Spacewalkers will replace a faulty navigational aid Friday to ensure that a cargo spacecraft in June docks safely with the International Space Station.
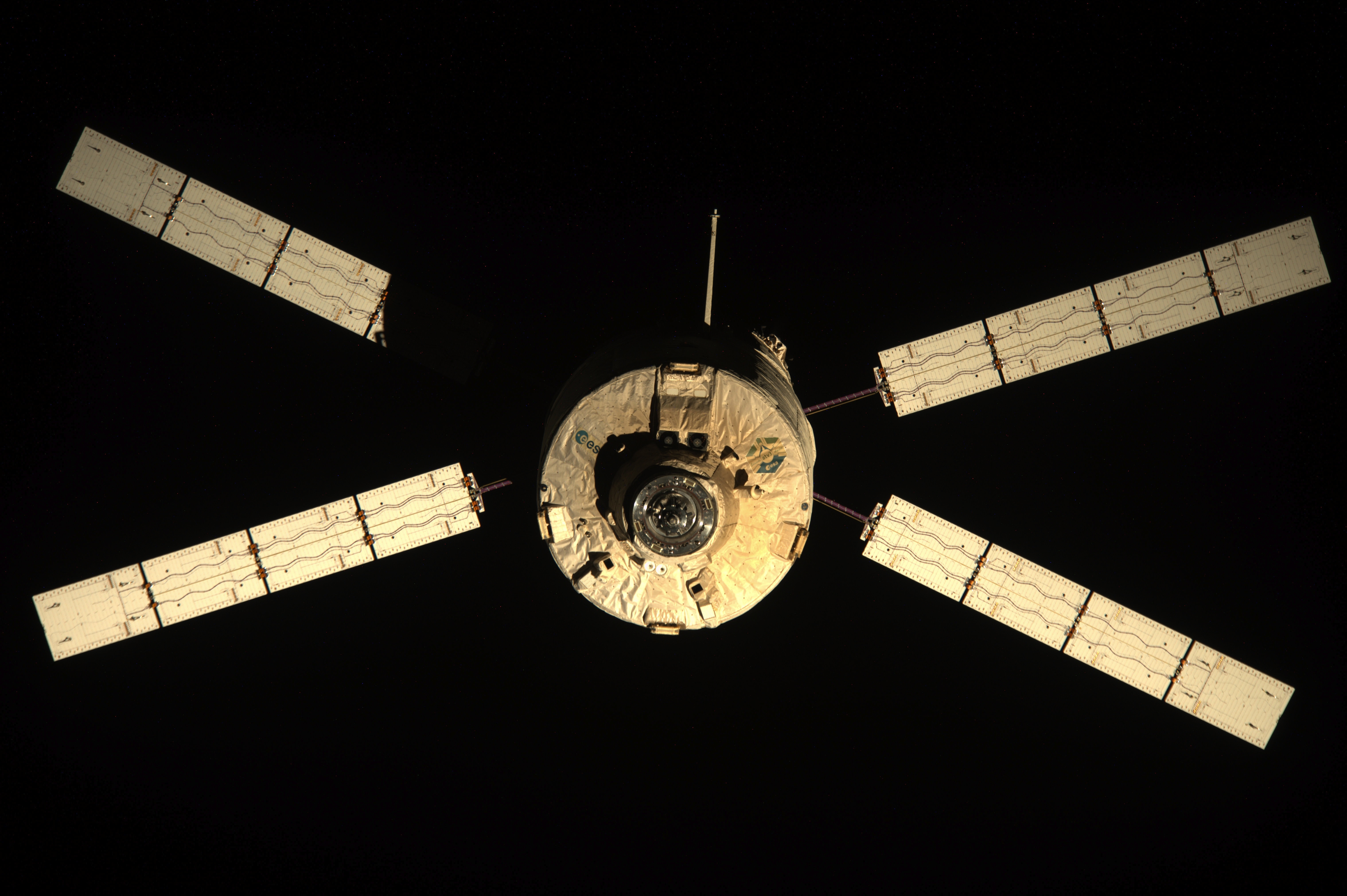
Expedition 35 cosmonauts Pavel Vinogradov and Roman Romanenko will venture into space to remove and replace a broken retroreflector on the Russian Zvezda station module. The first spacecraft to use the new retroreflector will be the European Space Agency’s automated transfer vehicle (ATV) Albert Einstein, which is scheduled to dock with the station in June.
The ATV has a videometer on board that shoots laser beams at retroreflectors on the outside of the station. Then, the videometer analyzes the pattern of light that is returned. Based on this pattern, it navigates towards the station and in for a docking.
Albert Einstein will carry about two tons of cargo to the station, including water, oxygen, and extra fuel to boost the space station’s orbit. Tipping the scales at 44,611 pounds (20,235 kg), this ATV will be the heaviest ever lifted by an Ariane rocket.
Replacing the retroreflector won’t be the cosmonauts’ only task. They’ll retrieve an experiment, called Biorisk, that is supposed to evaluate how much microbes affect spacecraft structures. They may also take the Vinoslivost experiment (which looks at how exposed materials behave in space) back inside, depending on how much time they have.

These experiments are part of the long-term mandate of the station’s activities to study how well people and structures survive after years in space. Based on the results, engineers back on Earth can make adjustments for spacecraft under development, making them more robust for long-term missions.
Additionally, the cosmonauts plan to install the Obstanovka experiment, which will look at “space weather” in the Earth’s ionosphere. This region of the atmosphere is where auroras arise after the Sun’s particles strike the area.
Besides producing these pretty patterns, space weather has a darker side: it can cause communications shortouts or hurt satellites. That’s why NASA has the Solar Dynamics Observatory and other spacecraft keeping a close eye on the sun. The agency wants to improve space weather predictions to protect infrastructure on Earth.
You can watch Expedition 35’s first spacewalk on NASA Television at 9:30 a.m. EDT (1:30 p.m. UTC) on Friday. The cosmonauts should head outside around 10:06 a.m. EDT (2:06 p.m. UTC). This could change depending on how quickly the cosmonauts depressurize the Pirs airlock and complete their pre-spacewalk checklist.
This spacewalk will be the seventh for Vinogradov and the first for Romanenko. Including this upcoming spacewalk, there have been 167 spacewalks performed to construct the space station and do maintenance.