[/caption]
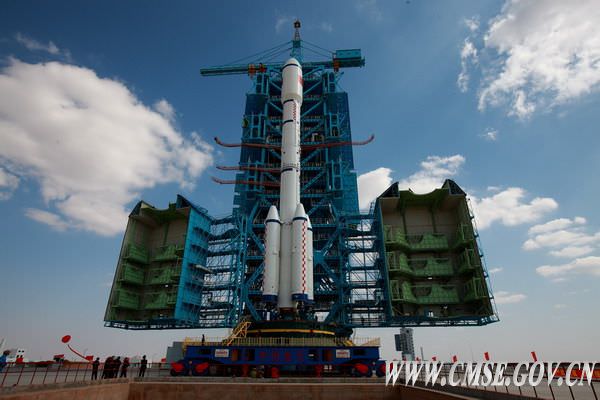
China’s human spaceflight program is gearing up to take a highly significant “Leap forward in Space” after their “Tiangong 1” prototype space station was rolled out to the remote Gobi desert launch pad at the countries Jiuquan Satellite Launching Center in Gansu Province in anticipation of blastoff sometime this week.
Space officials from the Chinese Manned Space Engineering Office have now confirmed that liftoff of the 8.5 ton Tiangong 1 human rated module atop a Long March CZ-IIF booster rocket is slated to take place during a launch window that extends from Sept. 27 to Sept. 30. The launch was delayed a few days after the recent launch failure of a similar Chinese rocket, the Long March IIC.
China’s burgeoning space efforts come directly on the heels of the voluntary US shutdown of the Space Shuttle program, thereby dismantling all US capability to launch humans into space from American soil for several years until about 2014 at a minimum.
The US manned spaceflight capability gap will be stretched out even further if NASA’s budget for commercial space taxis and the newly proposed SLS launch system is cut by political leaders in Washington, DC.

On Sept. 20, the integrated Long March rocket and Tiangong module were wheeled out of China’s VAB while sitting on top of the Mobile Launch Platform and transferred to the launch gantry at Jiuguan.
The goal of the Tiangong 1 mission is to carry out China’s first human spaceflight related rendezvous and docking mission and to demonstrate that Chinese space engineers have mastered the complicated technology required for a successful outcome.
These skills are akin in complexity to NASA’s Gemini manned program of the 1960’s which paved the way for NASA’s Apollo missions and led directly to the first manned landing on the moon in 1969 by Apollo 11.
Chinas stated goal is to construct a 60 ton Skylab sized space station in earth orbit by 2020.
Check out this CCTV video for further details and imagery of the Chinese space hardware which shows the how China will expand the reach and influence of their space program.
View this Chinese video from NDTV for a glimpse at Chinas long range Space Station plans.
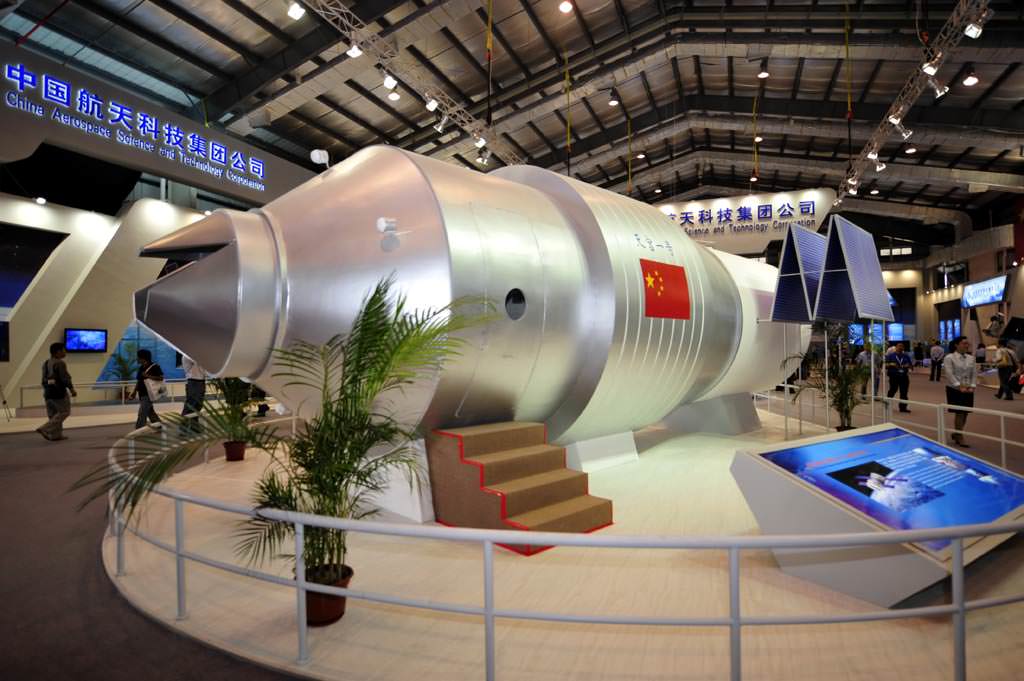
The 40 foot long Tiangong 1 space platform is unmanned and will serve as the docking target for China’s manned Shenzhou capsules in a series of stepping stone learning flights. It is solar powered and equipped to operate in a man-tended mode for short duration missions and in an unmanned mode over the long term.
The initial rendezvous and docking mission will be conducted by the Shenzhou 8 spacecraft, which will fly in an unmanned configuration for the first docking test. Shenzhou 8 is scheduled to soar to space before the end of 2011.
If successful, China plans to quickly follow up with the launch of two manned Shenzhou flights to dock at Tiangong 1 during 2012 – namely Shenzhou 9 & Shenzhou 10.
The multi astronaut chinese crews would float into Tiangong 1 and remain on board for a short duration period of a few days or weeks. The crew would conduct medical, space science and technology tests and experiments.
China’s first female astronaut may be selected to fly as a crew member on one of the two Shenzhou flights in 2012.
Meanwhile, all American astronauts will be completely dependent on the Russian Soyuz capsule for trips to the International Space Station. Russia is still working to correct the third stage malfunction which doomed the recent Progress cargo resupply launch and put a halt to Soyuz launches.
Engineers and technicians are in the process of checking out all Tiangong 1 systems and preliminary weather reports from Chinese media appear favorable for launch.
Shenzhou 8 has also been delivered to the Jinquan launch complex for check out of all systems
Get set for China’s attempt at a ‘Space Spectacular’