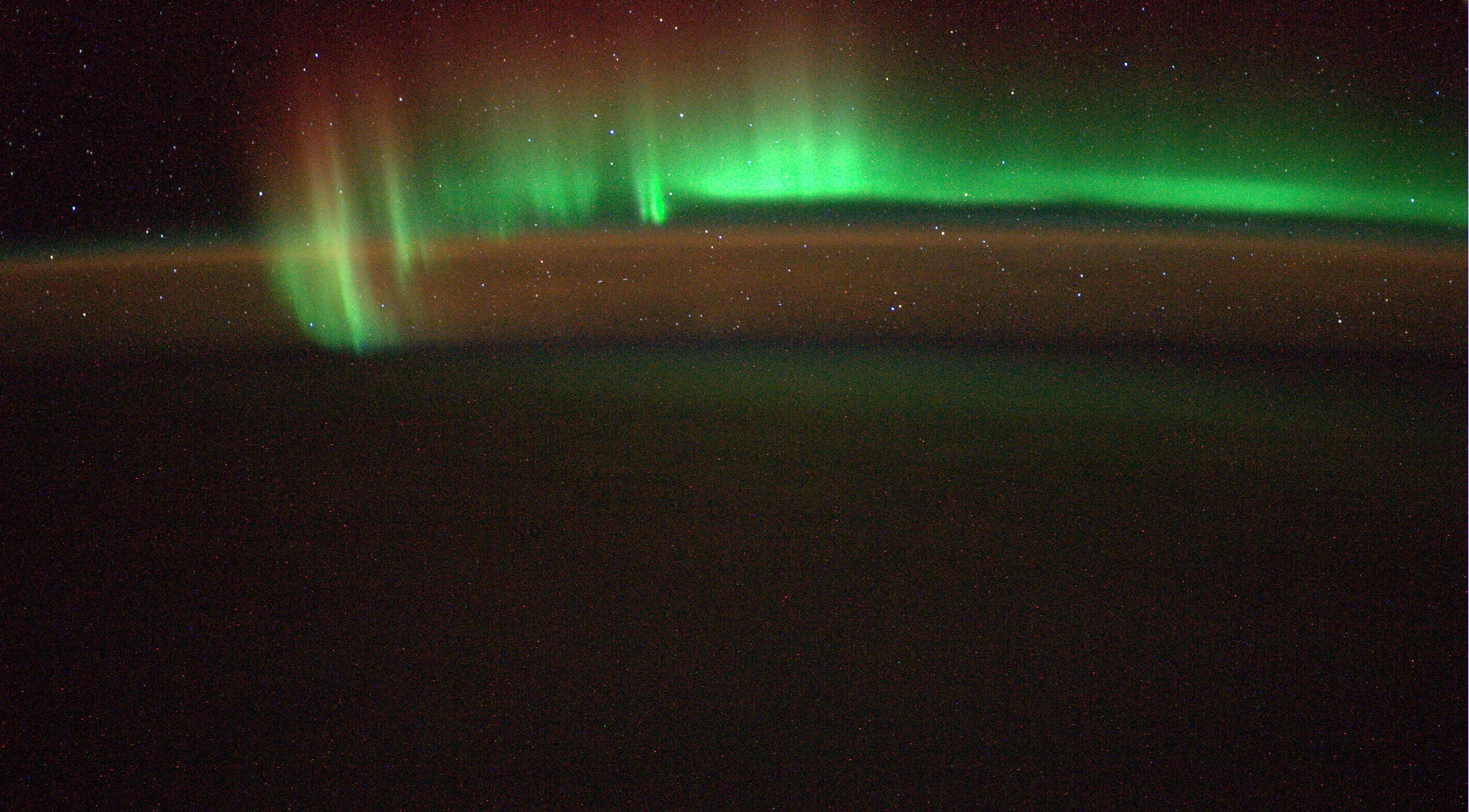
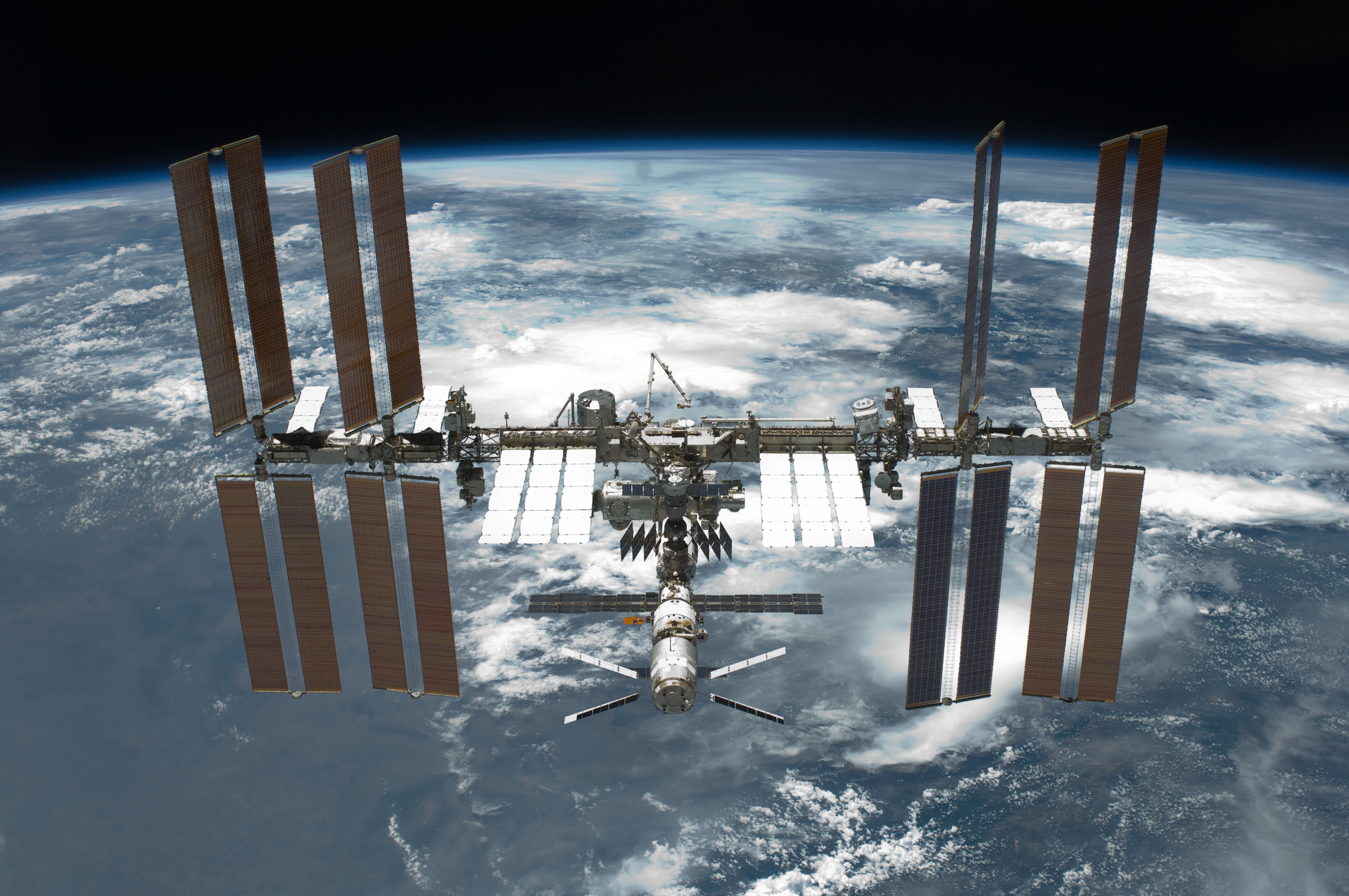
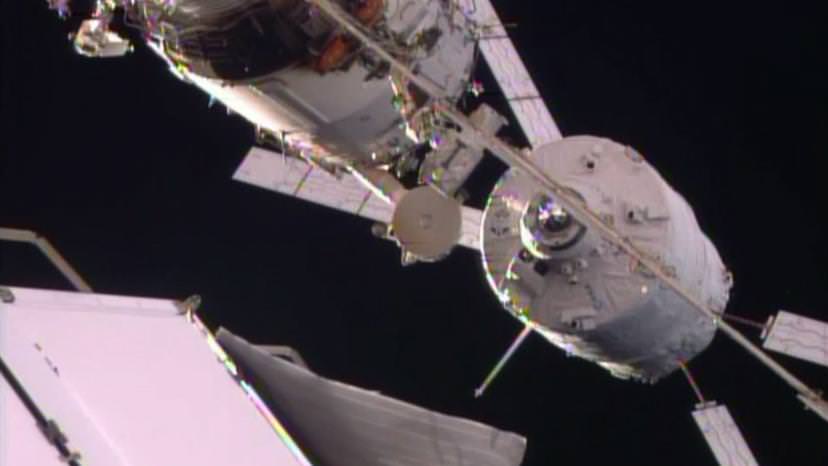
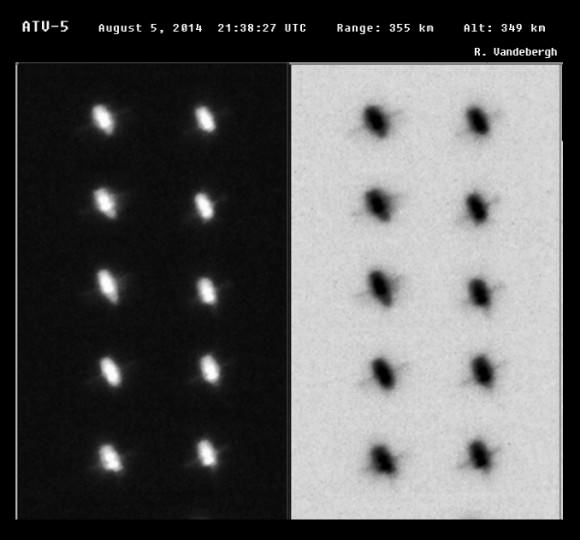
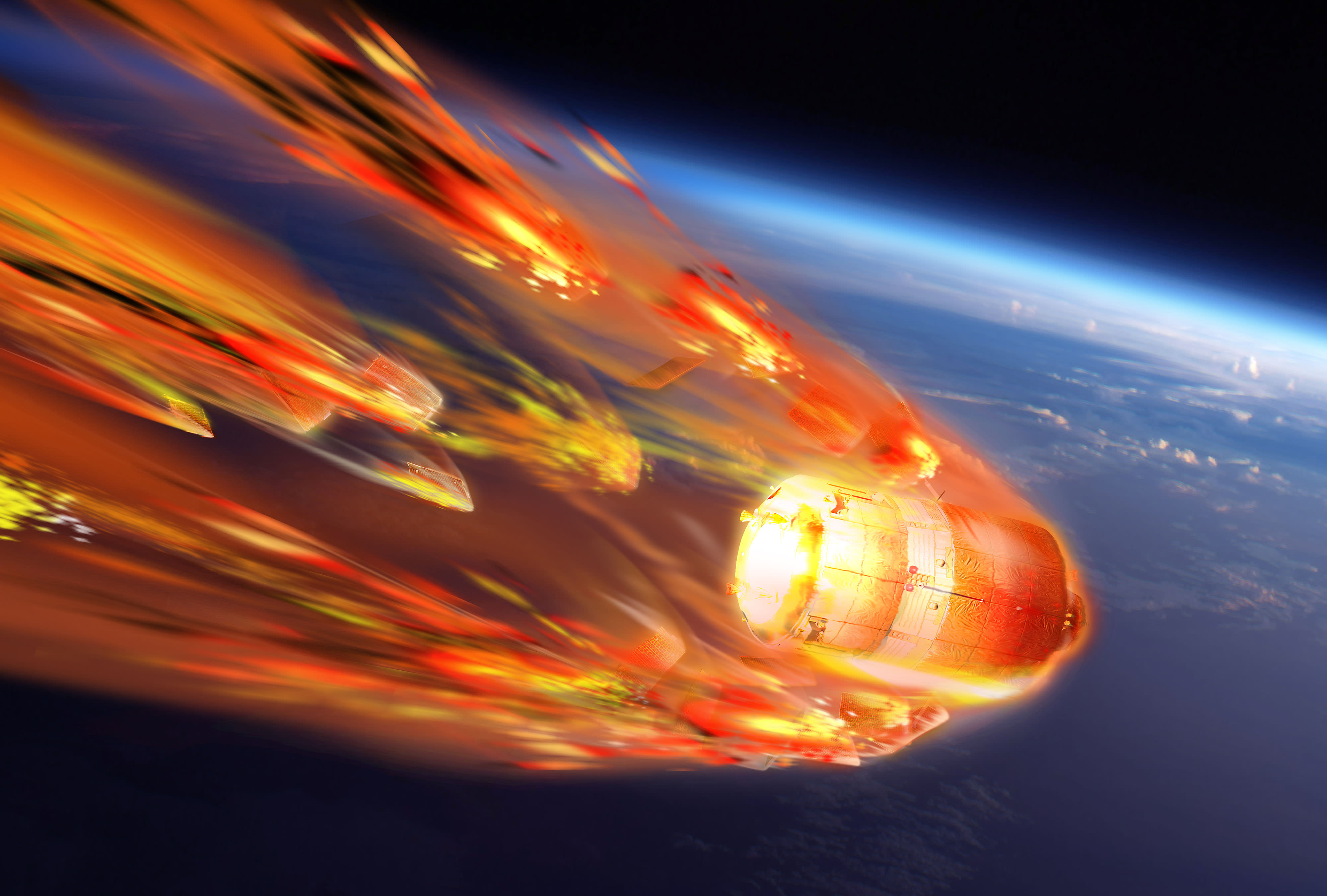
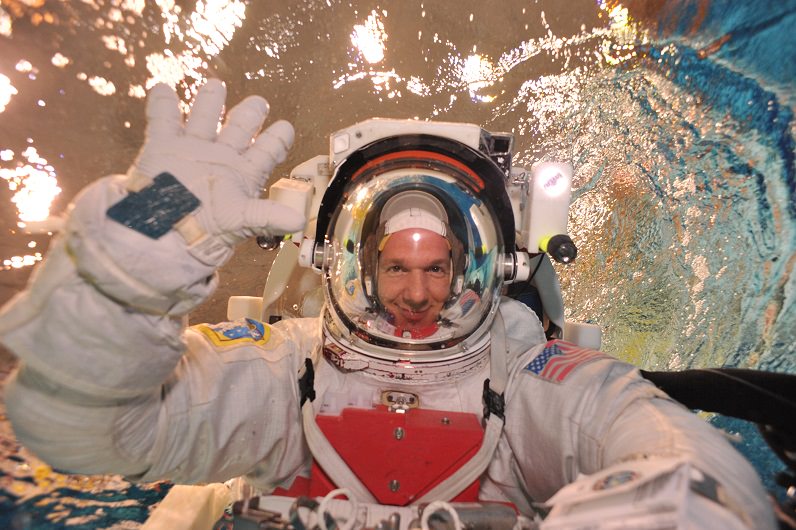
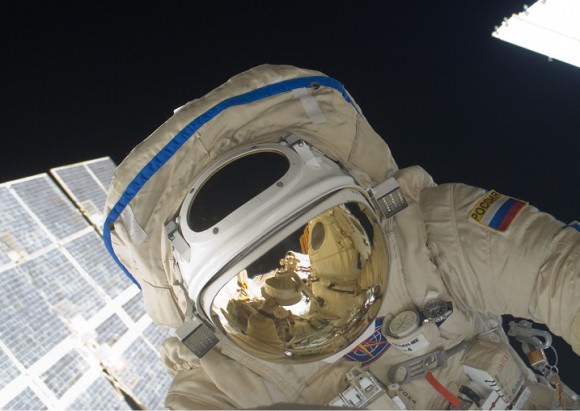
Video Caption: Watch the Earth roll by through the perspective of German astronaut Alexander Gerst in this 4K six-minute timelapse video of images taken from on board the International Space Station (ISS) during 2014. Credit: Alexander Gerst/ESA
ESA astronaut Alexander Gerst from Germany who recently returned from a six month voyage to the International Space Station (ISS) has a special Christmas gift for all – a stunning six-minute timelapse compilation of his favorite images of Earth taken during his “Blue Dot” mission in 2014.
“A 4K timelapse showing our planet in motion, from my favourite Earth images taken during the Blue Dot mission,” wrote Gerst in connection with his spectacular timelapse video released to coincide with Christmastime.
“I wish all of you a merry Christmas! It was a wild year for me, thanks for joining me on this fascinating journey!” said Gerst in English.
“Wünsche euch allen fröhliche Weihnachten! War ein wildes Jahr für mich, vielen Dank, dass ihr mit dabei wart!” said Gerst in German.
You can watch the Earth roll by through Gerst’s perspective in this six-minute timelapse video combining over 12,500 images taken during his six-month mission aboard the ISS that shows the best our beautiful planet has to offer.
“Marvel at the auroras, sunrises, clouds, stars, oceans, the Milky Way, the International Space Station, lightning, cities at night, spacecraft and the thin band of atmosphere that protects us from space,” according to the video’s description.
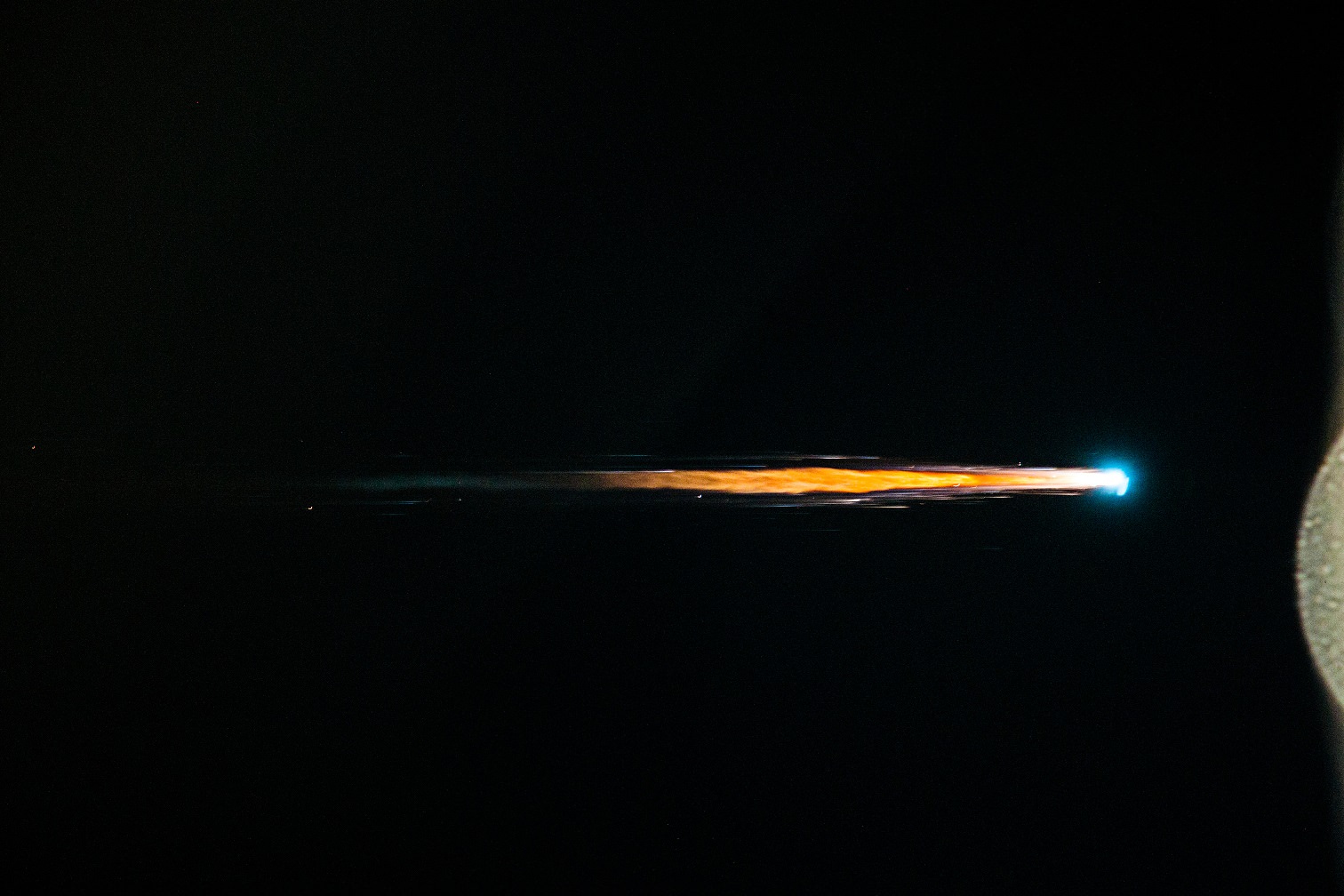
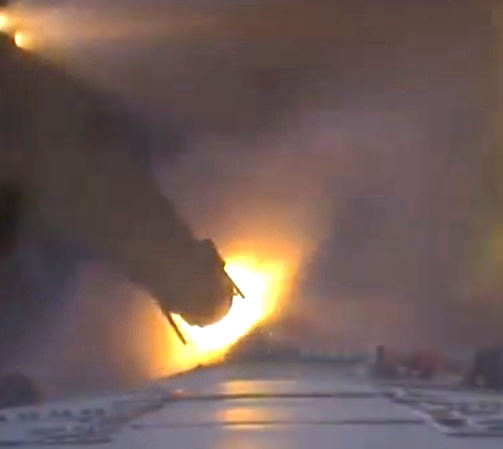
Gerst would often would set cameras to automatically take pictures at regular intervals while doing his science research or preparing for the docking of other spacecraft at the ISS in order to get the timelapse effect shown in the video.
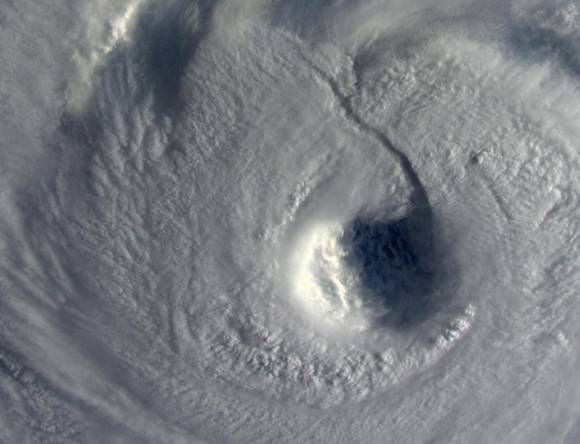

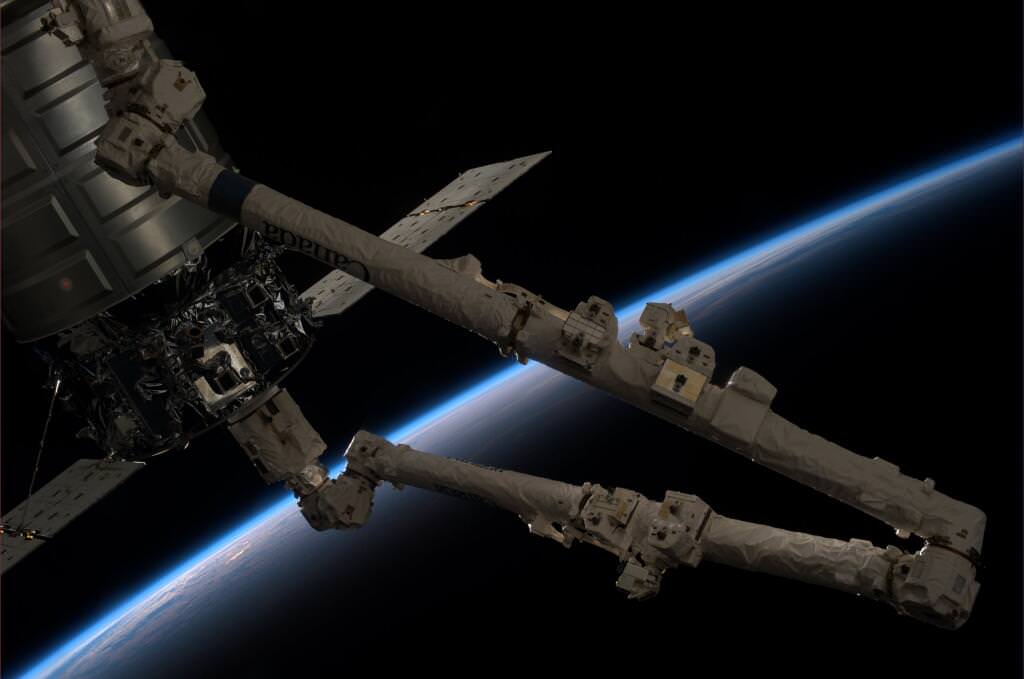
The robotic arm capture and berthing of the SpaceX Dragon cargo ship and the release of the Orbital Sciences Cygnus cargo freighter are particularly magnificent in a rarely seen timelapse glimpse of visiting vehicles that are absolutely essential to keeping the station afloat, stocked, and humming with research activities.
Gerst served aboard the ISS between May and November this year as a member of the Expedition 40 and 41 crews.
Gerst launched to the ISS on his rookie space flight on May 28, 2014, aboard the Russian Soyuz TMA-13M capsule along with Russian cosmonaut Maxim Suraev and NASA astronaut Reid Wiseman.
They joined the three station flyers already aboard – cosmonauts Alexander Skvortsov & Oleg Artemyev, and astronaut Steve Swanson – to restore the station crew complement to six.
Gerst and Wiseman became well known and regarded for their prolific and expertly crafted photography skills.

They returned to Earth safely on Nov. 10, 2014, with a soft landing on the Kazakh steppes.
Alex is Germany’s third astronaut to visit the ISS. He conducted a spacewalk with Wiseman on Oct. 7 while aboard. He is trained as a geophysicist and a volcanologist.

Read my story detailing Christmas 2014 festivities with the new crews at the ISS – here.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and planetary science and human spaceflight news.