[/caption]
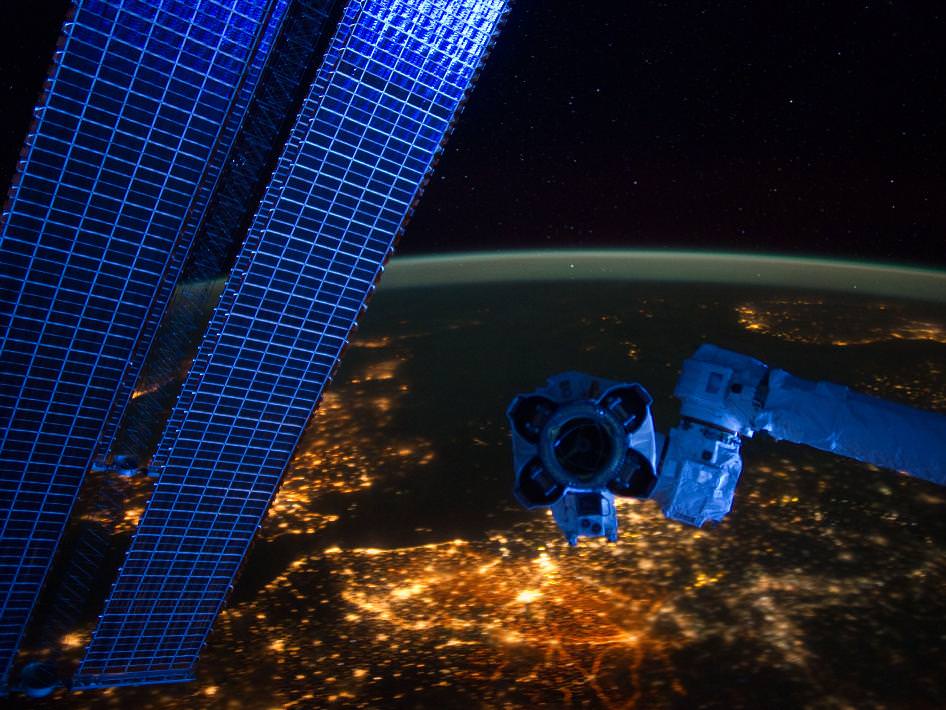
An amazing panorama revealing Western Europe’s ‘Cities at Night’ with hardware from the stations robotic ‘hand’ and solar arrays in the foreground was captured by the crew in a beautiful new image showing millions of Earth’s inhabitants from the Earth-orbiting International Space Station (ISS).
The sweeping panoramic vista shows several Western European countries starting with the British Isles partially obscured by twin solar arrays at left, the North Sea at left center, Belgium and the Netherlands (Holland) at bottom center, and the Scandinavian land mass at right center by the hand, or end effector, of the Canadian-built ISS robotic arm known as the Space Station Remote Manipulator System (SSRMS) or Canadarm2.

Coincidentally European Space Agency astronaut Andre Kuipers from Holland (photo at left) is currently aboard the ISS, soaring some 400 kilometers (250 miles) overhead.
The panoramic image was taken by the ISS residents on January 22, 2012.
The Expedition 30 crew of six men currently serving aboard the ISS (photo below) hail from the US, Russia and Holland.
NASA astronaut Dan Burbank is the commander of Expedition 30 and recently snapped awesome photos of Comet Lovejoy.
“Cities at Night” – Here’s a portion of a relevant ISS Blog post from NASA astronaut Don Pettit on Jan. 27, 2012:
“Cities at night are different from their drab daytime counterparts. They present a most spectacular display that rivals a Broadway marquee. And cities around the world are different. Some show blue-green, while others show yellow-orange. Some have rectangular grids, while others look like a fractal-snapshot from Mandelbrot space.”
“Patterns in the countryside are different in Europe, North America, and South America. In space, you can see political boundaries that show up only at night. As if a beacon for humanity, Las Vegas is truly the brightest spot on Earth. Cities at night may very well be the most beautiful unintentional consequence of human activity,” writes NASA astronaut Don Pettit currently residing aboard the ISS.