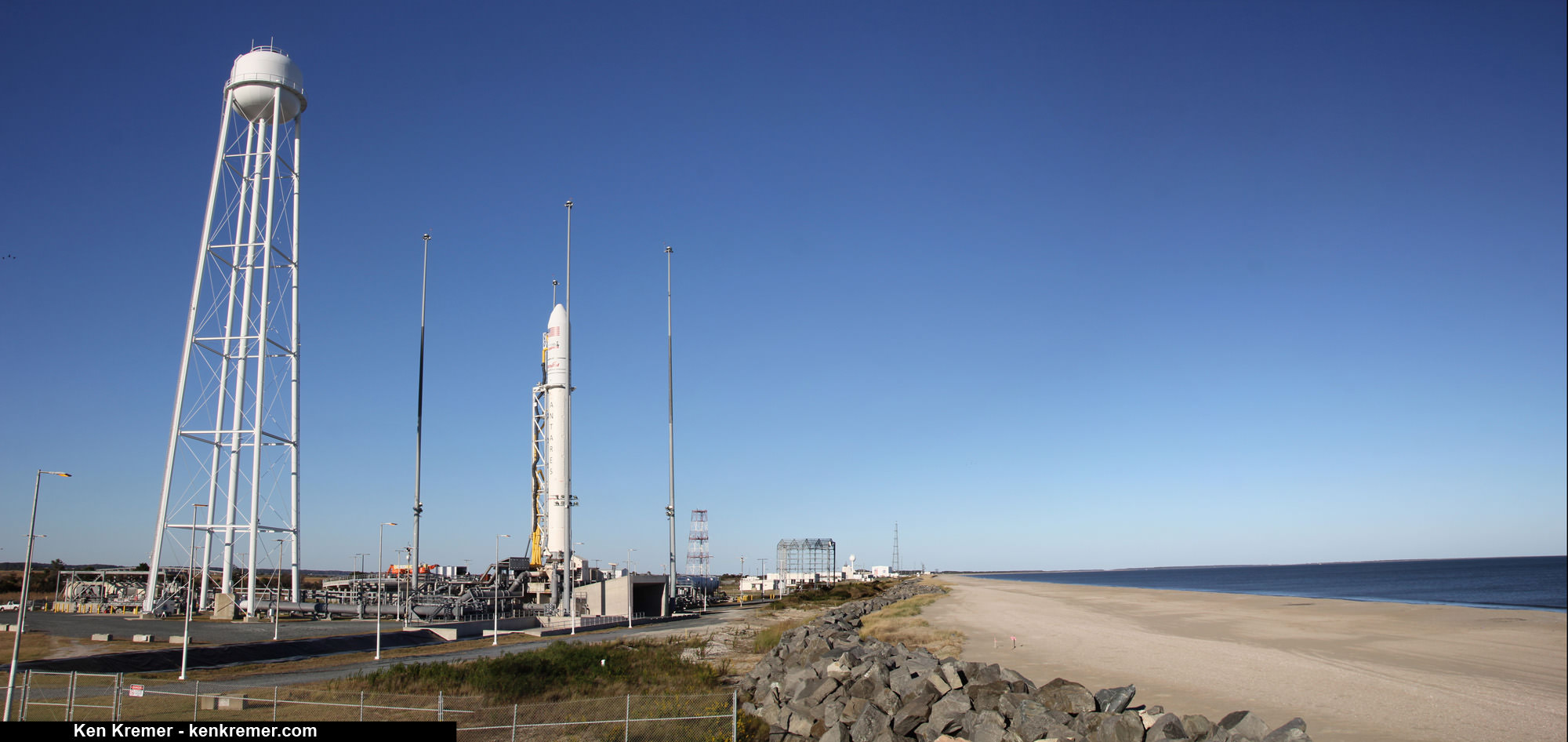

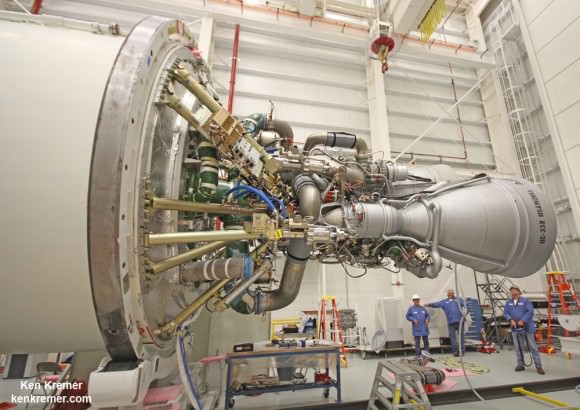
The key milestone was to successfully re-engine Antares with a new type of first stage engine that completely eliminates use of the original AJ26 engines that were refurbished 40 year leftovers – the NK-33 from Russia’s abandoned manned moon landing program.
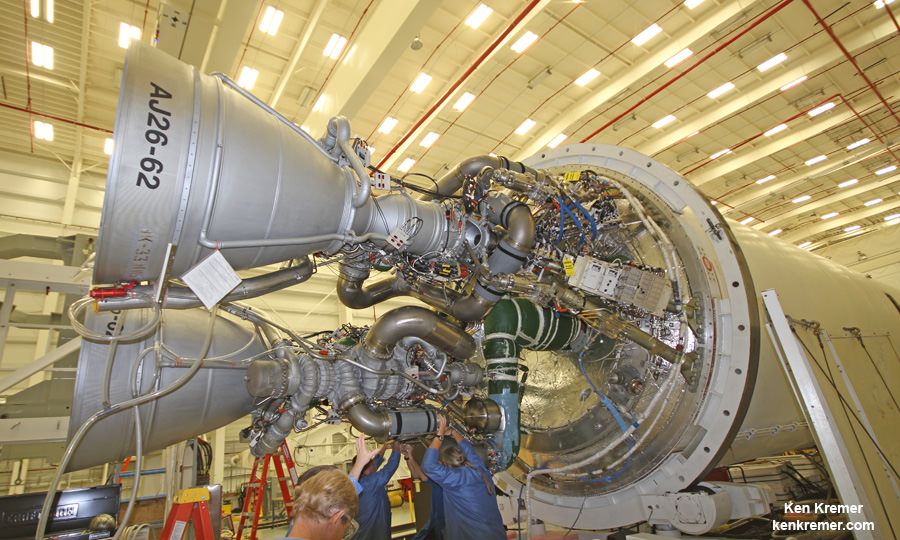
After the launch failure, Orbital managers decided to ditch the trouble plagued AJ-26 and “re-engineered” the vehicle with the new RD-181 Russian-built engines that were derived from the RD-191.

Orbital ATK holds a Commercial Resupply Services (CRS) contract from NASA worth $1.9 Billion to deliver 20,000 kilograms of research experiments, crew provisions, spare parts and hardware spread out over eight Cygnus cargo delivery flights to the ISS.
NASA has recently supplemented the CRS contract with three additional Cygnus resupply deliveries in 2017 and 2018.
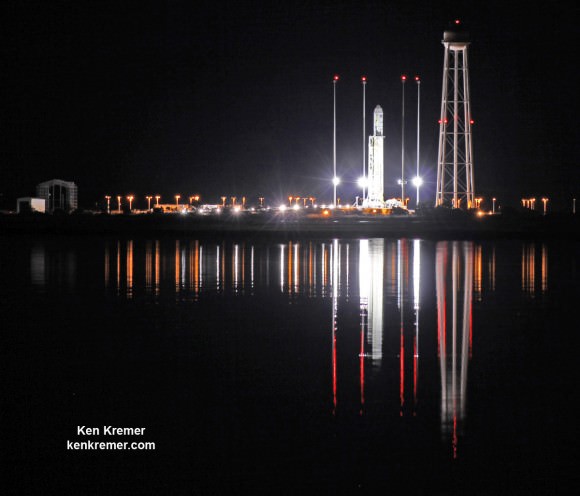
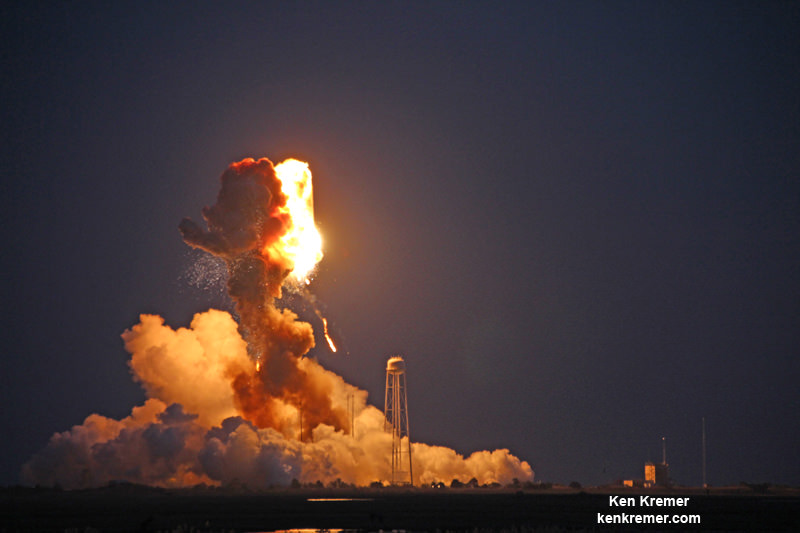
However, the Cygnus missions were put on hold when the third operational Antares/Cygnus flight was destroyed in a raging inferno about 15 seconds after liftoff on the Orb-3 mission from launch pad 0A at NASA’s Wallops Flight Facility on Virginia’s eastern shore.
Until Antares flights can safely resume, Orbital ATK has contracted with rocket maker United Launch Alliance (ULA) to launch a Cygnus cargo freighter atop an Atlas V rocket for the first time, in early December – as I reported here.
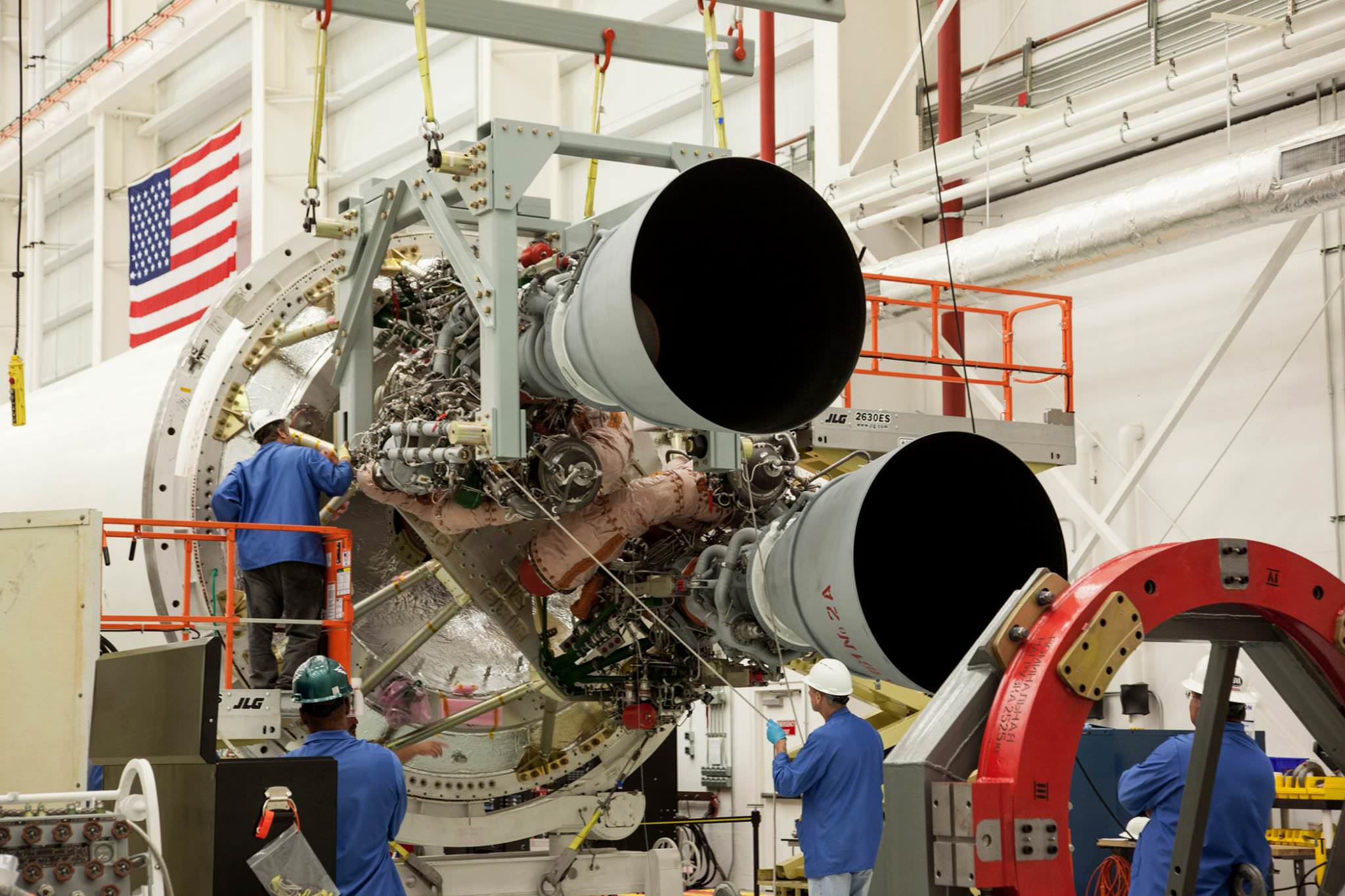
The Antares rocket is being upgraded with the new RD-181 main engines powering the modified first stage core structure that replace the troublesome AJ26 engines whose failure caused the Antares Orb-3 launch explosion on Oct. 28, 2014.

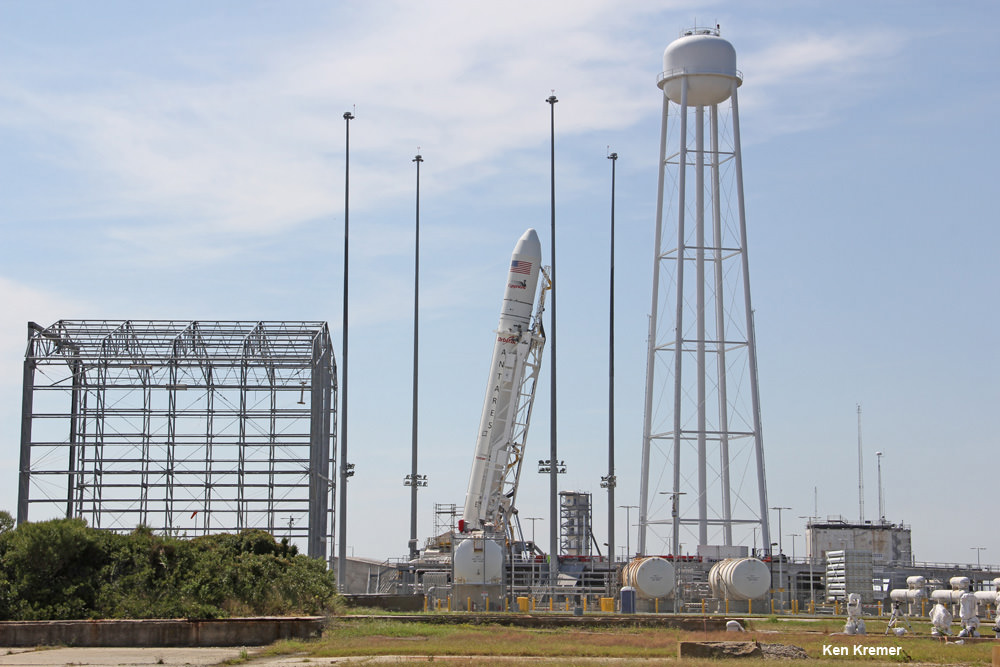
“We are making excellent progress in resuming our cargo delivery service to the International Space Station for NASA under the Commercial Resupply Services (CRS) contract,” said company officials.
Orbital ATK engineering teams have been working diligently on “integrating and testing the new RD-181 main engines.”
After engineers finished acceptance testing and certification of the RD-181, the first dual engine set was shipped to Orbital’s Wallops Island integration facility. They arrived in mid-July. A second set is due to arrive in the fall.
“The RD-181 engine provides extra thrust and higher specific impulse, significantly increasing the payload capacity of the Antares rocket. This state-of-the-art propulsion system is a direct adaptation of the RD-191 engine, which completed an extensive qualification and certification program in 2013, accumulating more than 37,000 seconds of total run time,” said Scott Lehr, President of Orbital ATK’s Flight Systems Group, in a statement.
Engineers and technicians have now “integrated the two RD-181 engines with a newly designed and built thrust frame adapter and modified first stage airframe.”
Then they will add new propellant feed lines and first stage avionics systems.
Then comes the moment of truth. A “hot fire” test on the launch pad will be conducted by either the end of 2015 or early 2016 “to verify the vehicle’s operational performance and compatibility of the MARS launch complex.”
“Significant progress has been made in the manufacture and test of the modified hardware components, avionics and software needed to support the new engines,” said Mike Pinkston, Vice President and General Manager of Orbital ATK’s Antares Program.
“We are solidly on track to resume flying Antares in 2016.”

Simultaneously, teams have been working hard to repair the Wallops launch pad which was damaged when the doomed Antares plummeted back to Earth and exploded in a hellish inferno witnessed by thousands of spectators and media including myself.
Repairs are expected to be completed by early 2016 to support a launch tentatively planned for as soon as March 2016.
SpaceX, NASA’s other commercial cargo company under contract to ship supplies to the ISS also suffered a launch failure of with their Falcon 9/Dragon cargo delivery rocket on June 28, 2015.
NASA is working with both forms to restart the critical ISS resupply train as soon as can safely be accomplished.
Be sure to read Ken’s earlier eyewitness reports about last October’s Antares failure at NASA Wallops and ongoing reporting about Orbital ATK’s recovery efforts – all here at Universe Today.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and Planetary science and human spaceflight news.
………….
Learn more about Orbital ATK, SpaceX, Boeing, ULA, Space Taxis, Mars rovers, Orion, SLS, Antares, NASA missions and more at Ken’s upcoming outreach events:
Aug 29-31: “MUOS-4 launch, Orion, Commercial crew, Curiosity explores Mars, Antares and more,” Kennedy Space Center Quality Inn, Titusville, FL, evenings