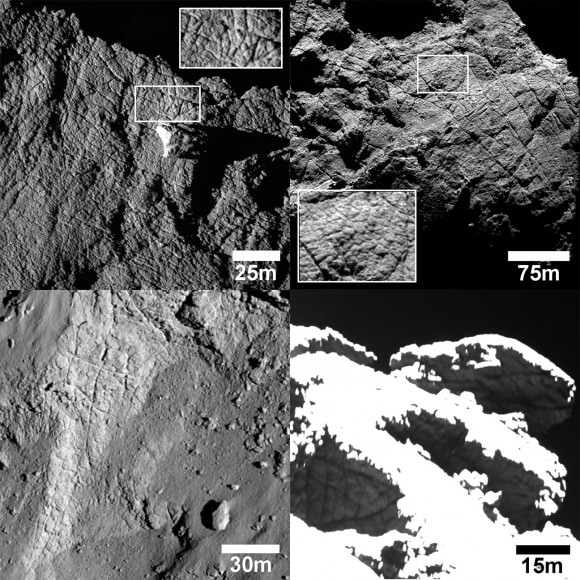
Sometimes, space probes that have long since ceased sending back data can still usher in new discoveries. That was the case recently when scientists used data from Rosetta, a probe that eventually crashed into comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko in 2016, to understand what changes occur on a comet’s surface as it continues its spin around the Sun.
Continue reading “How Long do Good Landing Sites Last on Comets?”A Flurry of Fall Binocular Comets
Fall 2021 offers up an all-night parade of challenging telescopic comets.
Ready for the next big one? If you’re like us, the surprise appearance of Comet F3 NEOWISE last summer was a great teaser of what could be. To be sure, we’re still long overdue for the next great naked eye comet, but there’s always a steady stream of fainter fuzzies out there for owners of large light buckets to hunt down. Fall of 2021 sees half a dozen comets knocking on binocular visibility around +10th magnitude, from dusk ‘til dawn. So without further fanfare, here are the best cometary targets for September into October 2021:
Continue reading “A Flurry of Fall Binocular Comets”New Image Shows the Rugged Landscape of Comet 67P
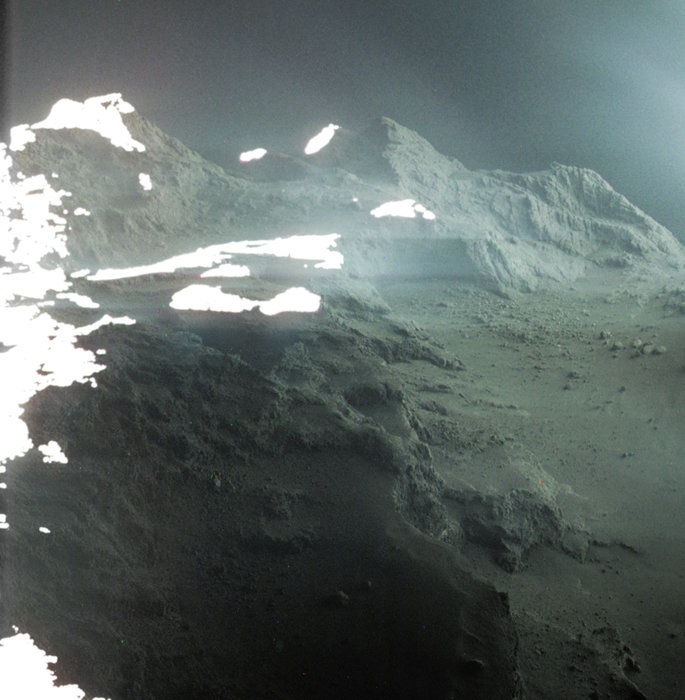

In March of 2004, the European Space Agency’s Rosetta spacecraft blasted off from French Guiana aboard an Ariane 5 rocket. After ten years, by November of 2014, the spacecraft rendezvoused with its target – Comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko (67P/C-G). Over the more than two years that followed, the spacecraft remained in orbit of this comet, gathering information on its surface, interior, and gas and dust environment.
And on September 30th, 2016, Rosetta came closer than ever to the surface of 67P/C-G and concluded its mission with a controlled impact onto the surface. Since that time, scientists have still been processing all the data the spacecraft collected during its mission. This included some awe-inspiring photographs of the comet’s surface that were obtained shortly after the spacecraft made its rendezvous with 67P/C-G.
Continue reading “New Image Shows the Rugged Landscape of Comet 67P”
I Can’t Stop Watching This Amazing Animation from Comet 67P
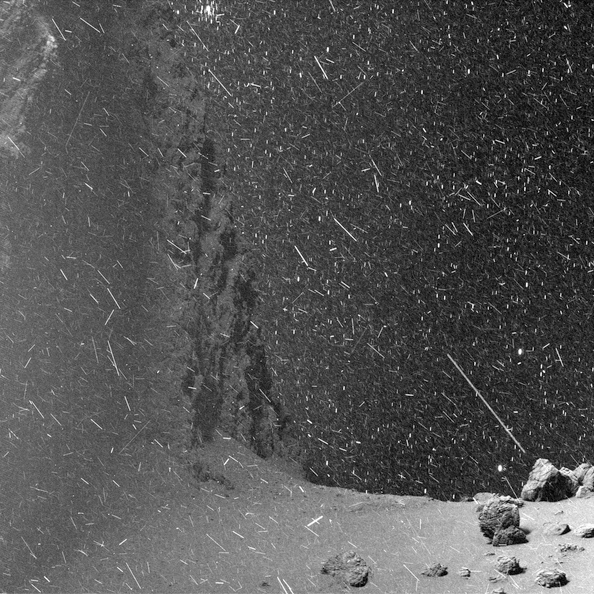

The European Space Agency’s Rosetta mission was an ambitious one. As the first-ever space probe to rendezvous with and then orbit a comet, Rosetta and its lander (Philae) revealed a great deal about the comet 67p/Churyumov-Gerasimenko. In addition to the learning things about the comet’s shape, composition and tail, the mission also captured some incredible images of the comet’s surface before it ended.
For instance, Rosetta took a series of images on June 1st, 2016, that showed what looks like a blizzard on the comet’s surface. Using these raw images (which were posted on March 22nd, 2018), twitter user landru79 created an eye-popping video that shows just what it would be like to stand on the comet’s surface. As you can see, its like standing in a blizzard on Earth, though scientists have indicated that it’s a little more complicated than that.
The video, which consists of 25 minutes worth of images taken by Rosetta’s Optical, Spectroscopic, and Infrared Remote Imaging System (OSIRIS), was posted by landru79 on April 23rd, 2018. It shows the surface of 67p/Churyumov-Gerasimenko on the loop, which lends it the appearance of panning across the surface in the middle of a snowstorm.
#ROSETTA ? OSIRIS #67P/CHURYUMOV-GERASIMENKO new albums ?–ROSETTA EXTENSION 2 MTP030– Miércoles 1 Junio 2016 all filters stacked pic.twitter.com/Bf173Z5g79
— landru79 (@landru79) April 23, 2018
However, according to the ESA, the effect is likely caused by three separate phenomena. For instance, the snow-like particles seen in the video are theorized to be a combination of dust from the comet itself as well as high-energy particles striking the camera. Because of OSIRIS’ charge-coupled device (CCD) – a radiation-sensing camera – even invisible particles appear like bright streaks when passing in front of it.
As for the white specks in the background, those are stars belonging to the Canis Major constellation (according to ESA senior advisor Mark McCaughrean). Since originally posting the video, landru79 has posted another GIF on Twitter (see below) that freezes the starfield in place. This makes it clearer that the comet is moving, but the stars are remaining still (at least, relative to the camera’s point of view).
And of course, the entire video has been sped up considerably for dramatic effect. According to a follow-up tweet posted by landru79, the first image was shot on June 1st, 2016 at 3.981 seconds past 17:00 (UTC) while the last one was shot at 170.17 seconds past 17:25.
Si apilamos todo el set alineando con las estrellas de fondo se distingue mejor que son estrellas y q es polvo (olvidaos de rayos cósmicos ) #ROSETTA ? OSIRIS #67P/CHURYUMOV-GERASIMENKO new albums ?–ROSETTA EXTENSION 2 MTP030– Miércoles 1 Junio 2016 all filters stacked? pic.twitter.com/UyZ628JxKP
— landru79 (@landru79) April 24, 2018
Still, one cannot deny that it is both captivating and draws attention to what Rosetta the mission accomplished. The mission launched in 2004 and reached 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko in 2014. After two years of gathering data, it was deliberately crashed on its surface in 2016. And yet, years later, what it revealed is still captivating people all over the world.
Further Reading: Live Science, Gizmodo
Rosetta’s 67P Is The Result Of A Collision Of Two Comets
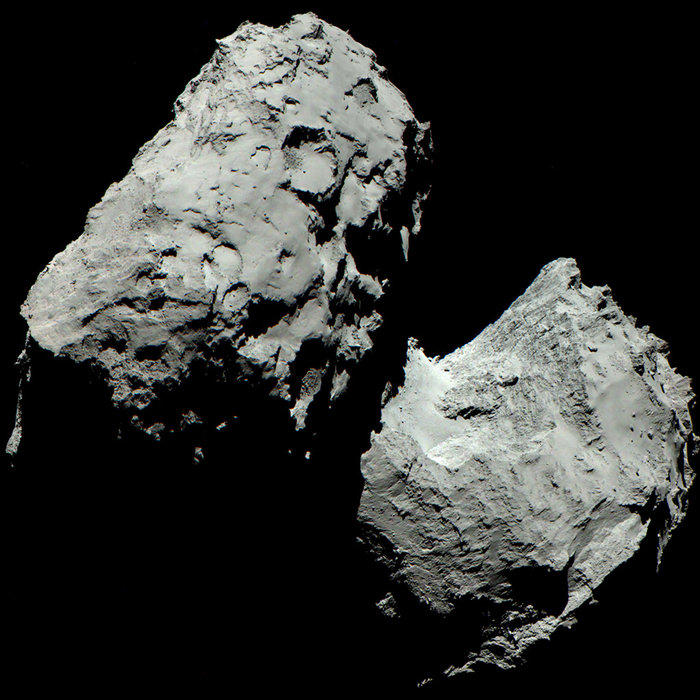

Ever since we’ve been able to get closer looks at comets in our Solar System, we’ve noticed something a little puzzling. Rather than being round, they’re mostly elongated or multi-lobed. This is certainly true of Comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko (67P or Chury for short.) A new paper from an international team coordinated by Patrick Michel at France’s CNRS explains how they form this way.
The European Space Agency (ESA) spacecraft Rosetta visited 67P in 2014, end even placed its lander Philae on the surface. Rosetta spent 17 months orbiting 67P, and at its closest approach, Rosetta was only 10 km (6 mi) from 67P’s surface. Rosetta’s mission ended with its guided impact into 67P’s surface in September, 2016, but the attempt to understand the comet and its brethren didn’t end then.
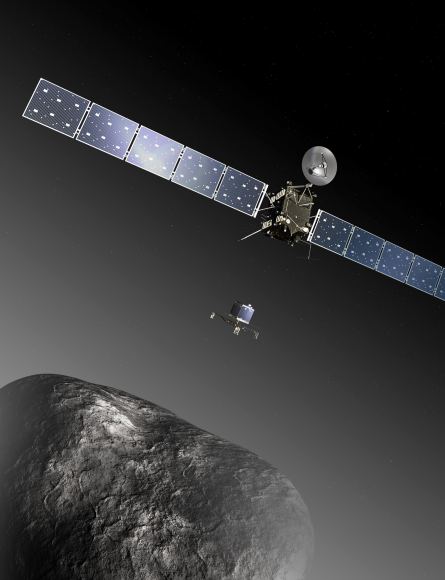

Though Rosetta’s pictures of 67P are the most detailed comet pictures we have, other spacecraft have visited other comets. And most of those other comets appear elongated or multi-lobed, too. Scientists explain these shapes with a “comet merger theory.” Two comets collide, creating the multi-lobed appearance of comets like 67P. But there’s been a problem with that theory.
In order for comets to merge and come out looking the way they do, they would have to merge very slowly, or else they would explode. They would also have to be very low-density, and be very rich in volatile elements. The “comet merger theory” also says that these types of gentle mergers between comets would have to have happened billions of years ago, in the early days of the Solar System.
The problem with this theory is, how could bodies like 67P have survived for so long? 67P is fragile, and subjected to repeated collisions in its part of the Solar System. How could it have retained its volatiles?
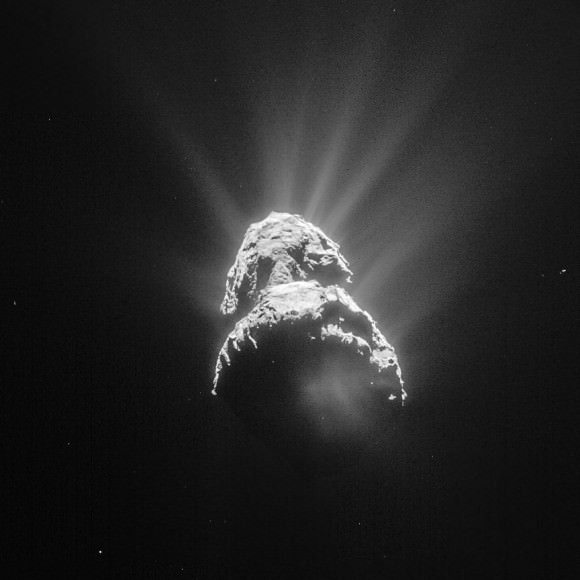

In the new paper, the research team ran a simulation that answers these questions.
The simulation showed that when two comets meet in a destructive collision, only a small portion of their material is pulverized and reduced to dust. On the sides of the comets opposite from the impact point, materials rich in volatiles withstand the collision. They’re still ejected into space, but their relative speed is low enough for them to join together in accretion. This process forms many smaller bodies, which keep clumping up until they form just one, larger body.
The most surprising part of this simulation is that this entire process may only take a few days, or even a few hours. The whole process explains how comets like 67P can keep their low density, and their abundant volatiles. And why they appear multi-lobed.

The simulation also answered another question: how can comets like 67P survive for so long?
The team behind the simulation thinks that the process can take place at speeds of 1 km/second. These speeds are typical in the Kuiper Belt, which is the disc of comets where 67P has its origins. In this belt, collisions between comets are a regular occurrence, which means that 67P didn’t have to form in the early days of the Solar System as previously thought. It could have formed at any time.
The team’s work also explains the surface appearance of 67P and other comets. They often have holes and stratified layers, and these features could have formed during re-accretion, or sometime after its formation.

One final point from the study concerns the composition of comets. One reason they’re a focus of such intense interest is their age. Scientists have always thought of them as ancient objects, and that studying them would allow us to look back into the primordial Solar System.
Though 67P—and other comets—may have formed much more recently than we used to believe, this process shows that there is no significant amount of heating or compaction during the collision. As a result, their original composition from the the early days of the Solar System is retained intact. No matter when 67P formed, it’s still a messenger from the formative days.
You can watch a video from the simulation here: http://www.dropbox.com/s/u7643hanvva57rp/Catastrophic%20disruptions.mp4?dl=0
Astronomers Think They Know Where Rosetta’s Comet Came From

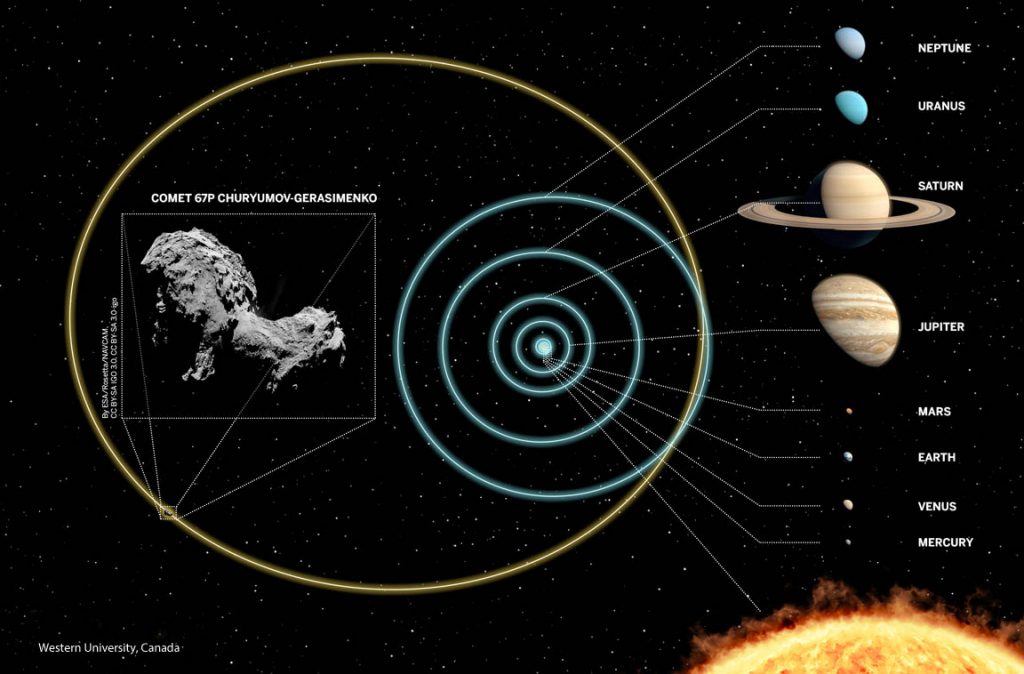
Rosetta’s Comet hails from a cold, dark place. Using statistical analysis and scientific computing, astronomers at Western University in Canada have charted a path that most likely pinpoints comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko’s long-ago home in the far reaches of the Kuiper Belt, a vast region beyond Neptune home to icy asteroids and comets.
According to the new research, Rosetta’s Comet is relative newcomer to the inner parts of our Solar System, having only arrived about 10,000 years ago. Prior to that, it spent the last 4.5 billion years in cold storage in a rough-and-tumble region of the Kuiper Belt called the scattered disk.

In the Solar System’s youth, asteroids that strayed too close to Neptune were scattered by the encounter into the wild blue yonder of the disk. Their orbits still bear the scars of those long-ago encounters: they’re often highly-elongated (shaped like a cigar) and tilted willy-nilly from the ecliptic plane up to 40°. Because their orbits can take them hundreds of Earth-Sun distances into the deeps of space, scattered disk objects are among the coldest places in the Solar System with surface temperatures around 50° above absolute zero. Ices that glommed together to form 67P at its birth are little changed today. Primordial stuff.
Watch how Rosetta’s Comet’s orbit has evolved since the comet’s formation
There are two basic comet groups. Most comets reside in the cavernous Oort Cloud, a roughly spherical-shaped region of space between 10,000 and 100,000 AU (astronomical unit = one Earth-Sun distance) from the Sun. The other major group, the Jupiter-family comets, owes its allegiance to the powerful gravity of the giant planet Jupiter. These comets race around the Sun with periods of less than 20 years. It’s thought they originate from collisions betwixt rocky-icy asteroids in the Kuiper Belt.
Fragments flung from the collisions are perturbed by Neptune into long, cigar-shaped orbits that bring them near Jupiter, which ropes them like calves with its insatiable gravity and re-settles them into short-period orbits.
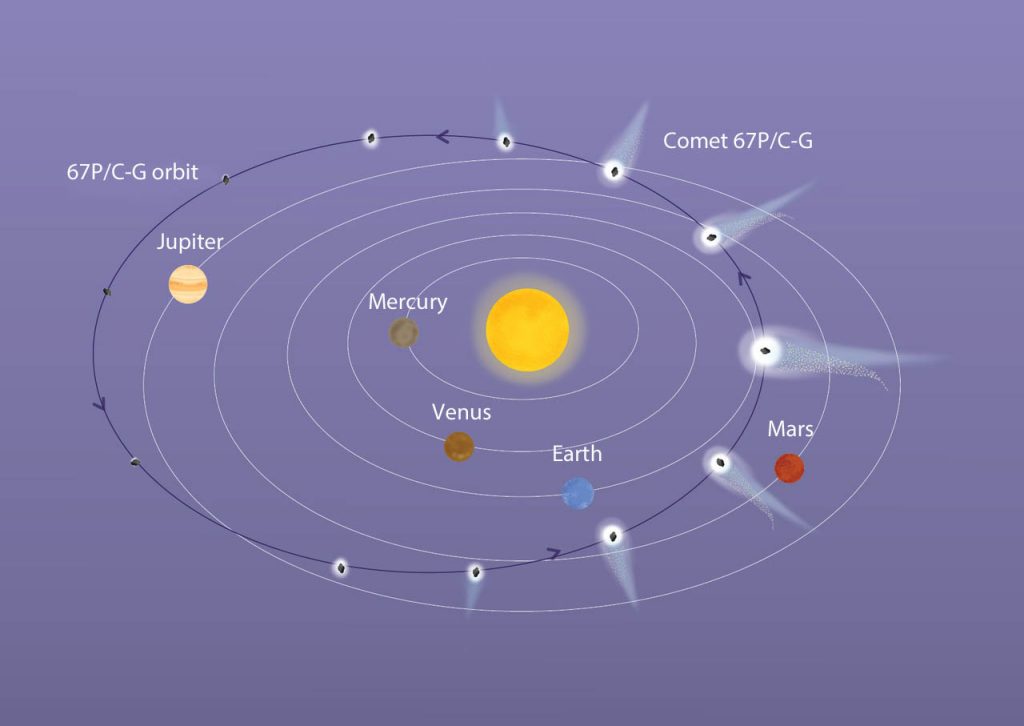
Mattia Galiazzo and solar system expert Paul Wiegert, both at Western University, showed that in transit, Rosetta’s Comet likely spent millions of years in the scattered disk at about twice the distance of Neptune. The fact that it’s now a Jupiter family comet hints of a possible long-ago collision followed by gravitational interactions with Neptune and Jupiter before finally becoming an inner Solar System homebody going around the Sun every 6.45 years.
By such long paths do we arrive at our present circumstances.
Bye, Bye Rosetta — We’ll Miss You!
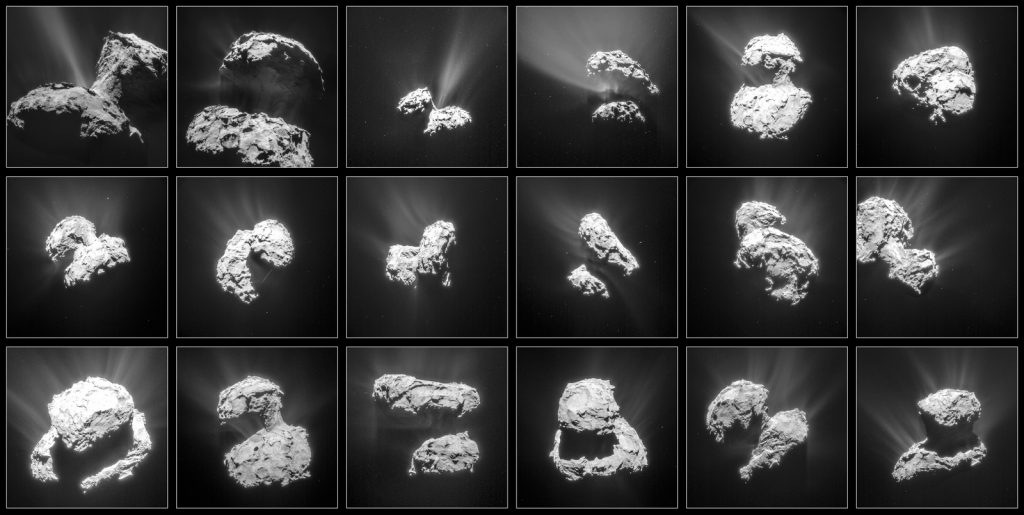

Rosetta awoke from a decade of deep-space hibernation in January 2014 and immediately got to work photographing, measuring and sampling comet 67P/C-G. On September 30 it will sleep again but this time for eternity. Mission controllers will direct the probe to impact the comet’s dusty-icy nucleus within 20 minutes of 10:40 Greenwich Time (6:40 a.m. EDT) that Friday morning. The high-resolution OSIRIS camera will be snapping pictures on the way down, but once impact occurs, it’s game over, lights out. Rosetta will power down and go silent.
Nearly three years have passed since Rosetta opened its eyes on 67P, this curious, bi-lobed rubber duck of a comet just 2.5 miles (4 km) across with landscapes ranging from dust dunes to craggy peaks to enigmatic ‘goosebumps’. The mission was the first to orbit a comet and dispatch a probe, Philae, to its surface. I think it’s safe to say we learned more about what makes comets tick during Rosetta’s sojourn than in any previous mission.
So why end it? One of the big reasons is power. As Rosetta races farther and farther from the Sun, less sunlight falls on its pair of 16-meter-long solar arrays. At mid-month, the probe was over 348 million miles (560 million km) from the Sun and 433 million miles (697 million km) from Earth or nearly as far as Jupiter. With Sun-to-Rosetta mileage increasing nearly 620,000 miles (1 million km) a day, weakening sunlight can’t provide the power needed to keep the instruments running.
Rosetta’s last orbits around the comet
Rosetta’s also showing signs of age after having been in the harsh environment of interplanetary space for more than 12 years, two of them next door to a dust-spitting comet. Both factors contributed to the decision to end the mission rather than put the probe back into an even longer hibernation until the comet’s next perihelion many years away.
Since August 9, Rosetta has been swinging past the comet in a series of ever-tightening loops, providing excellent opportunities for close-up science observations. On September 5, Rosetta swooped within 1.2 miles (1.9 km) of 67P/C-G’s surface. It was hoped the spacecraft would descend as low as a kilometer during one of the later orbits as scientists worked to glean as much as possible before the show ends.
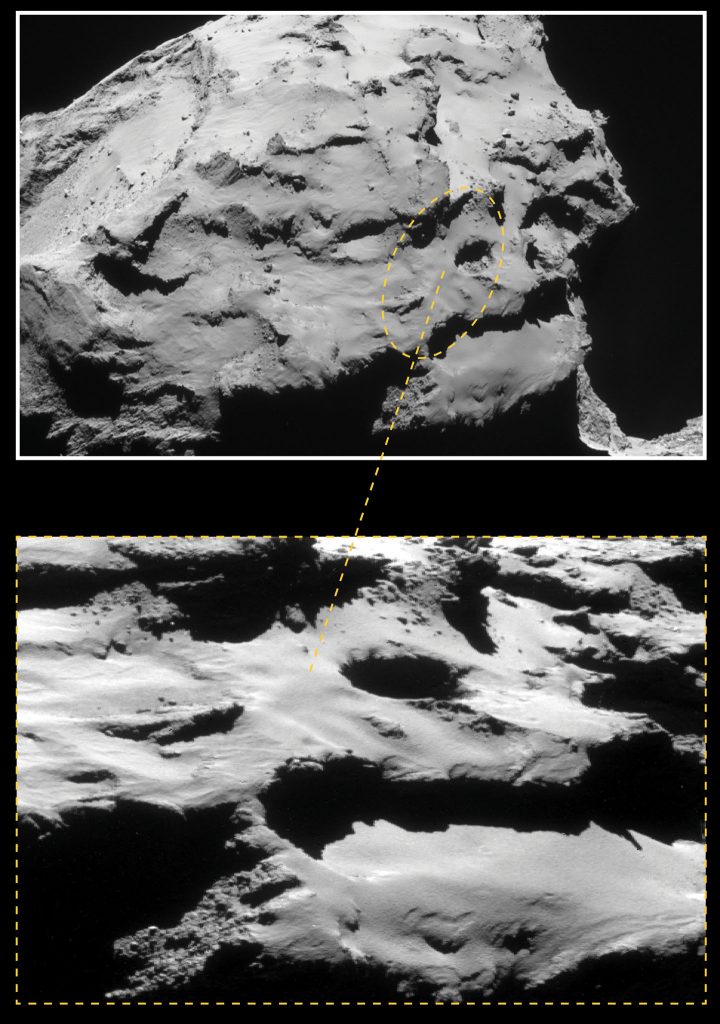

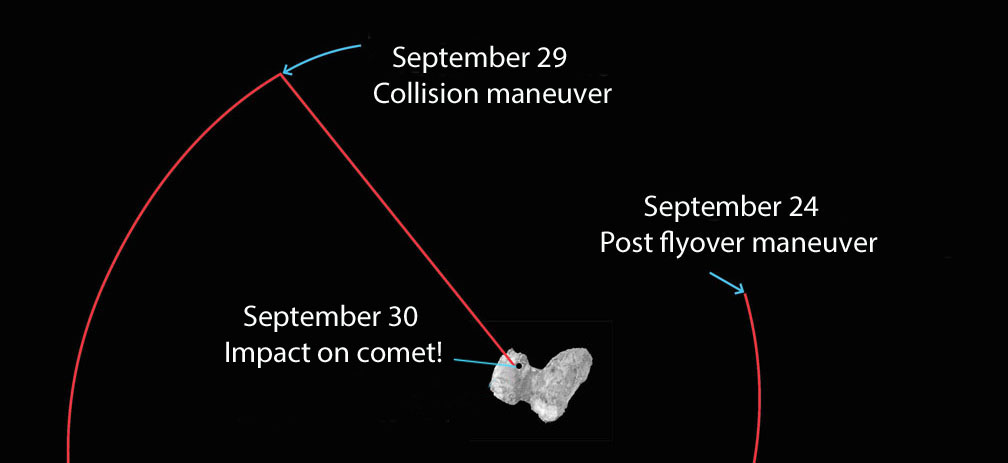
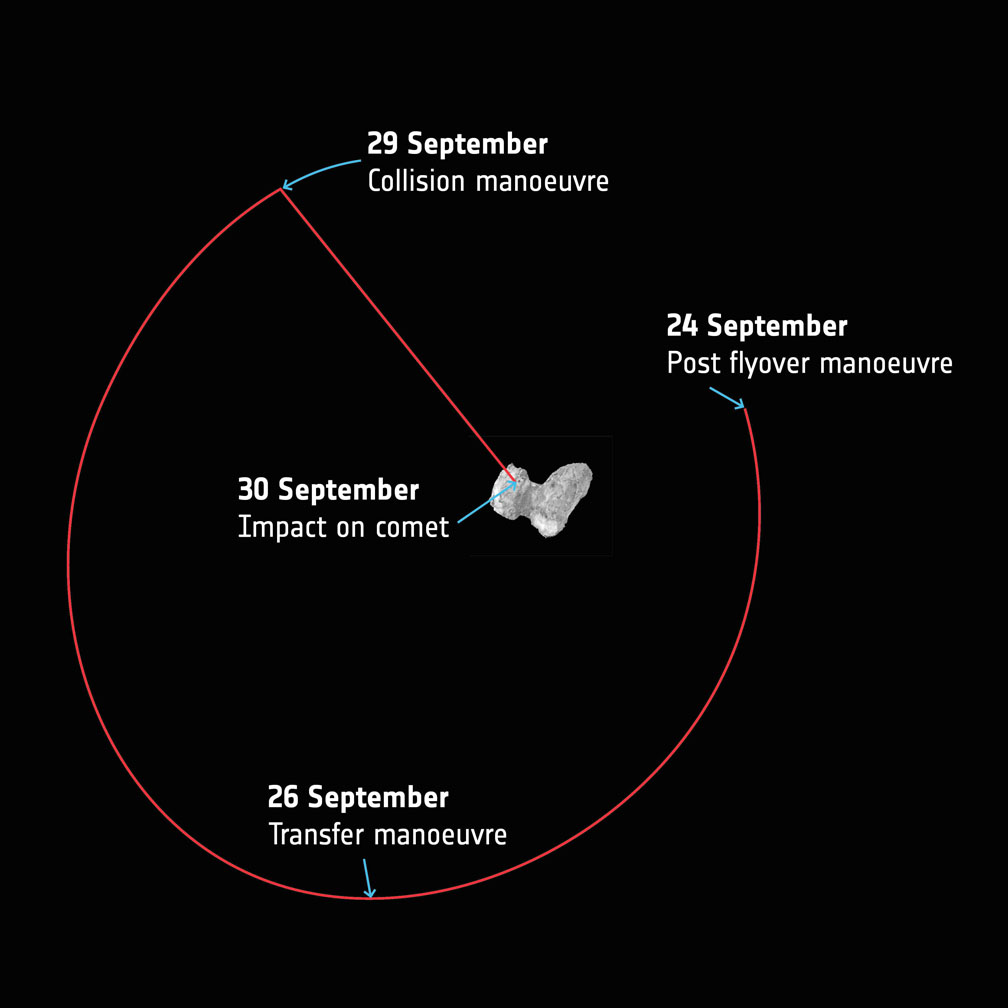
The final of 15 close flyovers will be completed today (Sept. 24) after which Rosetta will be maneuvered from its current elliptical orbit onto a trajectory that will eventually take it down to the comet’s surface on Sept. 30.
The beginning of the end unfolds on the evening of the 29th when Rosetta spends 14 hours free-falling slowly towards the comet from an altitude of 12.4 miles (20 km) — about 4 miles higher than a typical commercial jet — all the while collecting measurements and photos that will be returned to Earth before impact. The last eye-popping images will be taken from a distance of just tens to a hundred meters away.
The landing will be a soft one, with the spacecraft touching down at walking speed. Like Philae before it, it will probably bounce around before settling into place. Mission control expects parts of the probe to break upon impact.
Taking into account the additional 40 minute signal travel time between Rosetta and Earth on the 30th, confirmation of impact is expected at ESA’s mission control in Darmstadt, Germany, within 20 minutes of 11:20 GMT (7:20 a.m. EDT). The times will be updated as the trajectory is refined. You can watch live coverage of Rosetta’s final hours on ESA TV .
ESAHangout: Preparing for Rosetta’s grand finale
“It’s hard to believe that Rosetta’s incredible 12.5 year odyssey is almost over, and we’re planning the final set of science operations, but we are certainly looking forward to focusing on analyzing the reams of data for many decades to come,” said Matt Taylor, ESA’s Rosetta project scientist.
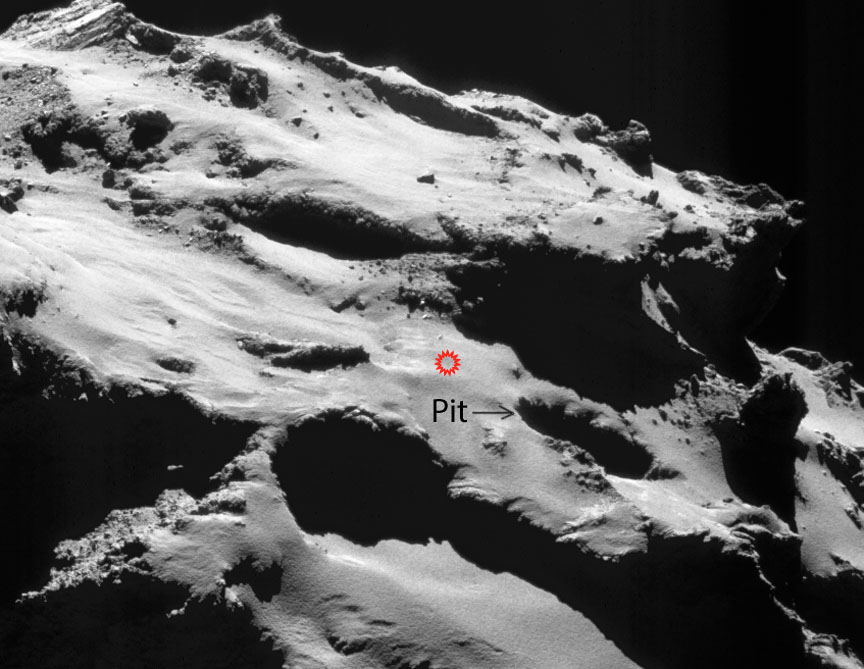

Plans call for the spacecraft to impact the comet somewhere within an ellipse about 1,300 x 2,000 feet (600 x 400 meters) long on 67P’s smaller lobe in the region known as Ma’at. It’s home to several active pits more than 328 feet (100 meters) in diameter and 160-200 feet (50-60 meters) deep, where a number of the comet’s dust jets originate. The walls of the pits are lined with fascinating meter-sized lumpy structures called ‘goosebumps’, which scientists believe could be early ‘cometesimals’, the icy snowballs that stuck together to create the comet in the early days of our Solar System’s formation.
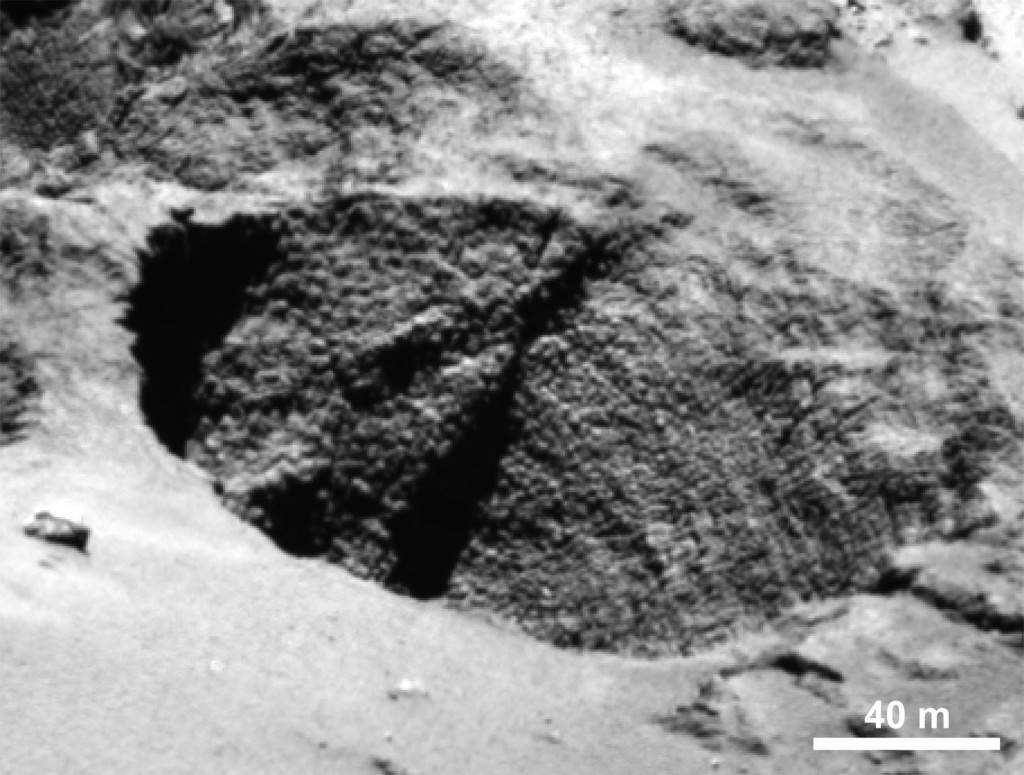

During free-fall, the spacecraft will target a point adjacent to a 425-foot (130 m) wide, well-defined pit that the mission team has informally named Deir el-Medina, after a structure with a similar appearance in an ancient Egyptian town of the same name. High resolution images should give us a spectacular view of these enigmatic bumps.
While we hate to see Rosetta’s mission end, it’s been a blast going for a 2-year-plus comet ride-along.
How to Find Rosetta’s Comet In Your Telescope

How would you like to see one of the most famous comets with your own eyes? Comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko plies the morning sky, a little blot of fuzzy light toting an amazing visitor along for the ride — the Rosetta spacecraft. When you look at the coma and realize a human-made machine is buzzing around inside, it seems unbelievable.

If you have a 10-inch or larger telescope, or you’re an experienced amateur with an 8-inch and pristine skies, 67P is within your grasp. The comet glows right around magnitude +12, about as bright as it will get this apparition. Periodic comets generally appear brightest around and shortly after perihelion or closest approach to the Sun, which for 67P/C-G occurred back on August 13.

You’ll be looking for a small, 1-arc-minute-diameter, compact, circular patch of nebulous light shortly before dawn when it’s highest in the east. Rosetta’s Comet will spend the remainder of August slicing across Gemini the Twins north of an nearly parallel to the ecliptic. I spotted 67P/C-G for the first time this go-round about a week ago in my 15-inch (37 cm) reflector. While it appears like a typical faint comet, thanks to Rosetta, we know this particular rough and tumble mountain of ice better than any previous comet. Photographs show rugged cliffs, numerous cracks due to the expansion and contraction of ice, blowholes that serve as sources for jets and smooth plains blanketed in fallen dust.

The jets are geyser-like sprays of dust and gas that loft grit and rocks from the comet’s interior and surface into space to create a coma or temporary atmosphere. This is what you’ll see in your telescope. And if you’re patient, you’ll even be able to catch this glowing tadpole on the move. I was surprised at its speed. After just 20 minutes, thanks to numerous field stars that acted as references, I could easily spot the comet’s eastward movement using a magnification of 245x.
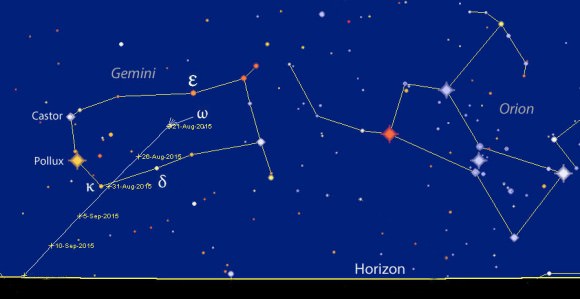
Tomorrow morning, 67P/C-G passes very close to the magnitude +5 star Omega Geminorum. While this will make it easy to locate, the glare may swamp the comet. Set your alarm for an hour before dawn’s start to allow time to set up a telescope, dark-adapt your eyes and track down the field where the comet will be that morning using low magnification.
Once you’ve centered 67P/C-G’s position, increase the power to around 100x-150x and use averted vision to look for a soft, fuzzy patch of light. If you see nothing, take it to the next level (around 200-250x) and carefully search the area. The higher the magnification, the darker the field of view and easier it will be to spot it.

Besides being relatively faint, the comet doesn’t get very high in the east before the onset of twilight. Low altitude means the atmosphere absorbs a share of the comet’s light, making it appear even fainter. Not that I want to dissuade you from looking! There’s nothing like seeing real 67P photons not to mention the adventure and sense of accomplishment that come from finding the object on your own.
As we advance into late summer and early fall, 67P/C-G will appear higher up but also be fading. Now through about August 27 and again from September 10-24 will be your best viewing times. That’s when the Moon’s absent from the sky.
Given the comet’s current distance from Earth of 165 million miles and apparent visual size of just shy of 1 arc minute, the coma measures very approximately 30,000 miles across. Rosetta orbits the comet’s 2.5-mile-long icy nucleus at a distance of about 115 miles (186 km), meaning it’s snug up against the nuclear center from our point of view on the ground.
If you do find and follow 67P/C-G, consider sharing your observations with the Pro-Amateur Collaborative Astronomy (PACA) campaign to help increase our knowledge of its behavior. Interested? Sign up HERE.
Rosetta Discovery of Surprise Molecular Breakup Mechanism in Comet Coma Alters Perceptions

A NASA science instrument flying aboard the European Space Agency’s (ESA) Rosetta spacecraft has made a very surprising discovery – namely that the molecular breakup mechanism of “water and carbon dioxide molecules spewing from the comet’s surface” into the atmosphere of comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko is caused by “electrons close to the surface.”
The surprising results relating to the emission of the comet coma came from measurements gathered by the probes NASA funded Alice instrument and is causing scientists to completely rethink what we know about the wandering bodies, according to the instruments science team.
“The discovery we’re reporting is quite unexpected,” said Alan Stern, principal investigator for the Alice instrument at the Southwest Research Institute (SwRI) in Boulder, Colorado, in a statement.
“It shows us the value of going to comets to observe them up close, since this discovery simply could not have been made from Earth or Earth orbit with any existing or planned observatory. And, it is fundamentally transforming our knowledge of comets.”
A paper reporting the Alice findings has been accepted for publication by the journal Astronomy and Astrophysics, according to statements from NASA and ESA.
Alice is a spectrograph that focuses on sensing the far-ultraviolet wavelength band and is the first instrument of its kind to operate at a comet.
Until now it had been thought that photons from the sun were responsible for causing the molecular breakup, said the team.
The carbon dioxide and water are being released from the nucleus and the excitation breakup occurs barely half a mile above the comet’s nucleus.
“Analysis of the relative intensities of observed atomic emissions allowed the Alice science team to determine the instrument was directly observing the “parent” molecules of water and carbon dioxide that were being broken up by electrons in the immediate vicinity, about six-tenths of a mile (one kilometer) from the comet’s nucleus.”
The excitation mechanism is detailed in the graphic below.
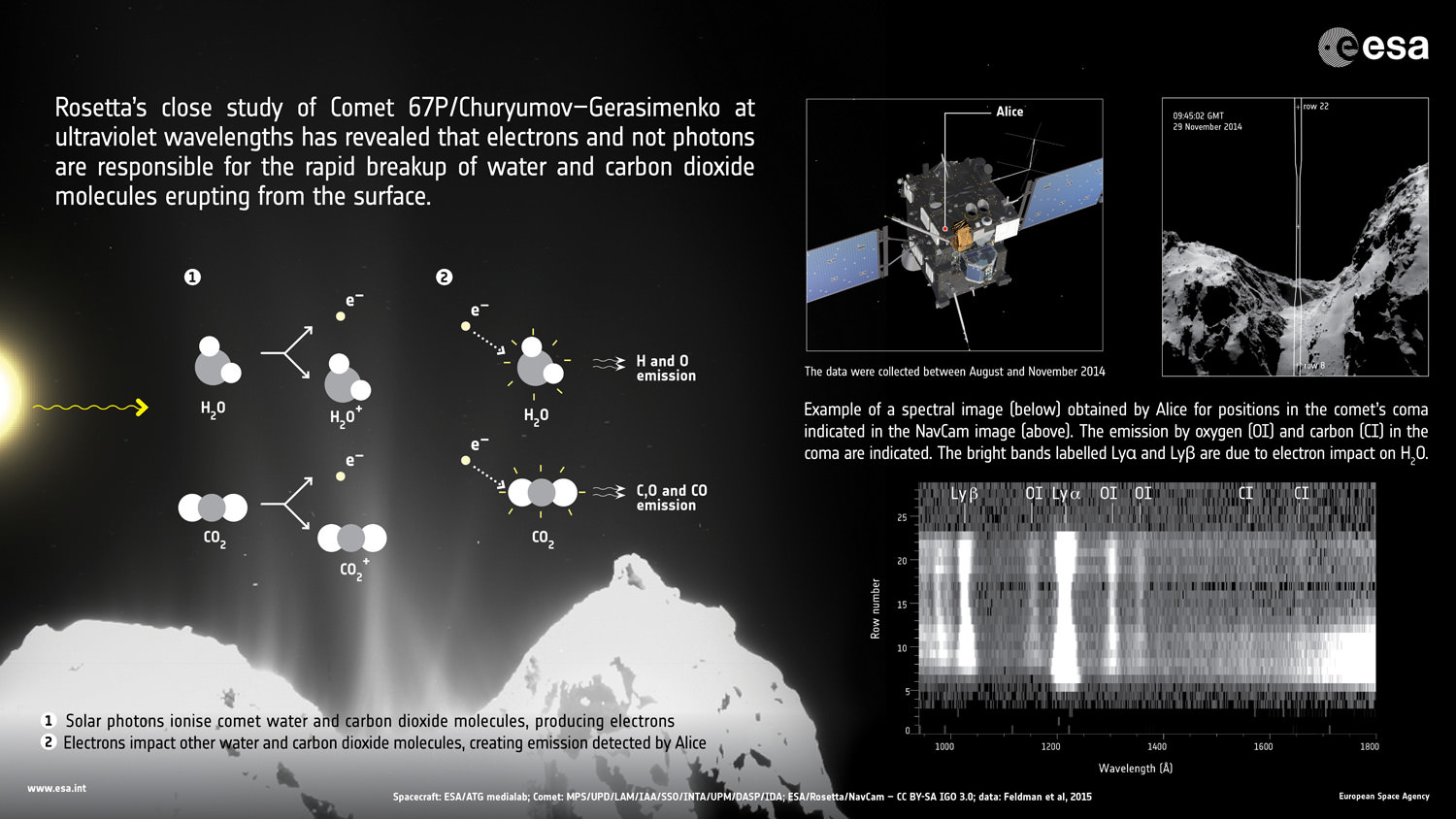
“The spatial variation of the emissions along the slit indicates that the excitation occurs within a few hundred meters of the surface and the gas and dust production are correlated,” according to the Astronomy and Astrophysics journal paper.
The data shows that the water and CO2 molecules break up via a two-step process.
“First, an ultraviolet photon from the Sun hits a water molecule in the comet’s coma and ionises it, knocking out an energetic electron. This electron then hits another water molecule in the coma, breaking it apart into two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen, and energising them in the process. These atoms then emit ultraviolet light that is detected at characteristic wavelengths by Alice.”
“Similarly, it is the impact of an electron with a carbon dioxide molecule that results in its break-up into atoms and the observed carbon emissions.”
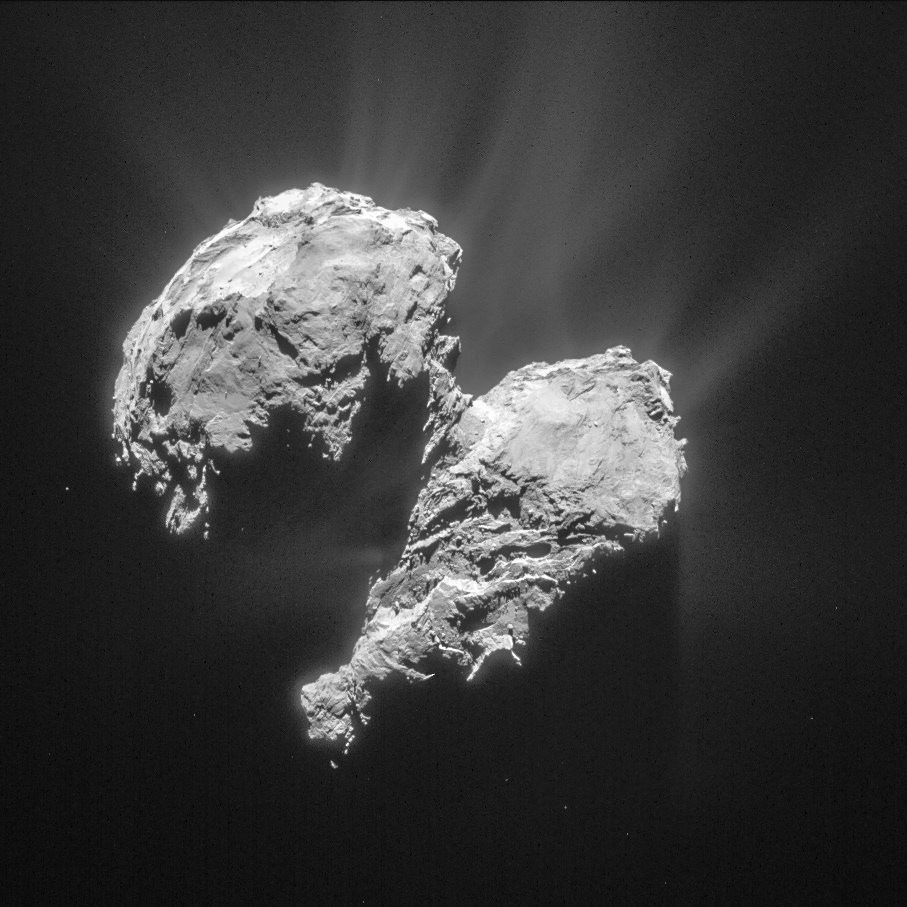
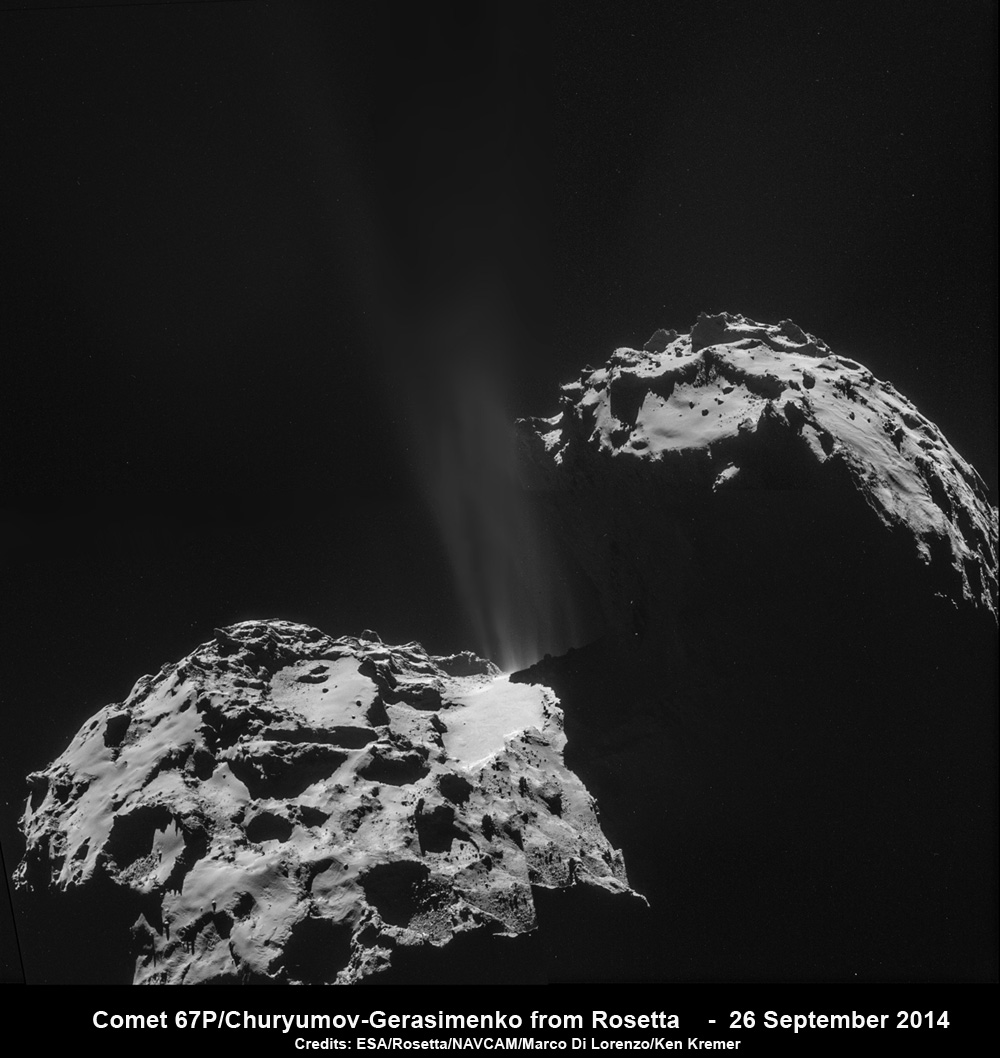
After a decade long chase of over 6.4 billion kilometers (4 Billion miles), ESA’s Rosetta spacecraft arrived at the pockmarked Comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko on Aug. 6, 2014 for history’s first ever attempt to orbit a comet for long term study.
Since then, Rosetta deployed the Philae landing craft to accomplish history’s first ever touchdown on a comets nucleus. It has also orbited the comet for over 10 months of up close observation, coming at times to as close as 8 kilometers. It is equipped with a suite 11 instruments to analyze every facet of the comet’s nature and environment.
Comet 67P is still becoming more and more active as it orbits closer and closer to the sun over the next two months. The pair reach perihelion on August 13, 2015 at a distance of 186 million km from the Sun, between the orbits of Earth and Mars.
Alice works by examining light emitted from the comet to understand the chemistry of the comet’s atmosphere, or coma and determine the chemical composition with the far-ultraviolet spectrograph.
According to the measurements from Alice, the water and carbon dioxide in the comet’s atmospheric coma originate from plumes erupting from its surface.
“It is similar to those that the Hubble Space Telescope discovered on Jupiter’s moon Europa, with the exception that the electrons at the comet are produced by solar radiation, while the electrons at Europa come from Jupiter’s magnetosphere,” said Paul Feldman, an Alice co-investigator from the Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore, Maryland, in a statement.

Other instruments aboard Rosetta including MIRO, ROSINA and VIRTIS, which study relative abundances of coma constituents, corroborate the Alice findings.
“These early results from Alice demonstrate how important it is to study a comet at different wavelengths and with different techniques, in order to probe various aspects of the comet environment,” says ESA’s Rosetta project scientist Matt Taylor, in a statement.
“We’re actively watching how the comet evolves as it moves closer to the Sun along its orbit towards perihelion in August, seeing how the plumes become more active due to solar heating, and studying the effects of the comet’s interaction with the solar wind.”
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and planetary science and human spaceflight news.
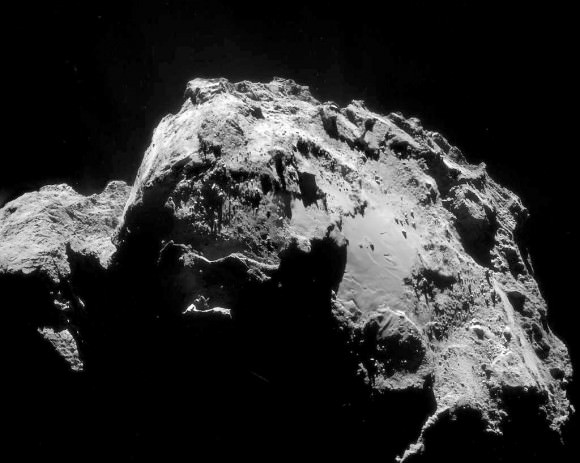
Rosetta to Snuggle Up to Comet 67P for Closest Encounter Yet

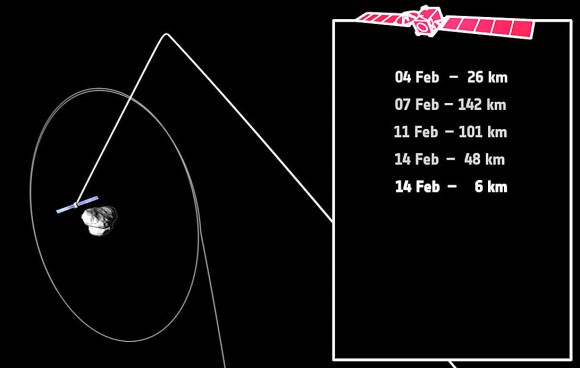
Who doesn’t like to snuggle up with their Valentine on Valentine’s Day? Rosetta will practically whisper sweet nothings into 67P’s ear on February 14 when it swings just 3.7 miles (6 km) above its surface, its closest encounter yet.
Rosetta had been orbiting the comet at a distance of some 16 miles (26 km) but beginning yesterday, mission controllers used the spacecraft’s thrusters to change its orbit in preparation for the close flyby. First, Rosetta will move out to a distance of roughly 87 miles (140 km) from the comet this Saturday before swooping in for the close encounter at 6:41 a.m. CST on Feb. 14. Closest approach happens over the comet’s larger lobe, above the Imhotep region.
The close encounter will provide opportunities for Rosetta’s science instruments to photograph 67P’s surface at high resolution across a range of wavelengths as well as get a close sniff of what’s inside its innermost coma or developing atmosphere. Scientists will also be looking closely at the outflowing gas and dust to see how it evolves during transport from the comet’s interior to the coma and tail.
As Rosetta swoops by its view of the comet will continuously change. Instruments will collect data on how 67P’s dust grains reflect light across a variety of orbital perspectives – from shadowless lighting with the Sun at the orbiter’s back to slanted lighting angles – to learn more about its properties.

“After this close flyby, a new phase will begin, when Rosetta will execute sets of flybys past the comet at a range of distances, between about 15 km (9 miles) and 100 km (62 miles),” said Sylvain Lodiot, ESA’s spacecraft operations manager.
During some of the close flybys, Rosetta trajectory will be almost in step with the comet’s rotation, allowing the instruments to monitor a single point on the surface in great detail as it passes by.
Helpful animation of how ESA mission controllers are changing Rosetta’s orbit to ready the probe for the Valentine’s Day flyby.
Perihelion, when the comet arcs closest to the Sun at a distance of 115.6 million miles (186 million km), occurs on August 13. Activity should be reaching its peak around that time. Beginning one month before, the Rosetta team will identify and closely examine one of the comet’s jets in wickedly rich detail.
“We hope to target one of these regions for a fly-through, to really get a taste of the outflow of the comet,” said Matt Taylor, ESA’s Rosetta project scientist.
Yum, yum. Can’t wait for that restaurant review!