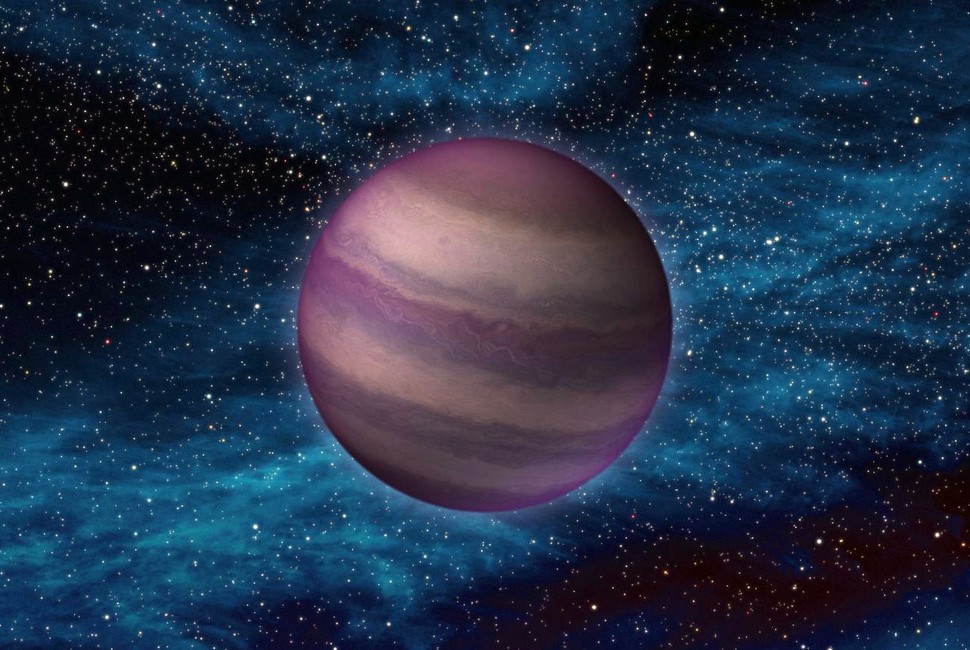
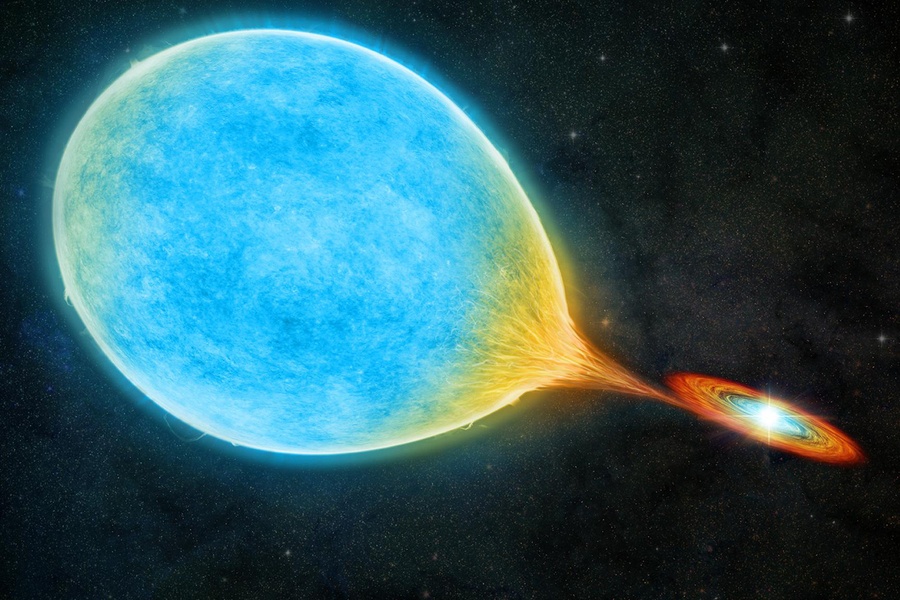
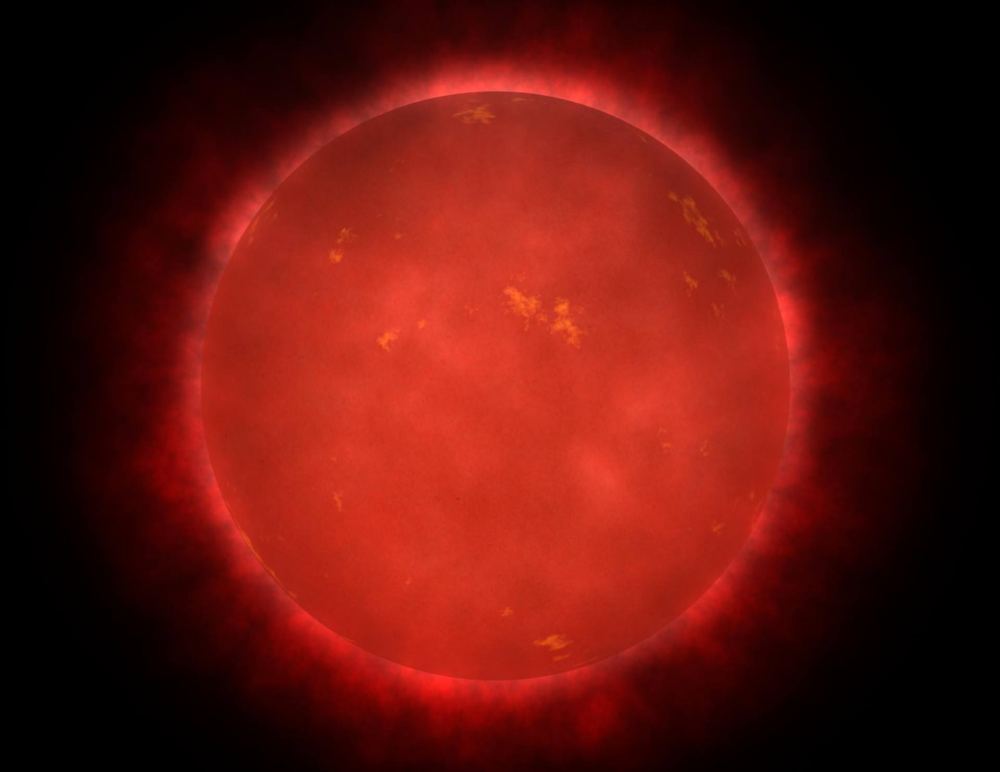
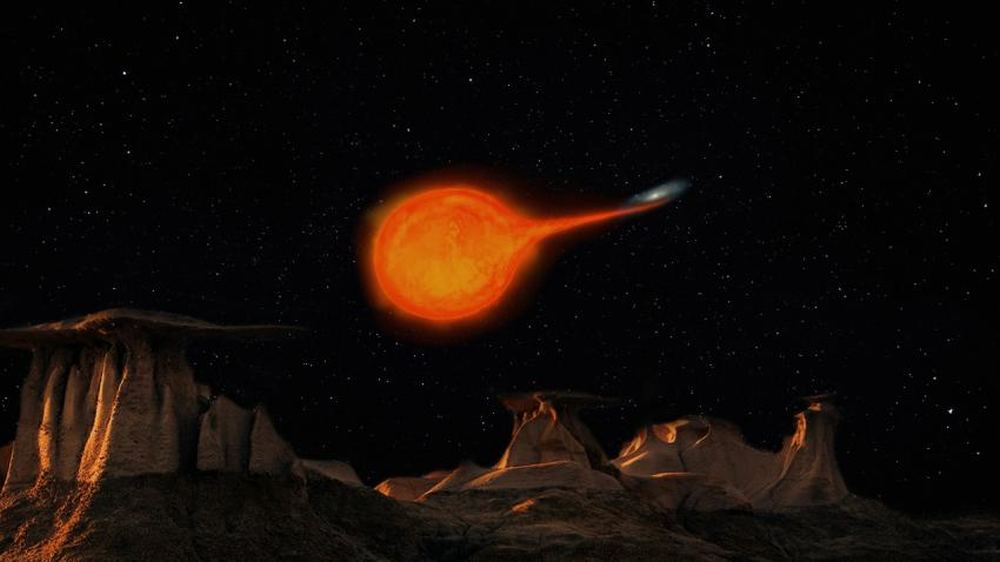
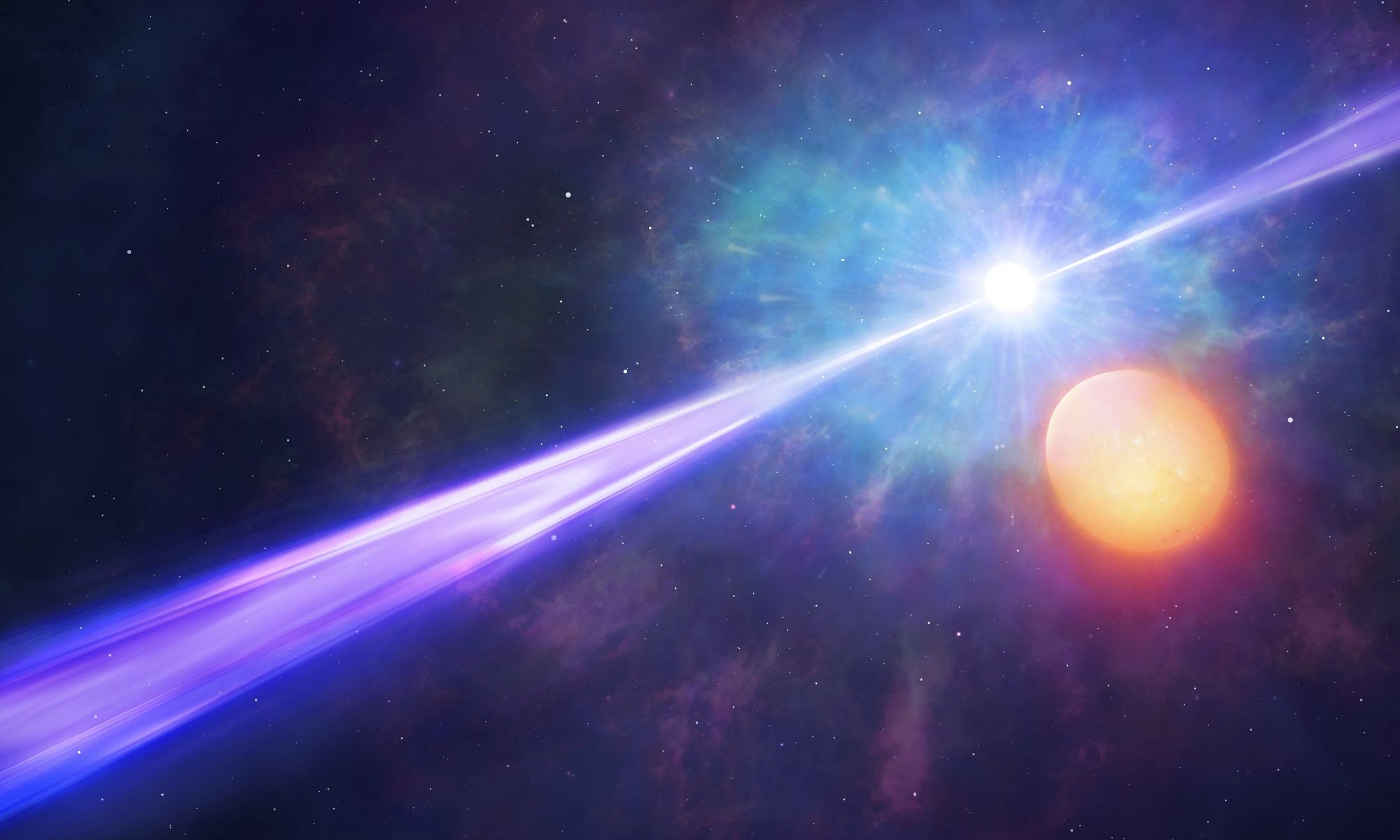
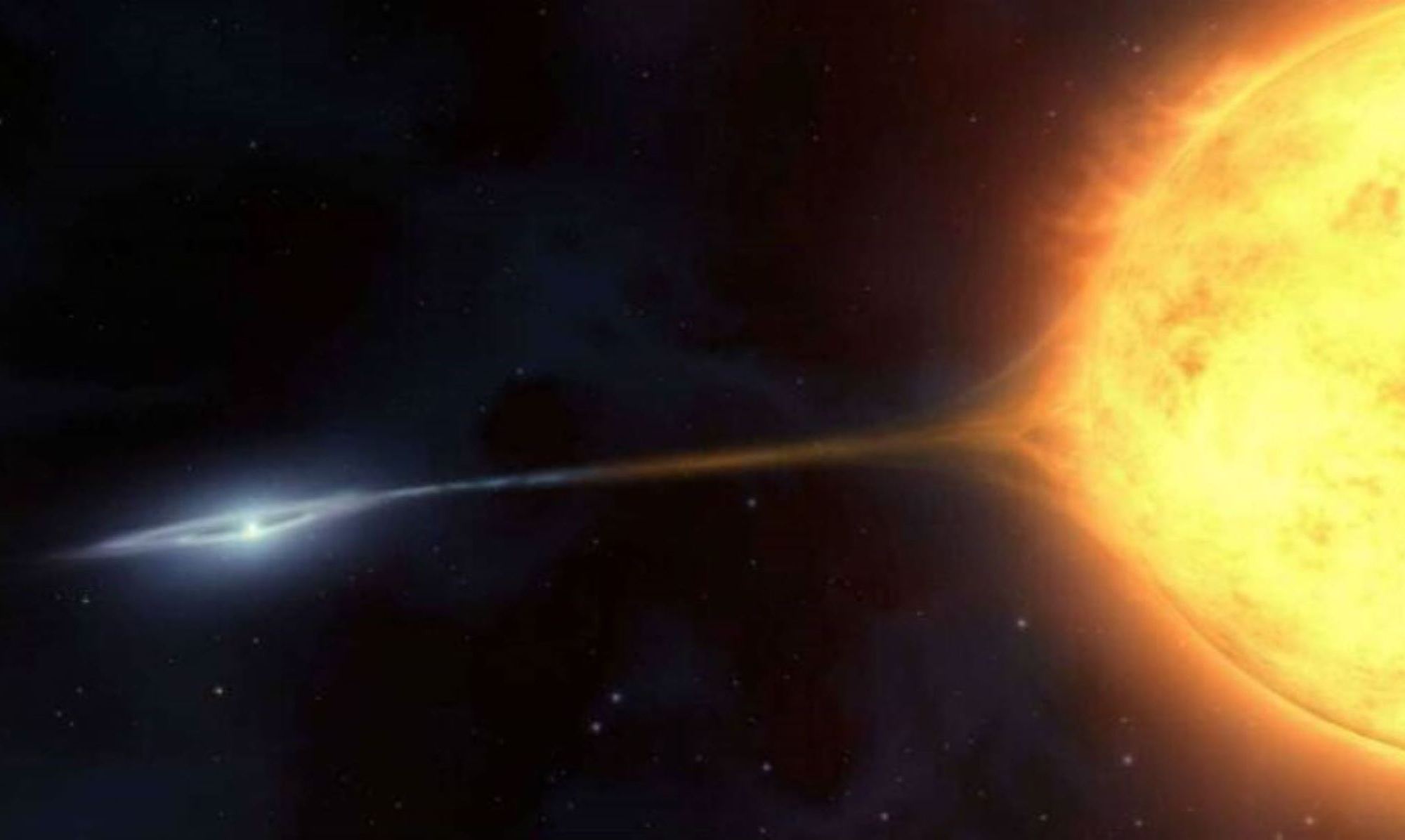
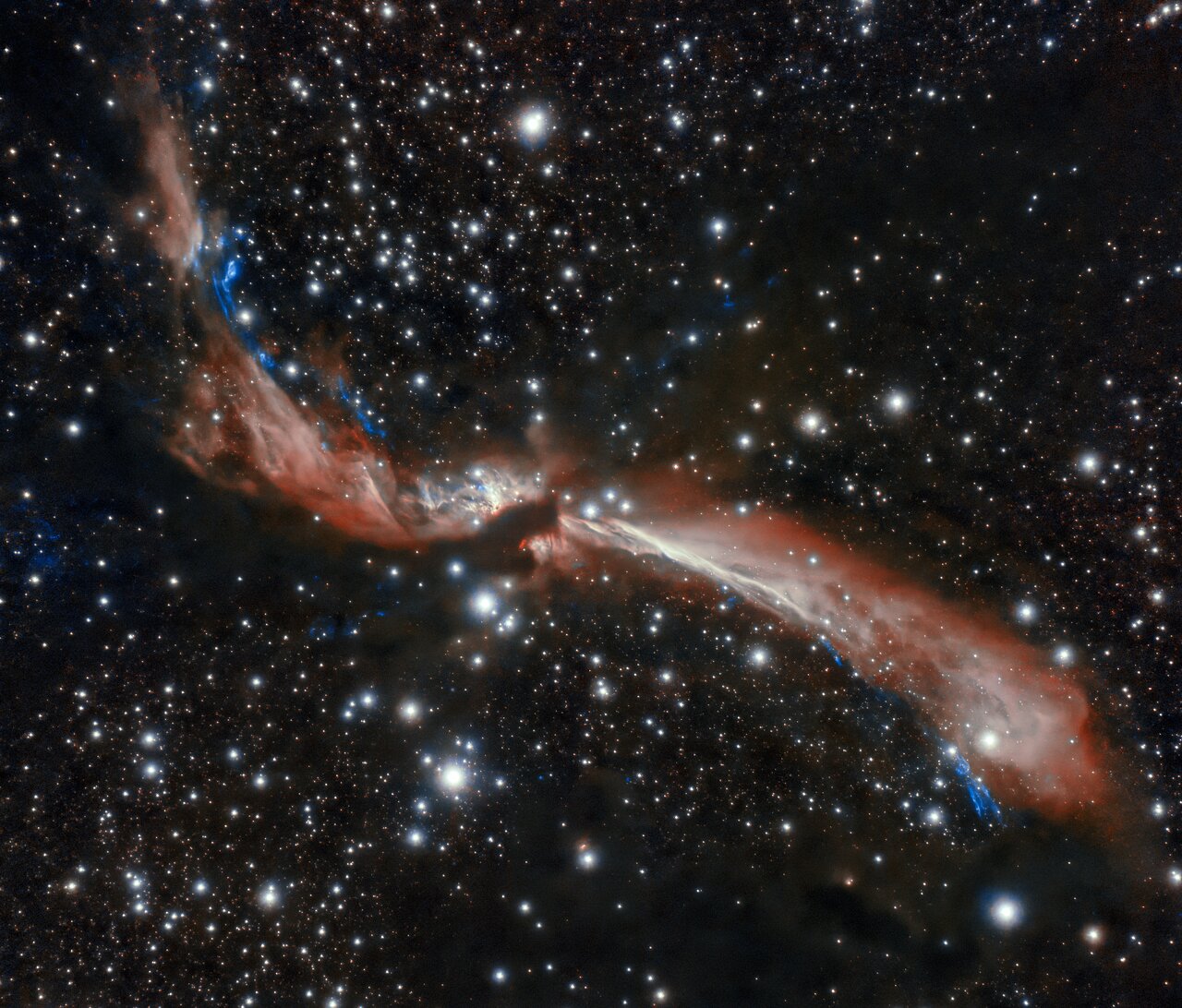
A team of astrophysicists has discovered a binary pair of ultra-cool dwarfs so close together that they look like a single star. They’re remarkable because they only take 20.5 hours to orbit each other, meaning their year is less than one Earth Day. They’re also much older than similar systems.
Continue reading “Binary Dwarf Stars Found Orbiting Each Other Every 20 Hours. They Were Once Almost Touching”Binary Dwarf Stars Found Orbiting Each Other Every 20 Hours. They Were Once Almost Touching